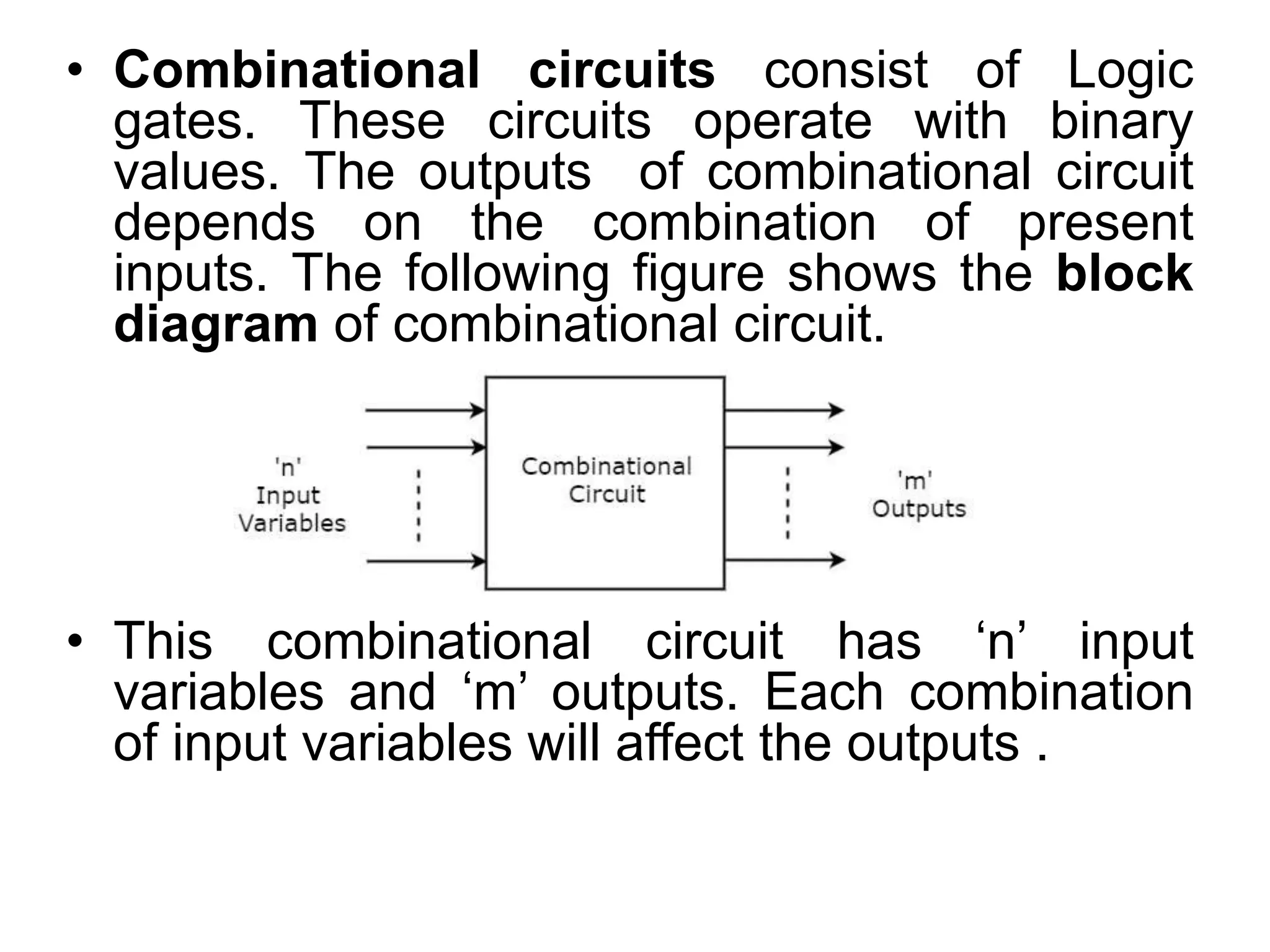
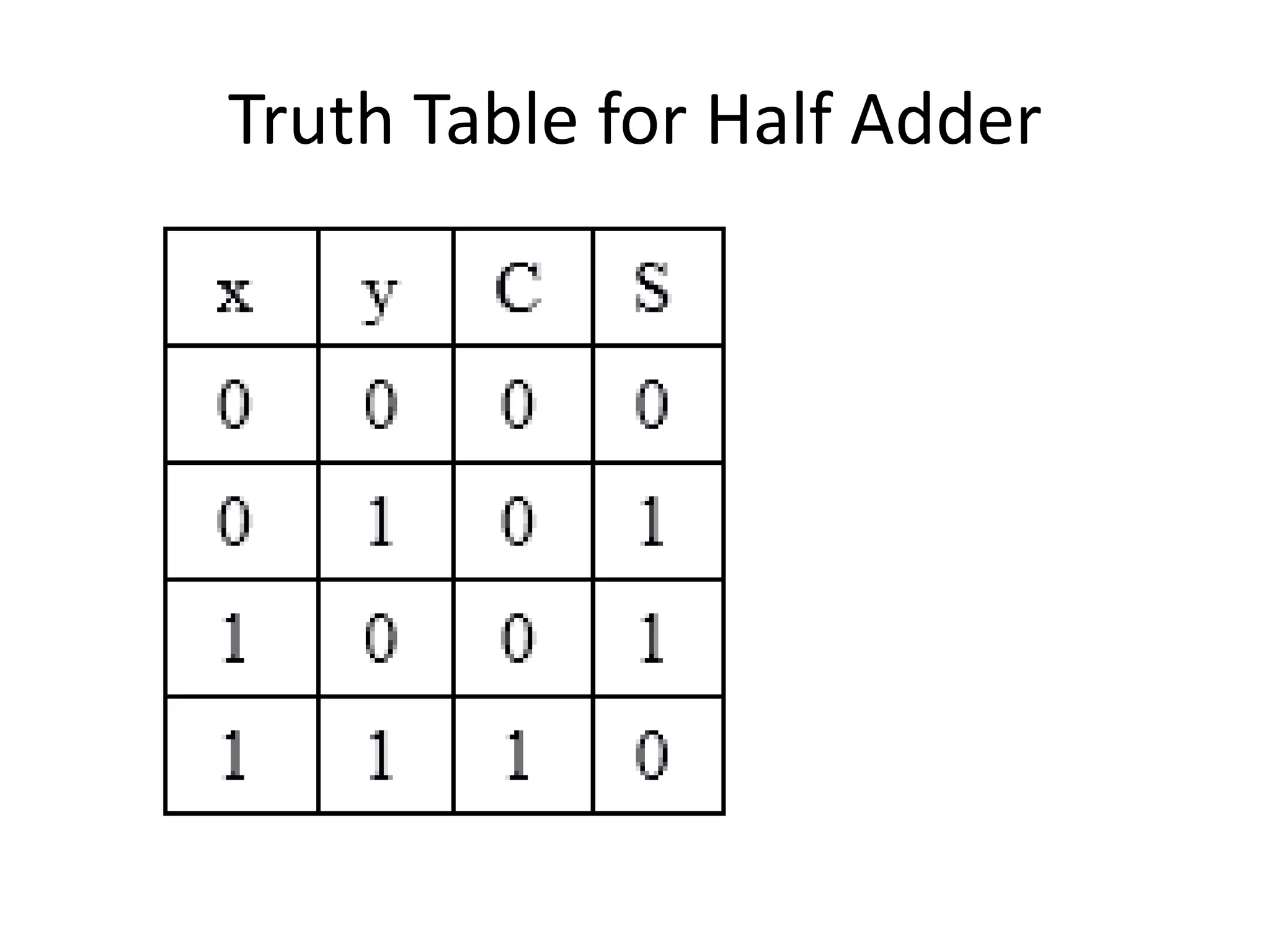
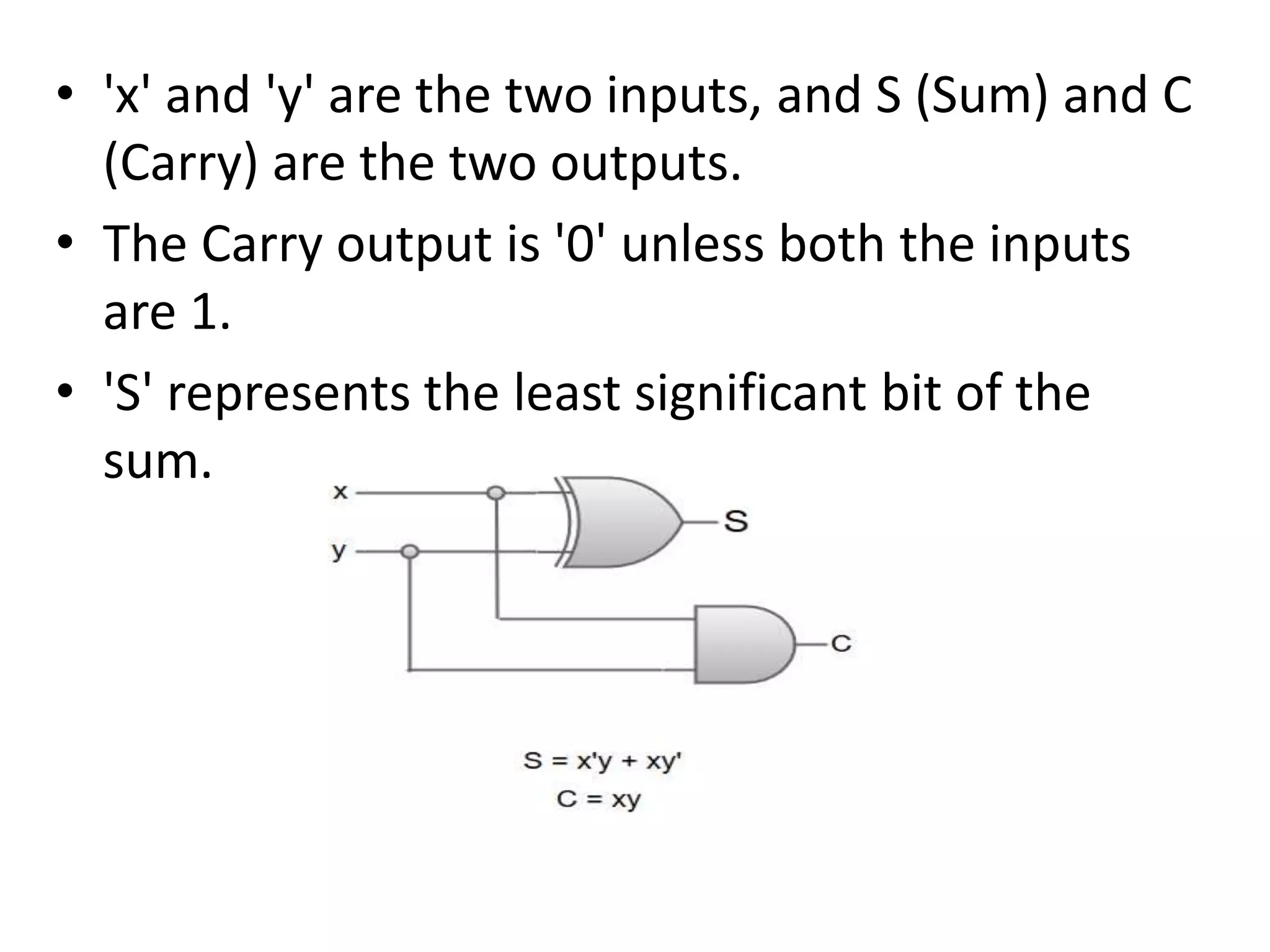
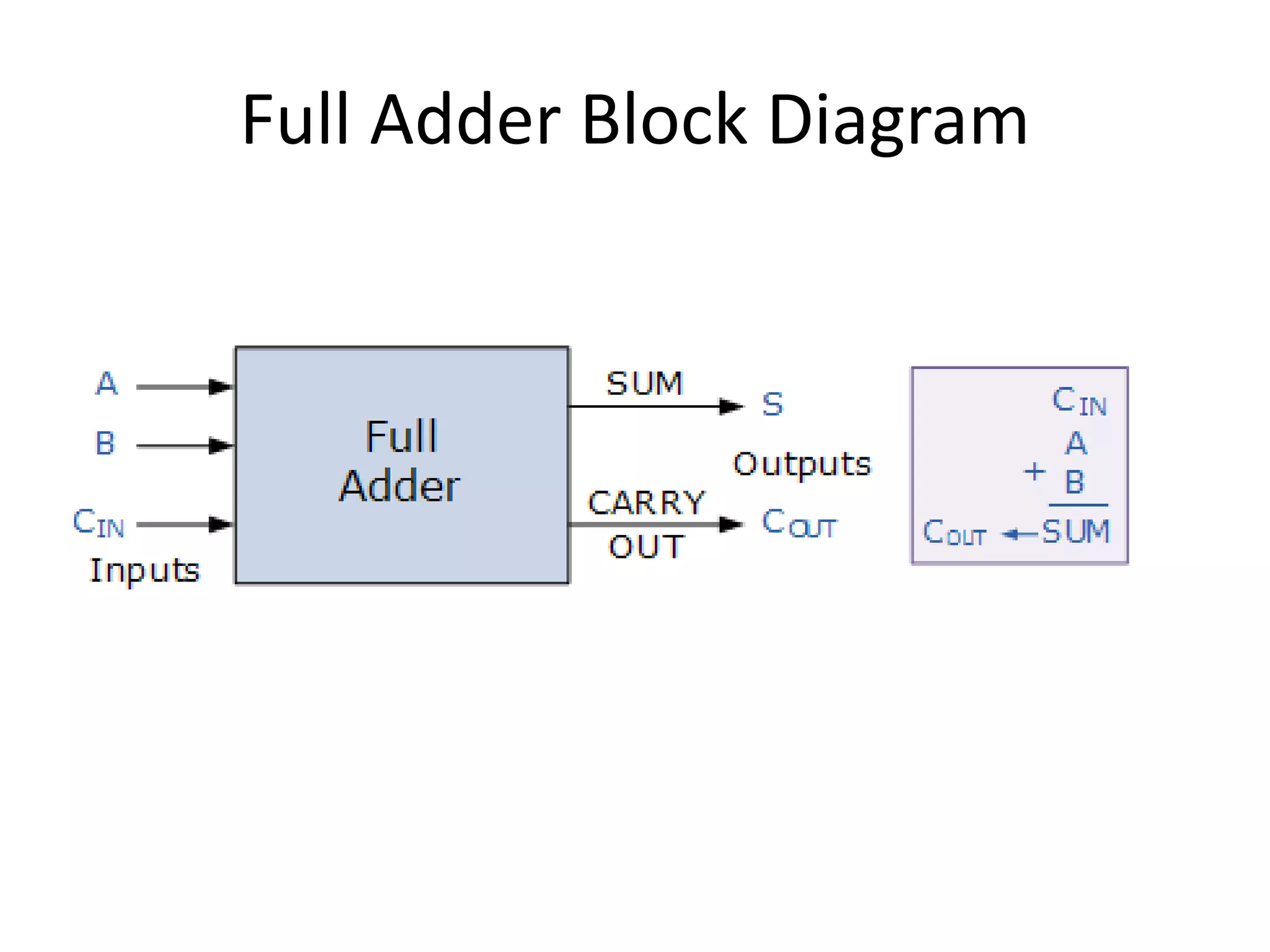
