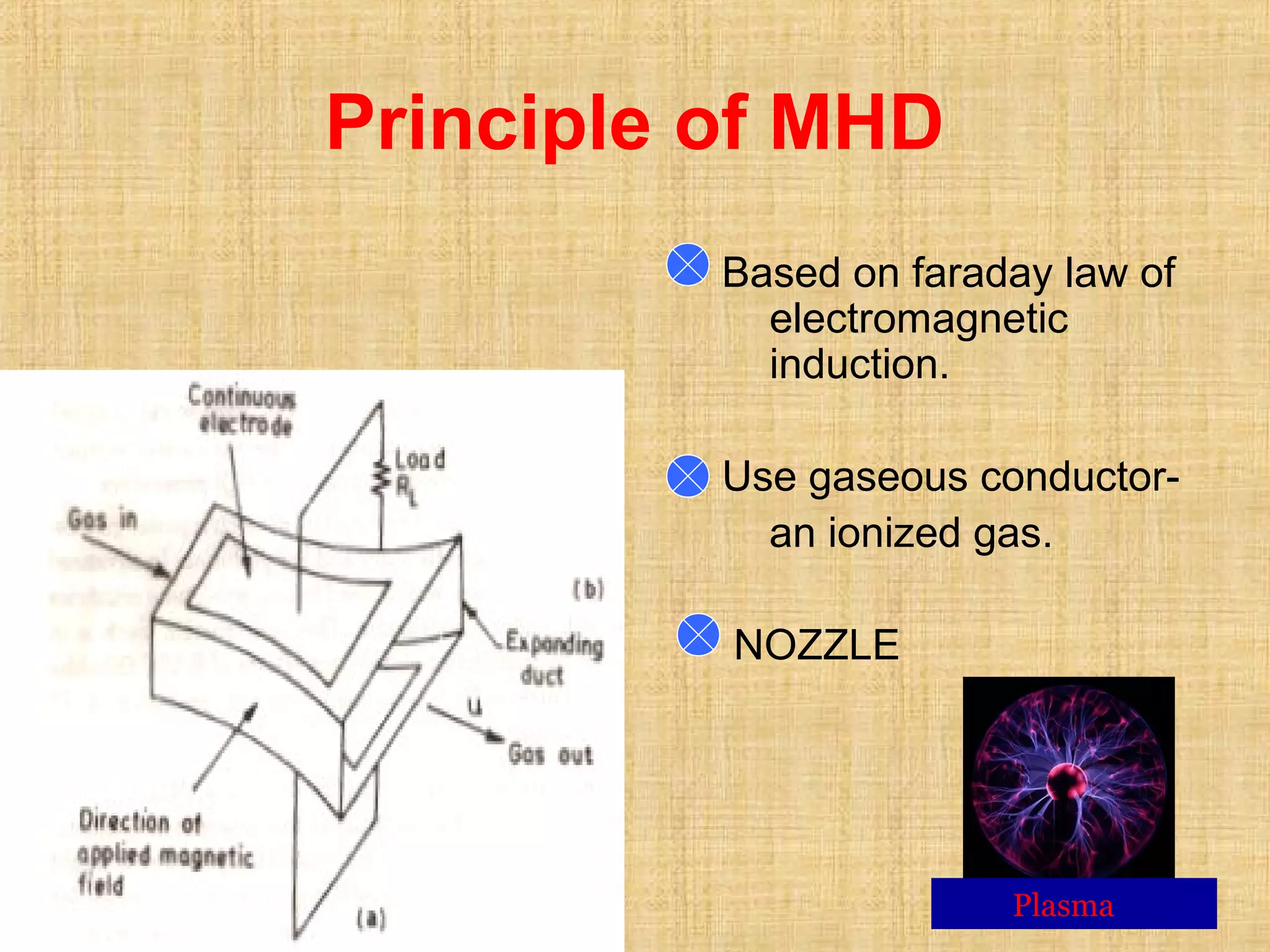