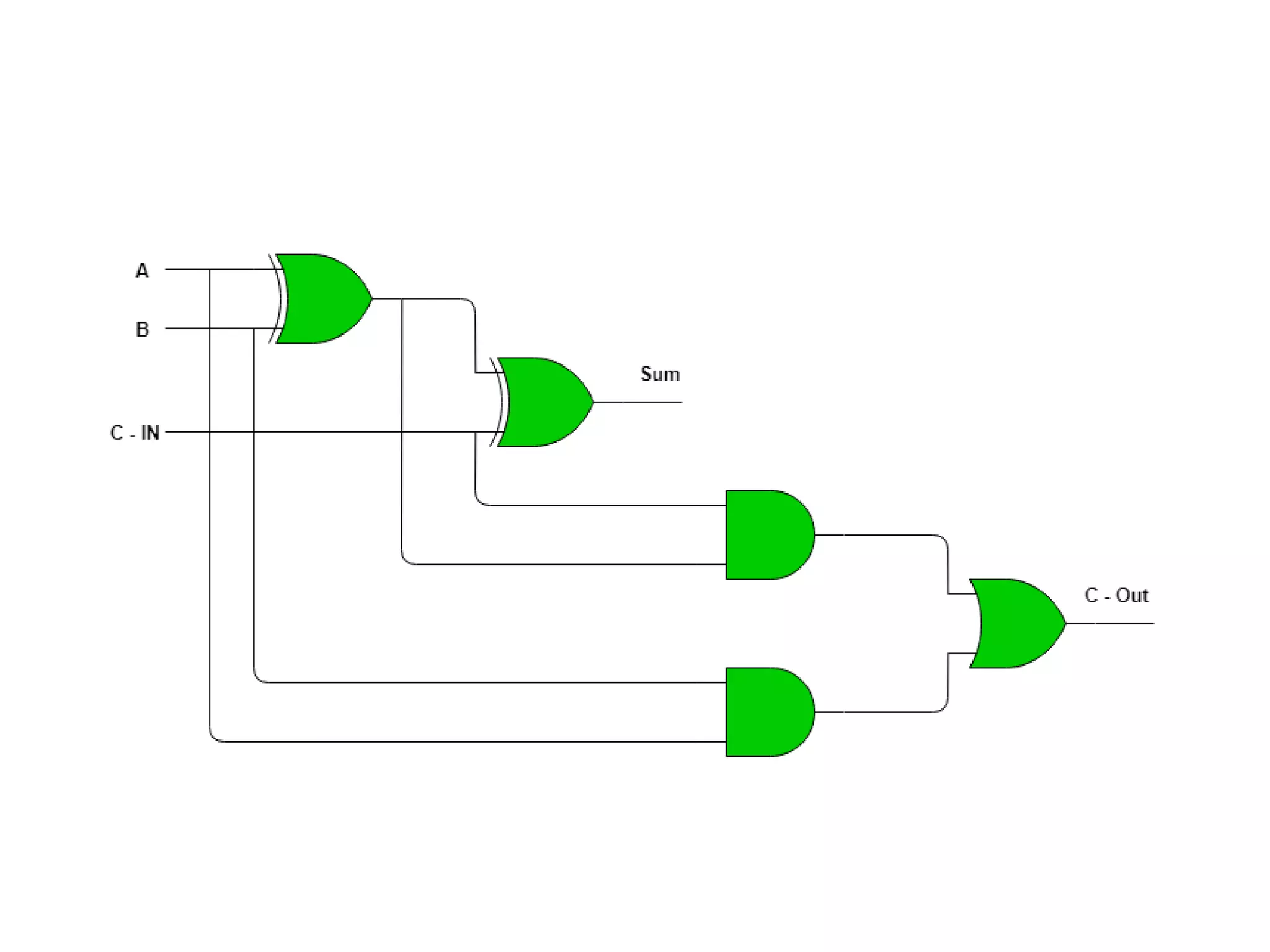
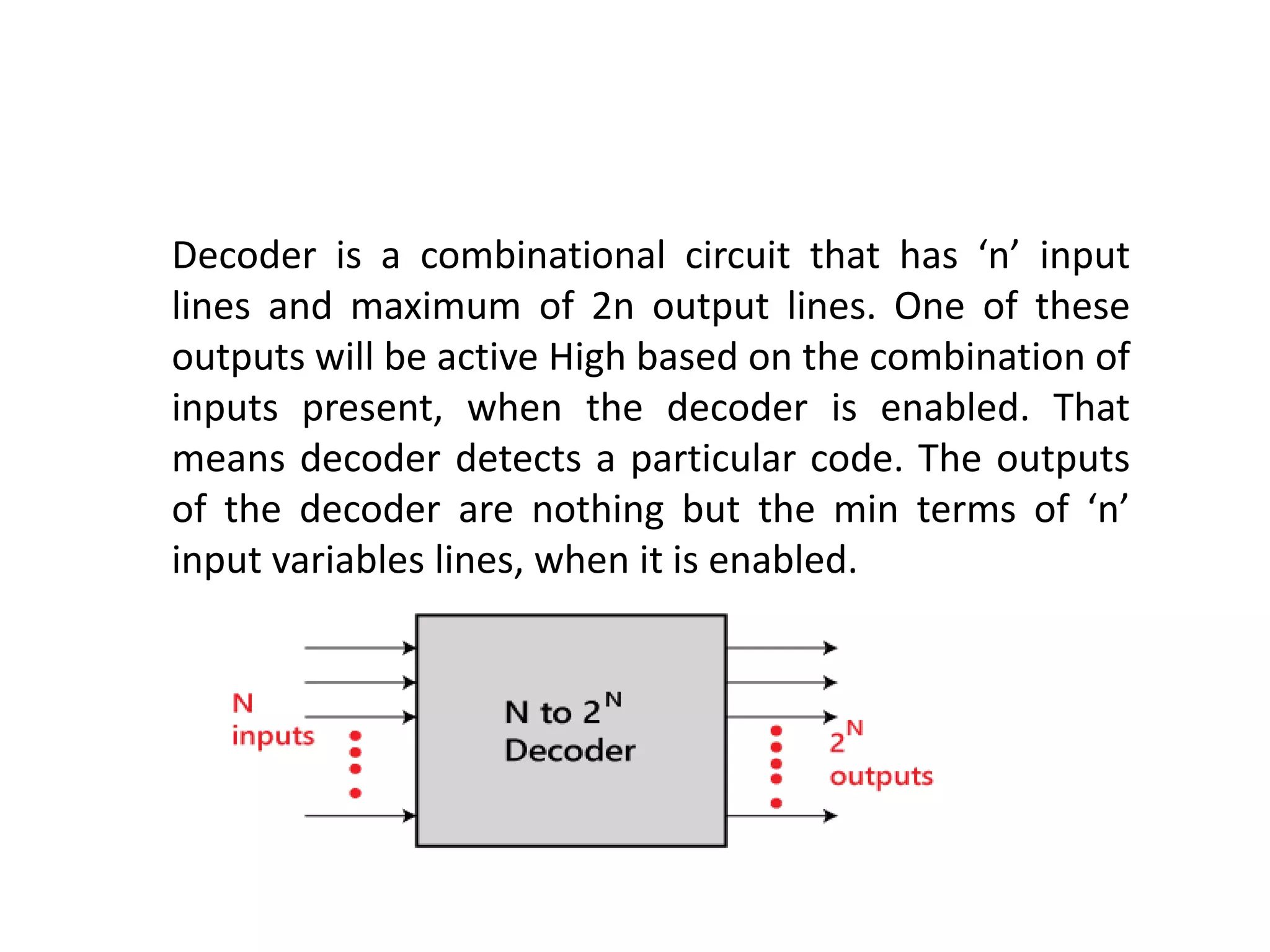
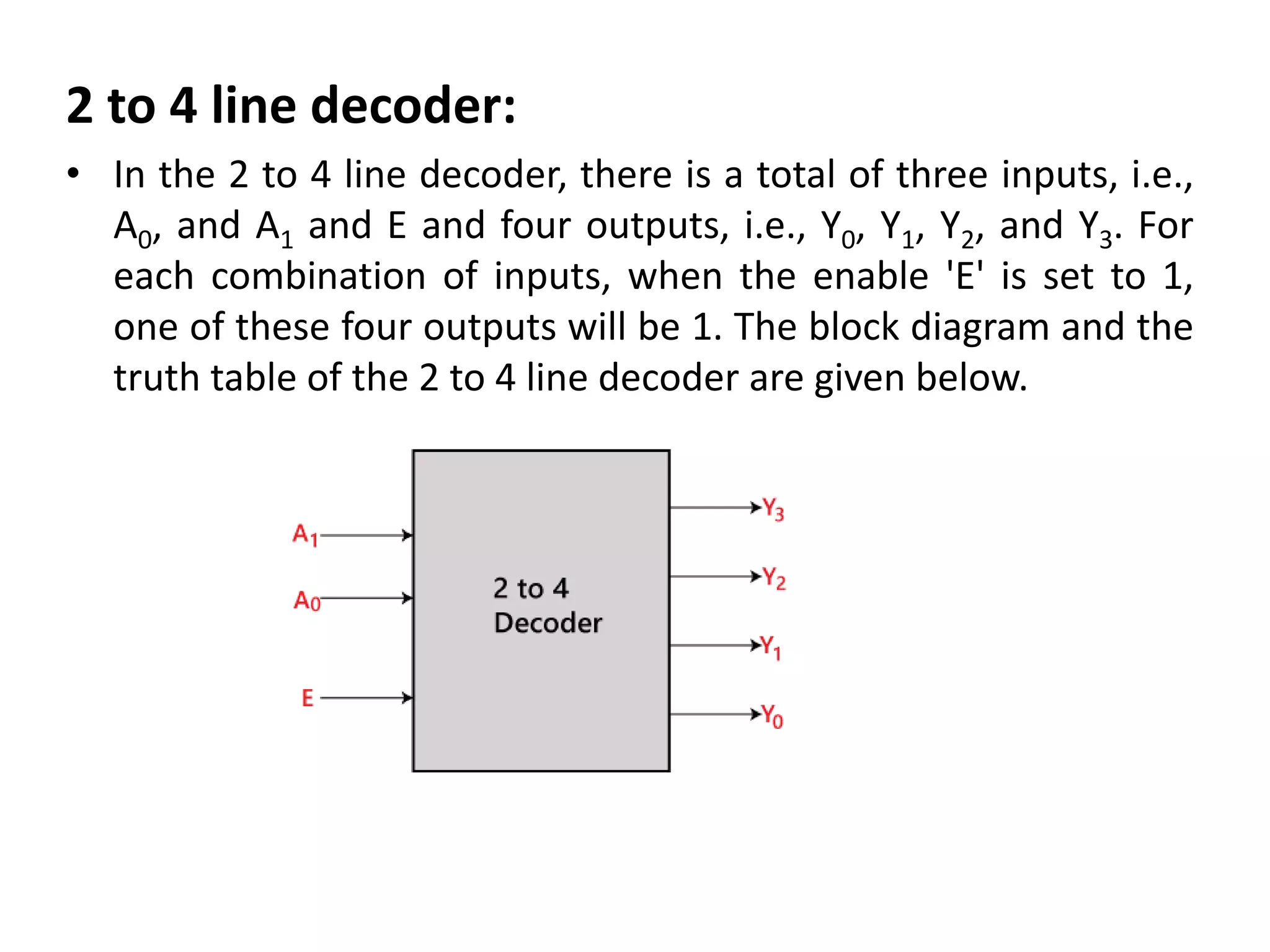
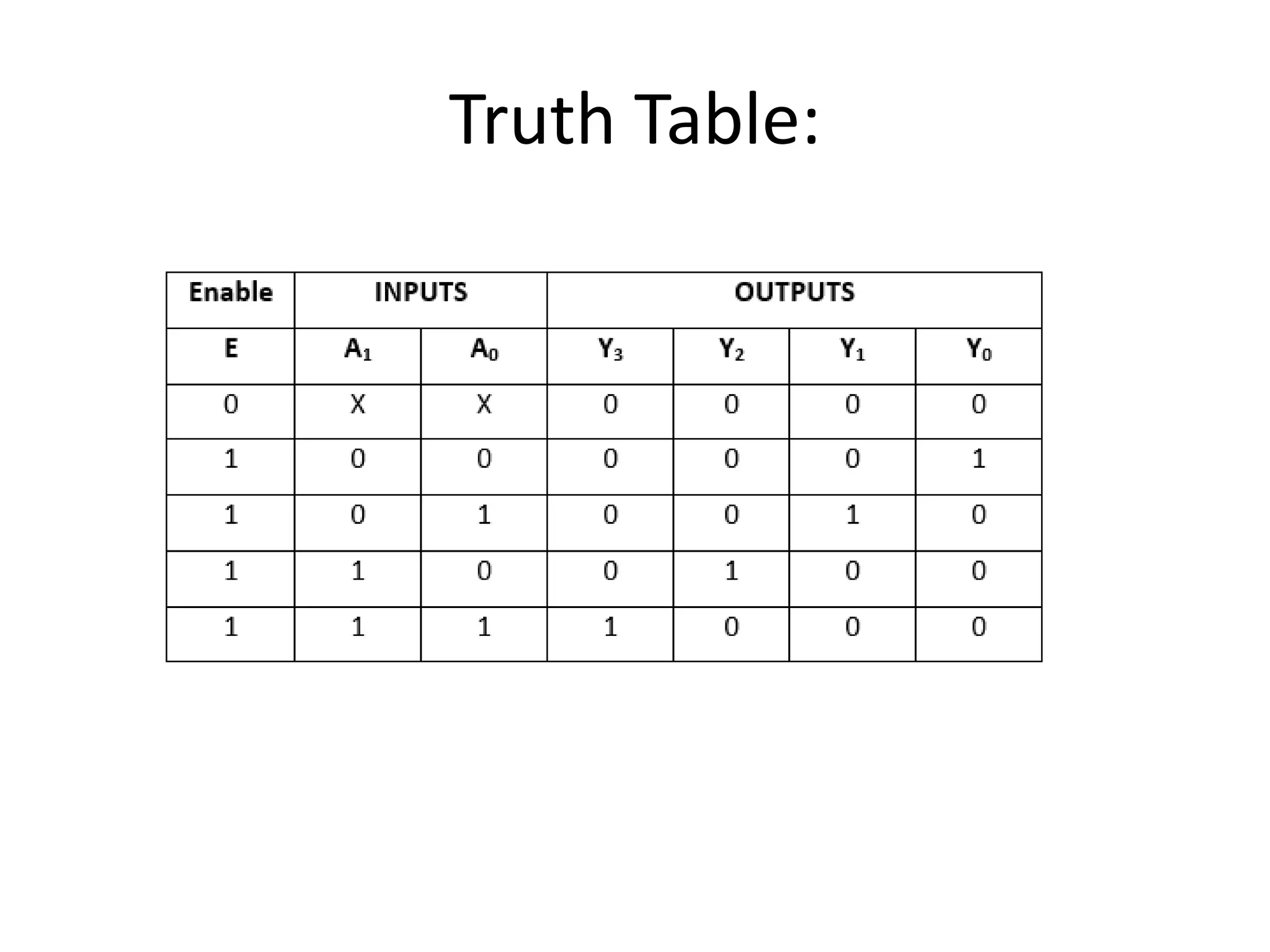
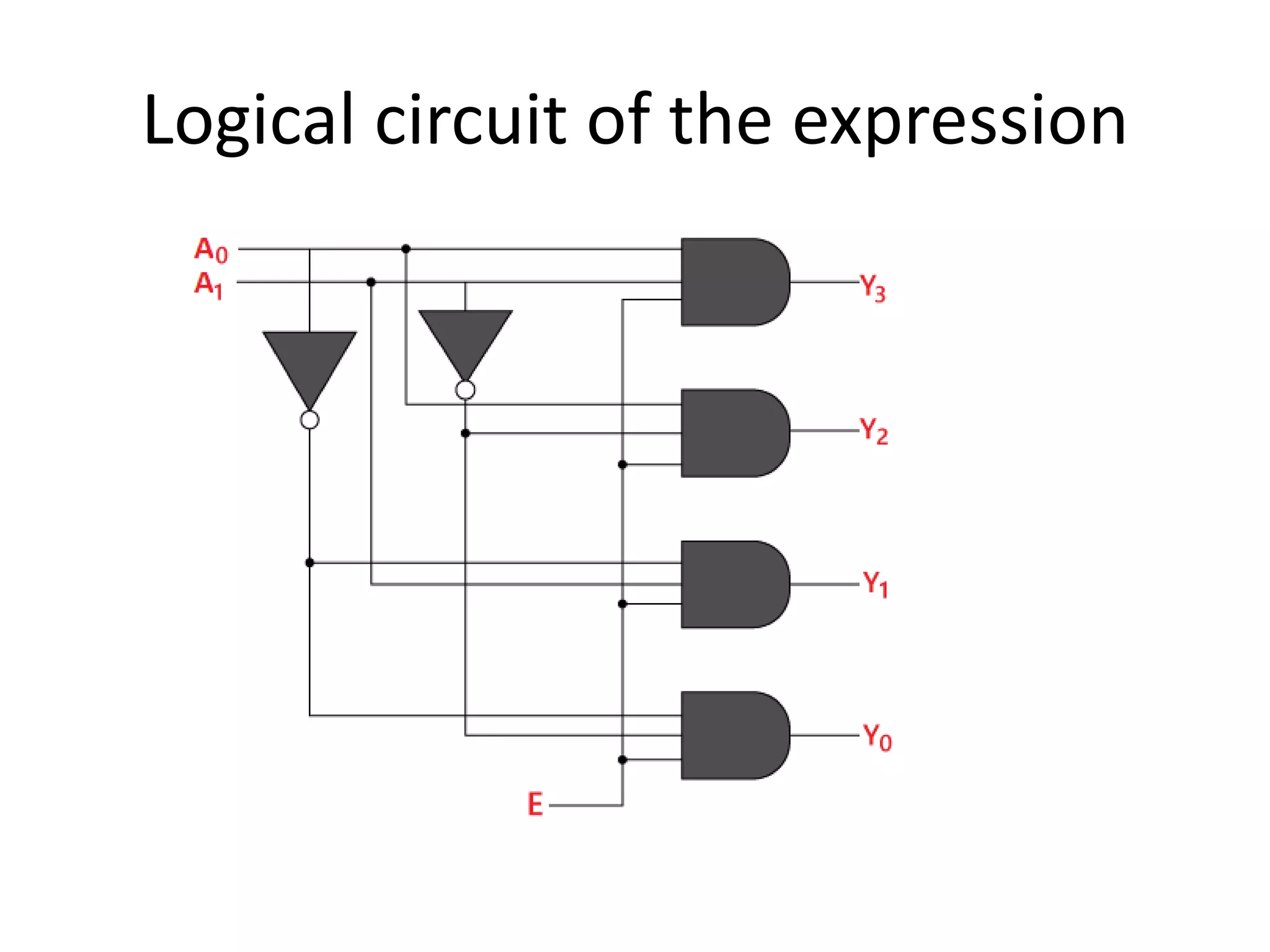
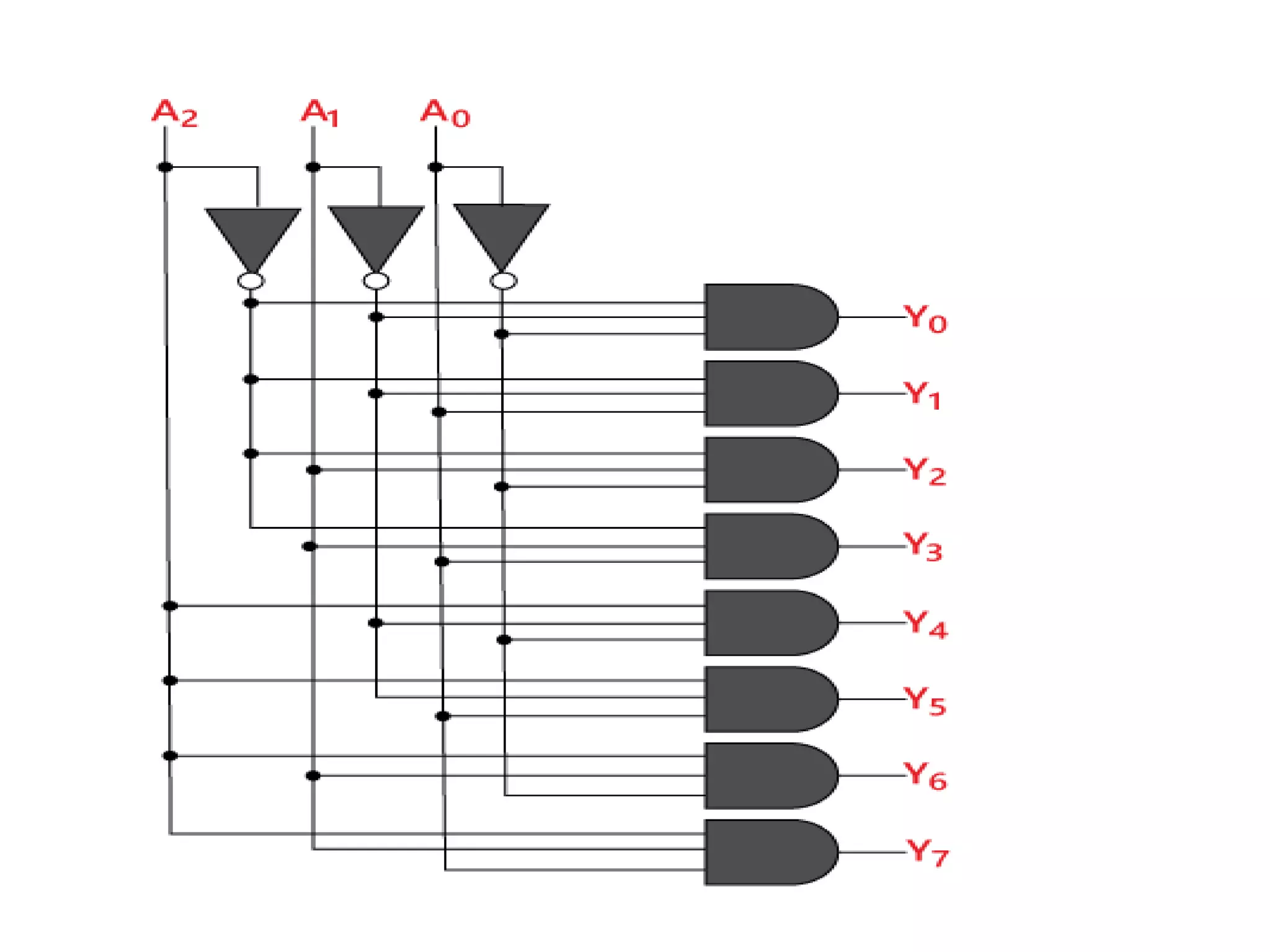
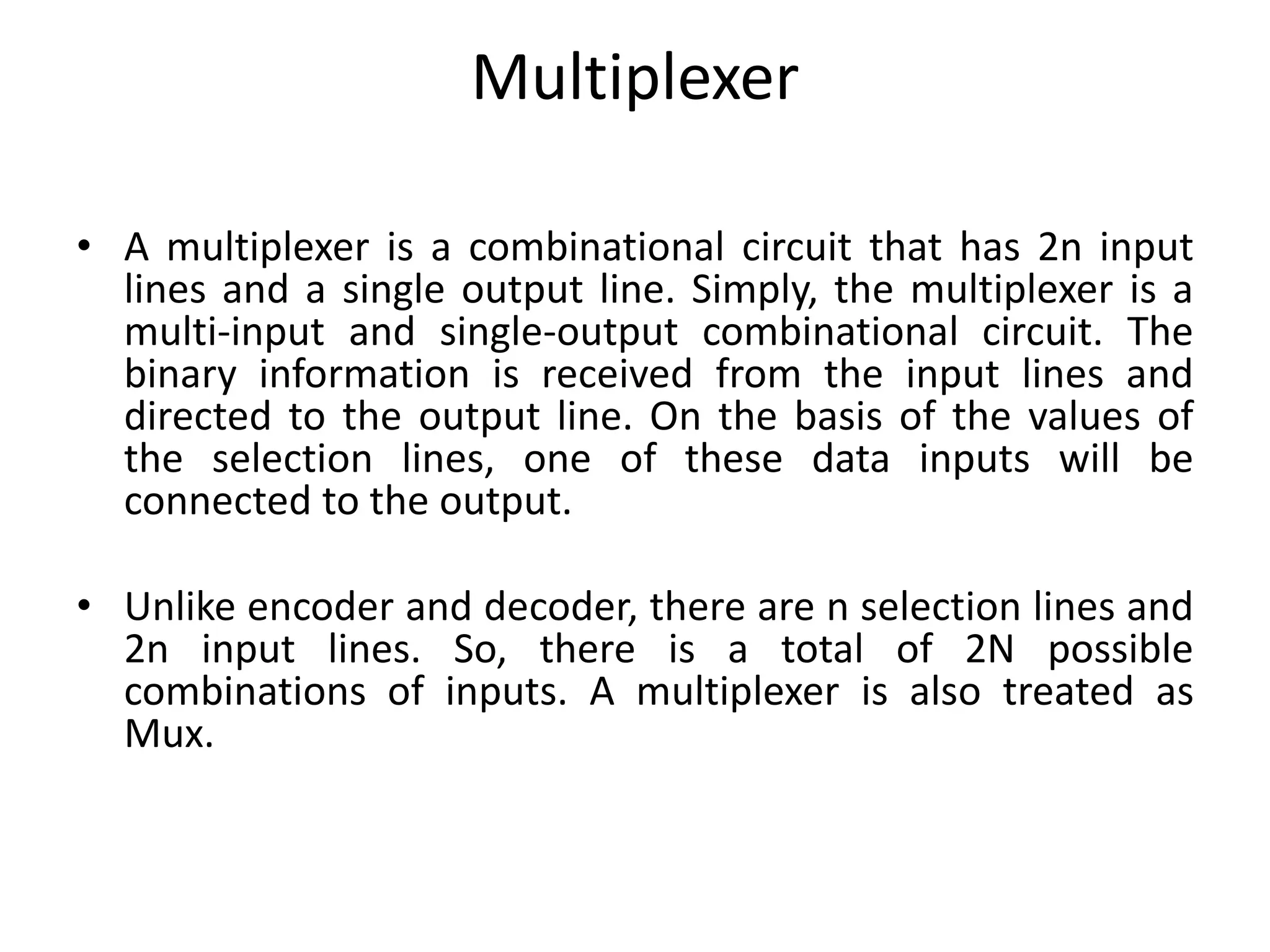