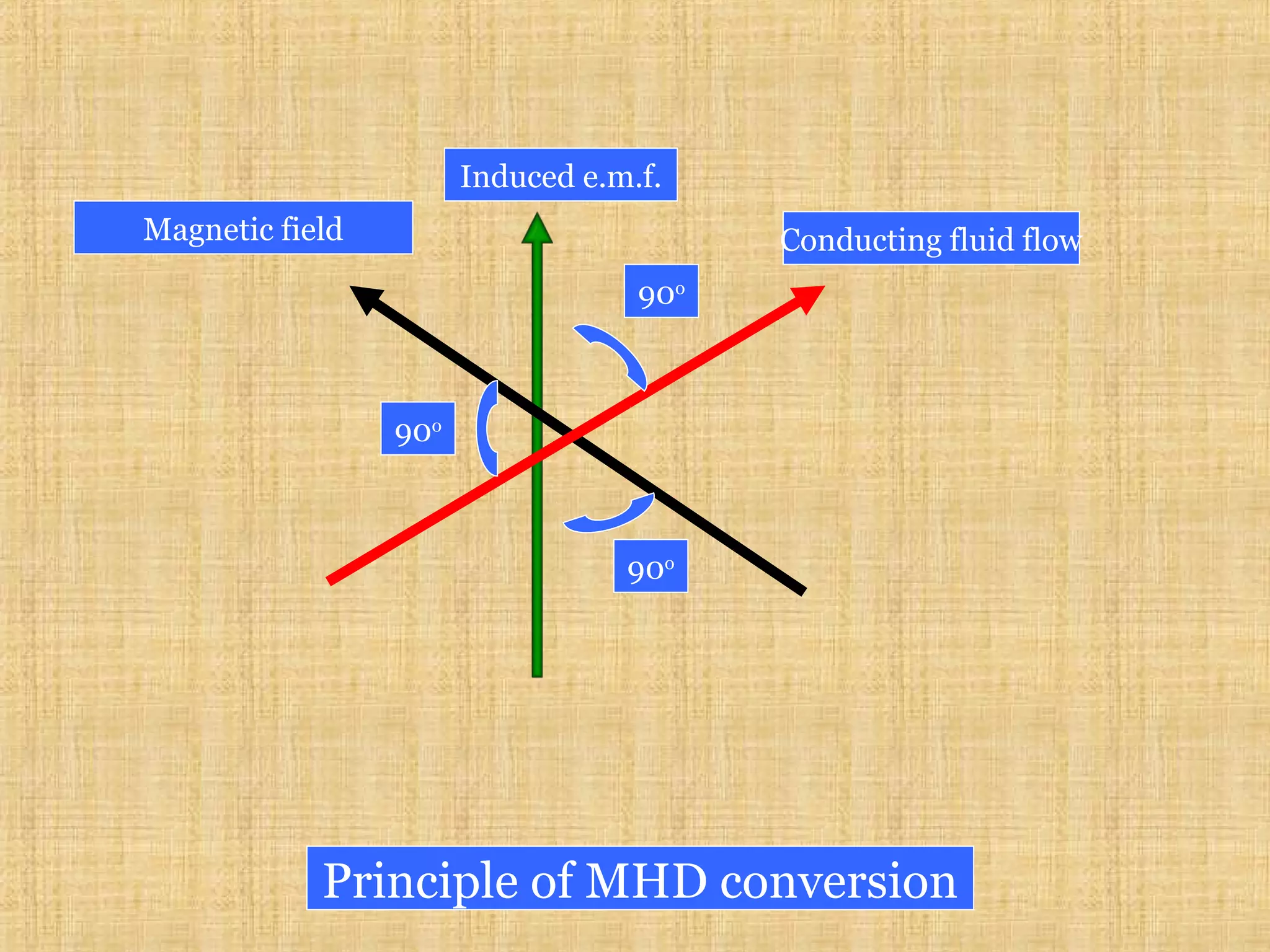
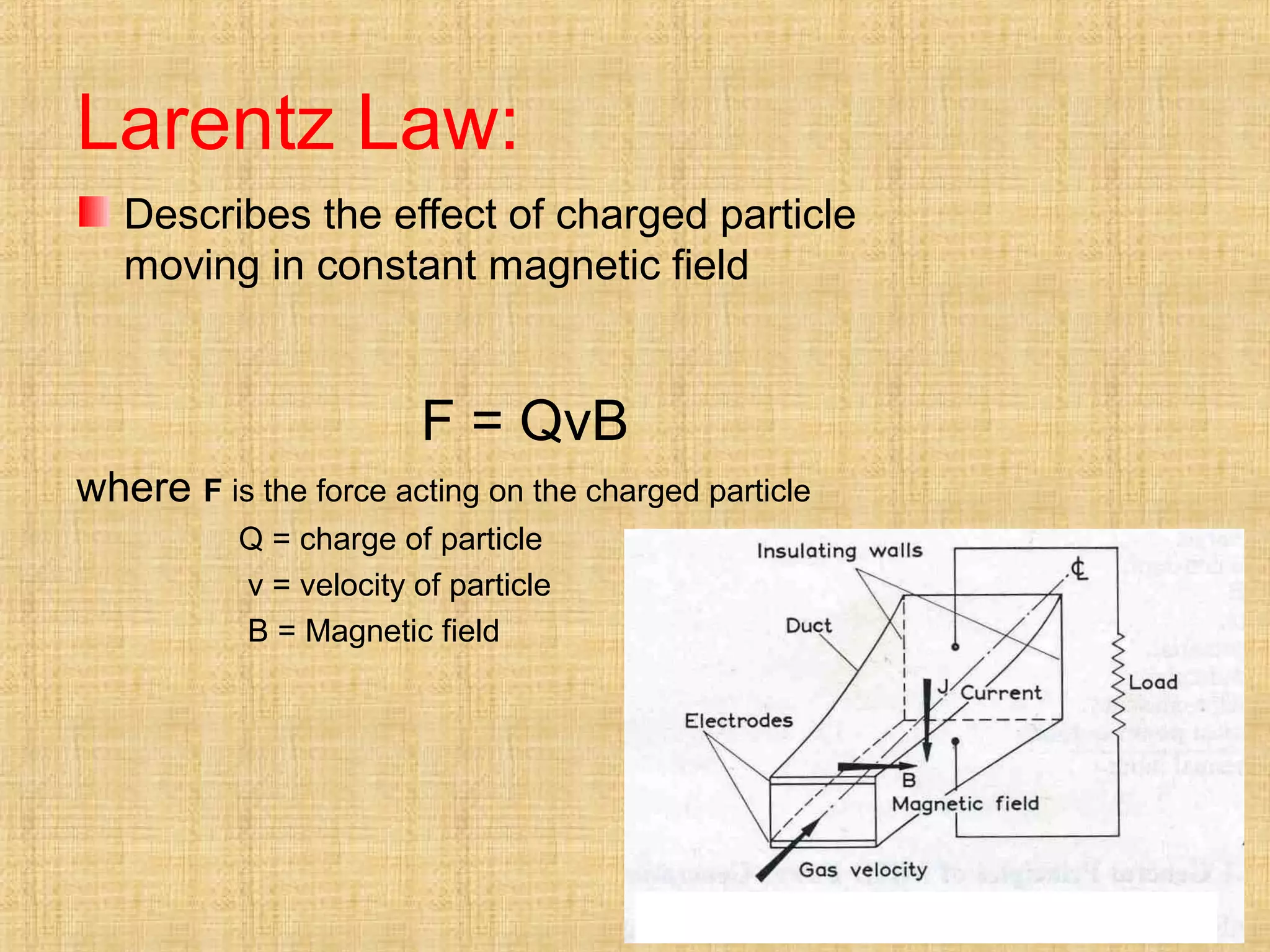