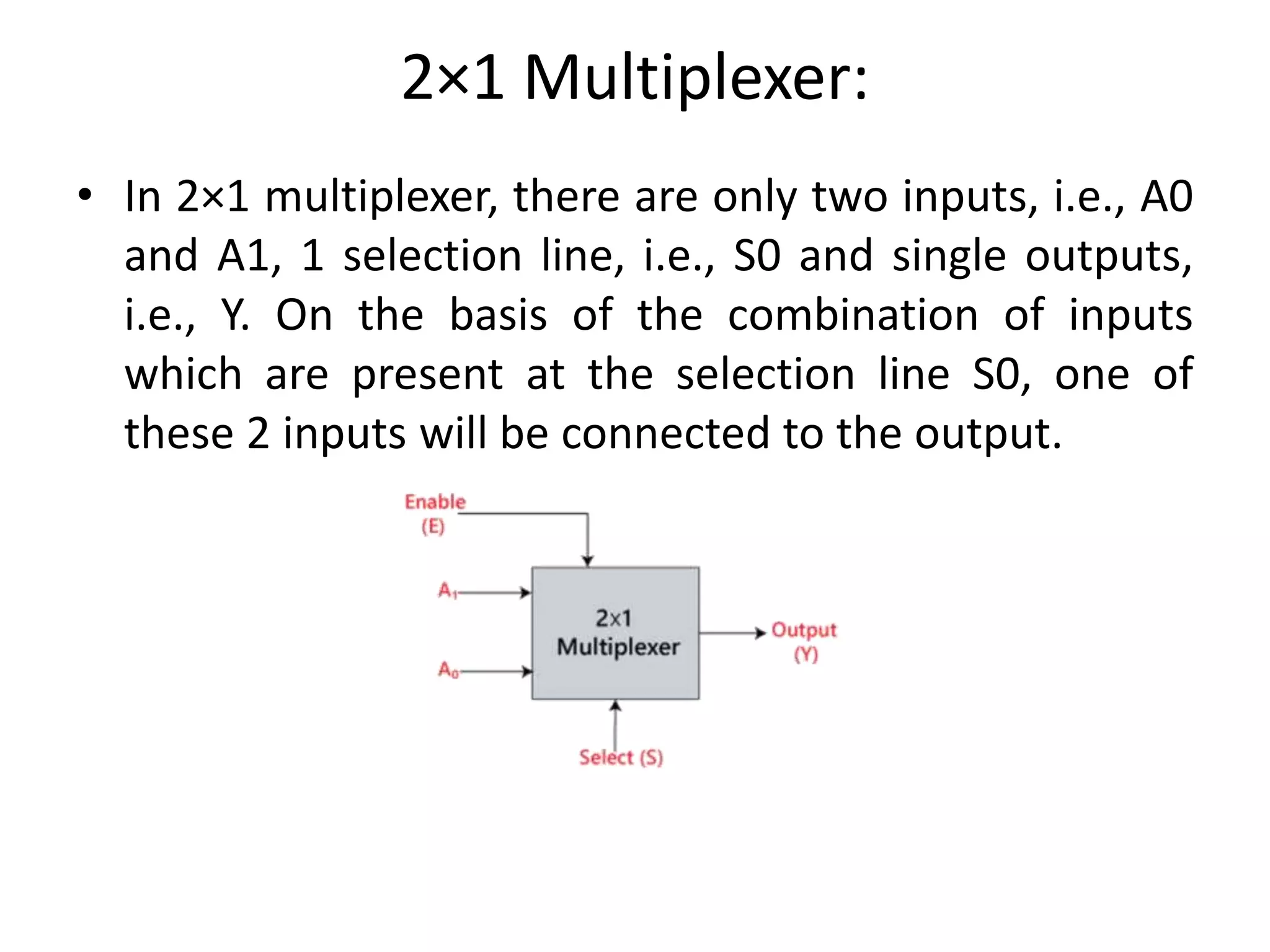
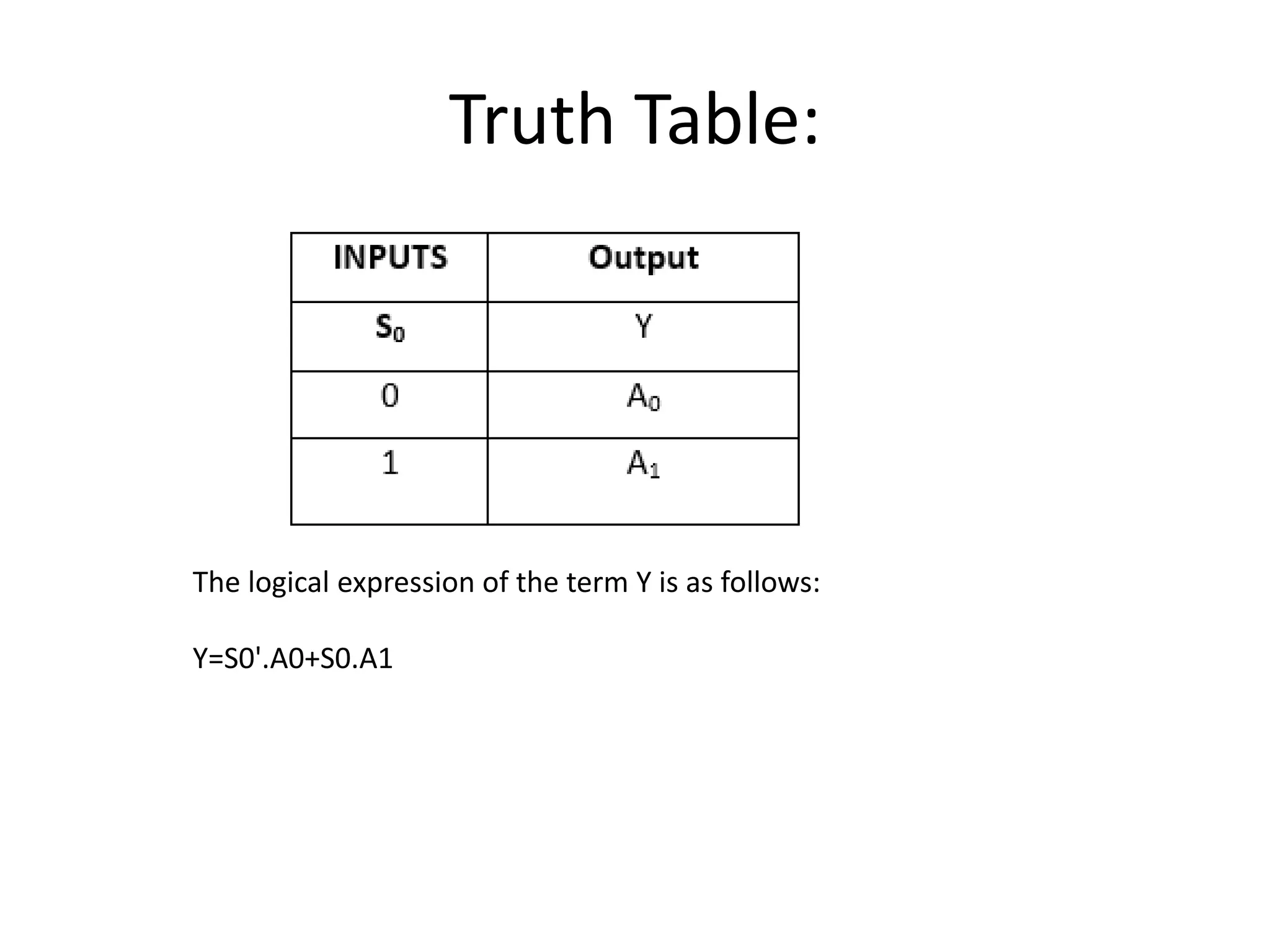
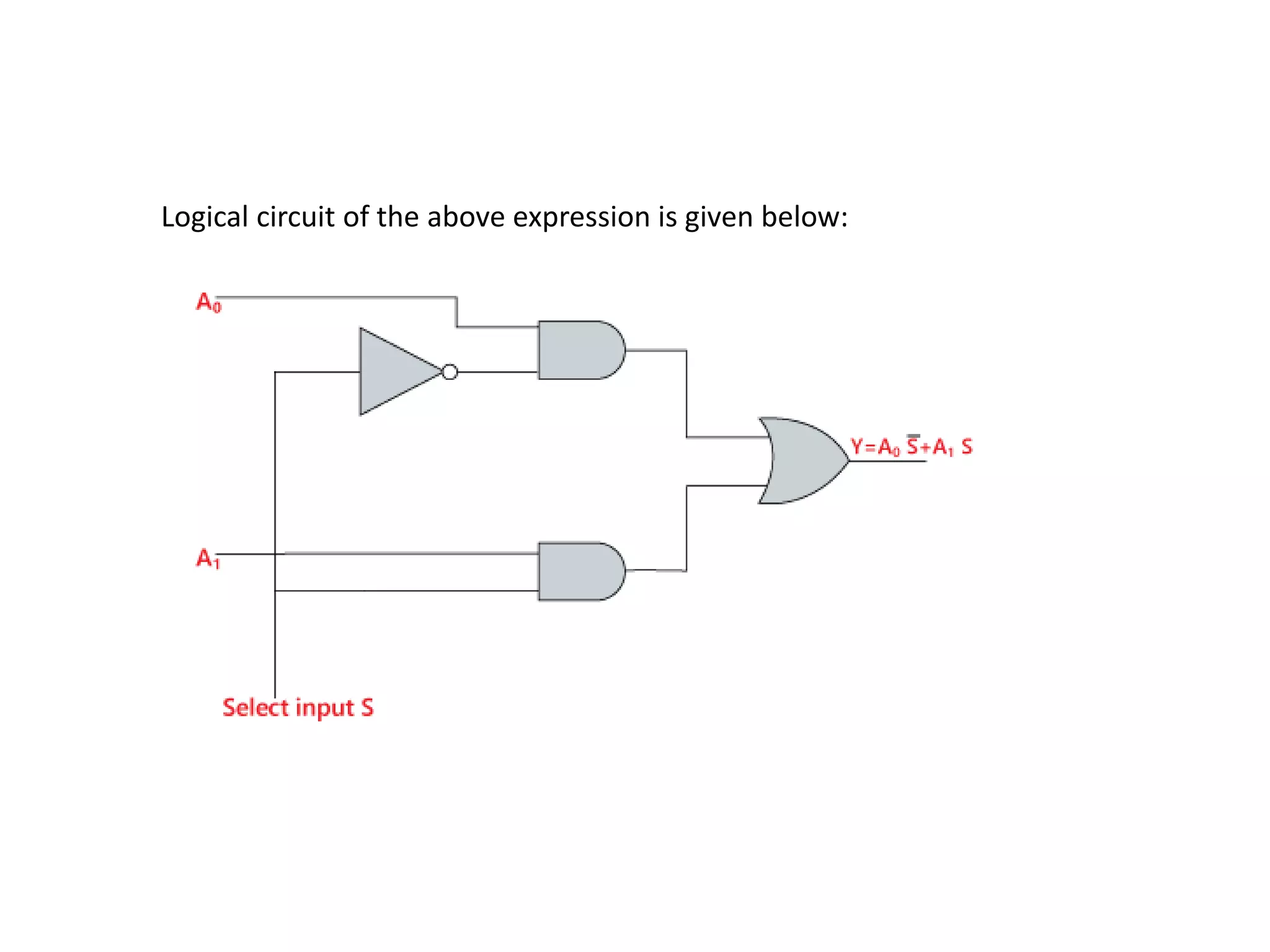
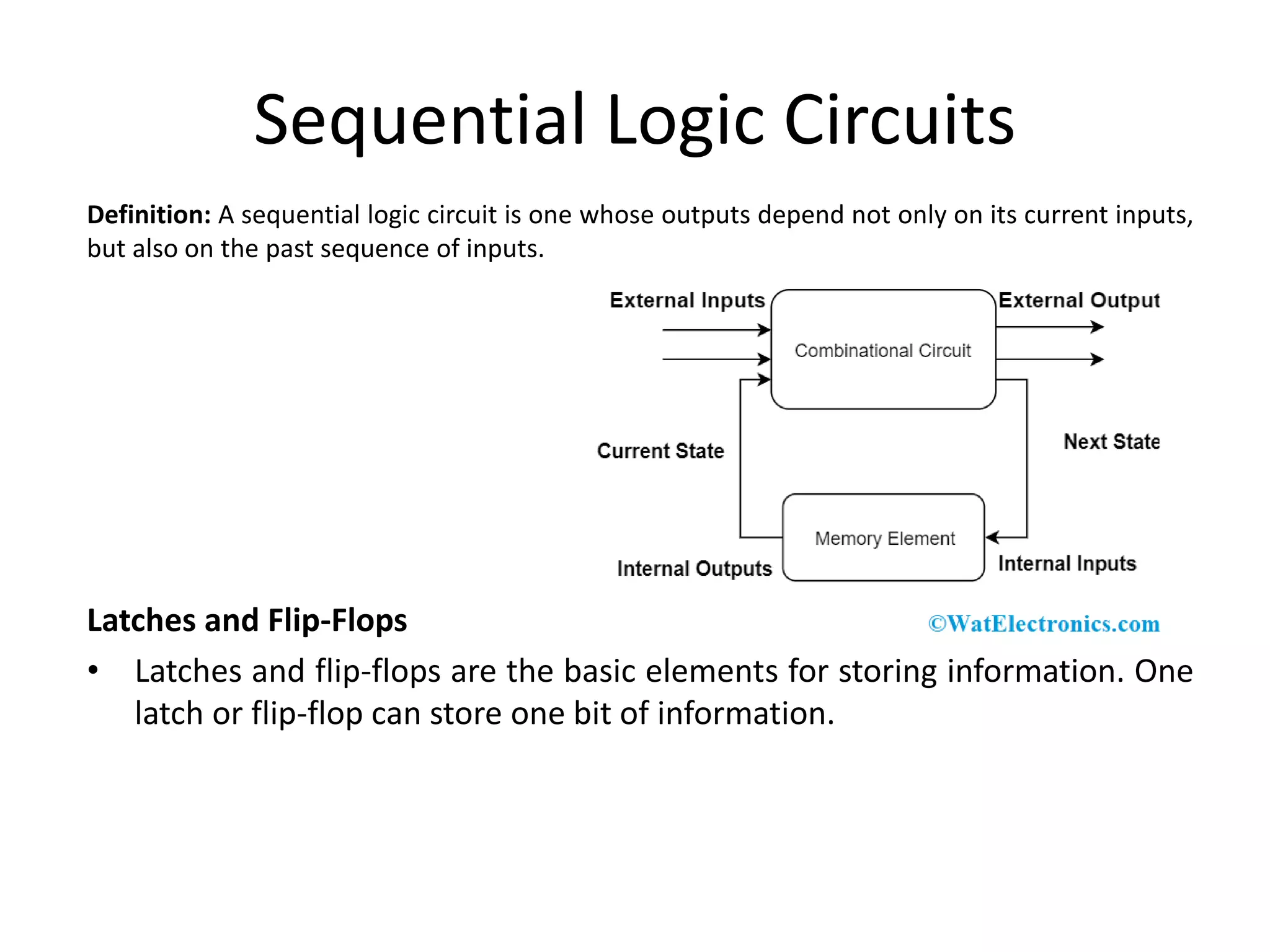
Combinational circuits are digital circuits whose outputs depend only on the current inputs. They do not have internal memory and include common components like multiplexers, decoders, and adders. A combinational circuit with n inputs can have up to 2^n possible output combinations. Common combinational circuits discussed in the document include half adders, full adders, decoders, and multiplexers along with their truth tables and applications. Sequential circuits differ in that their outputs depend on both current and previous inputs due to internal memory elements like latches and flip-flops.