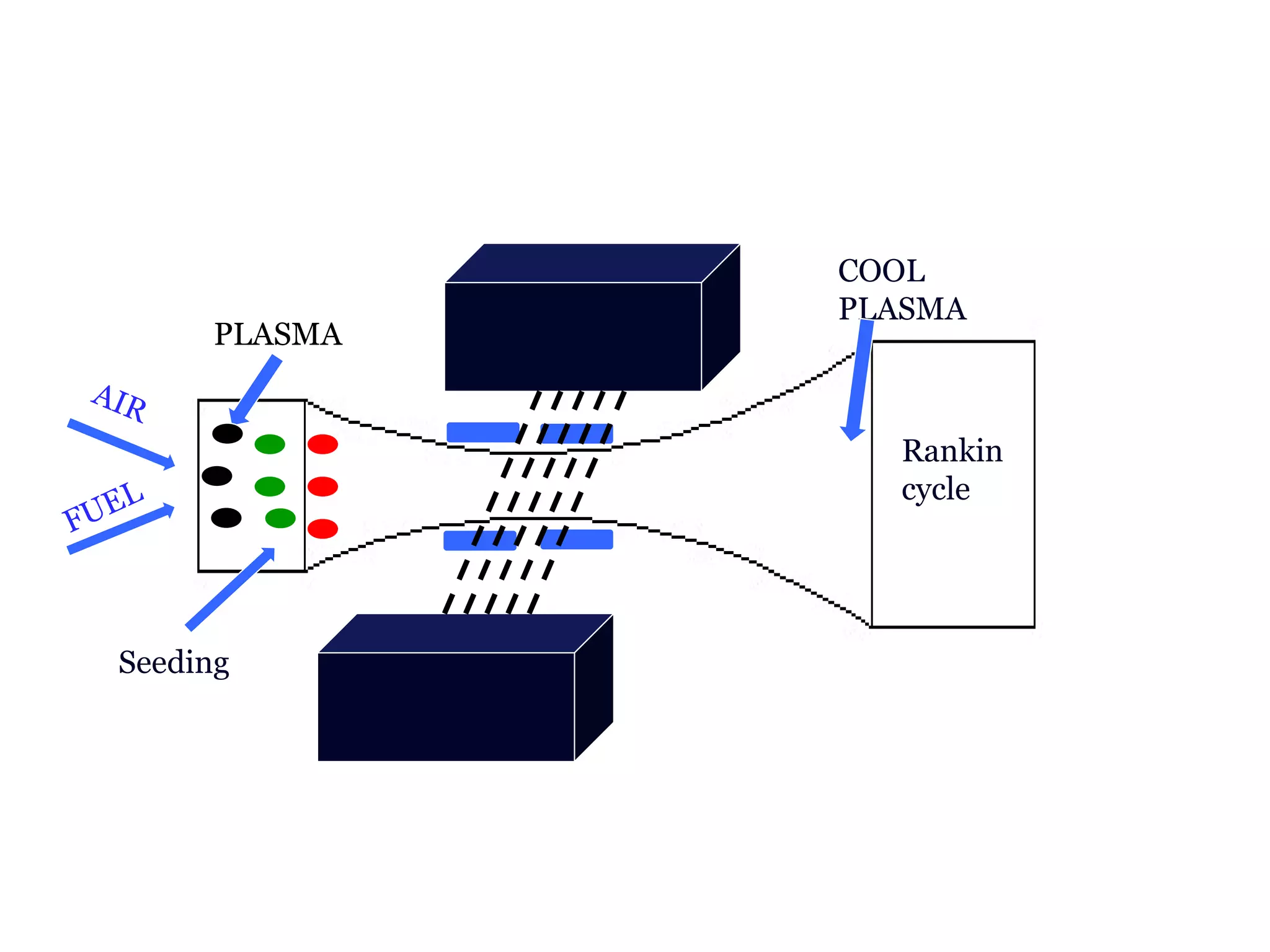
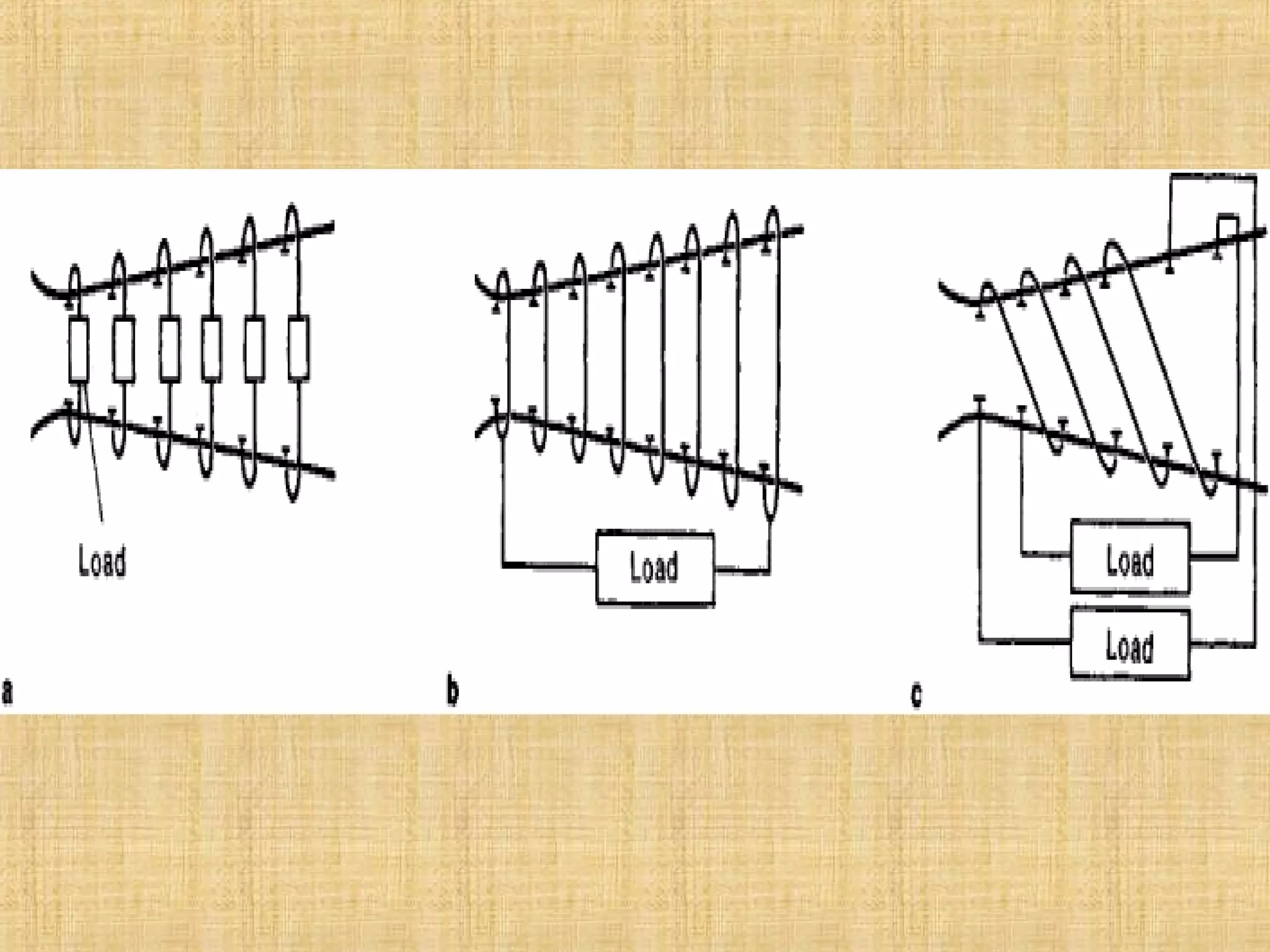
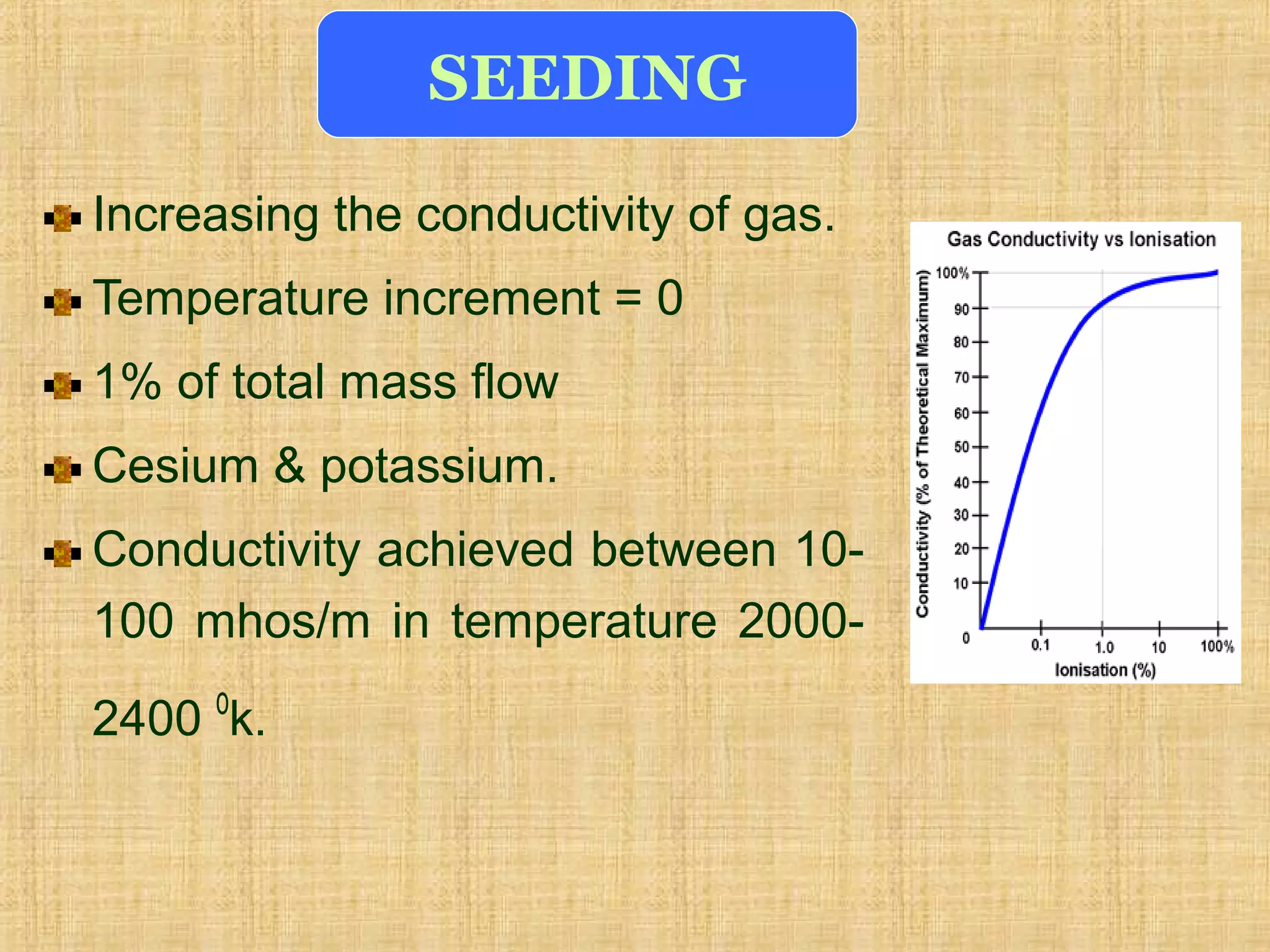
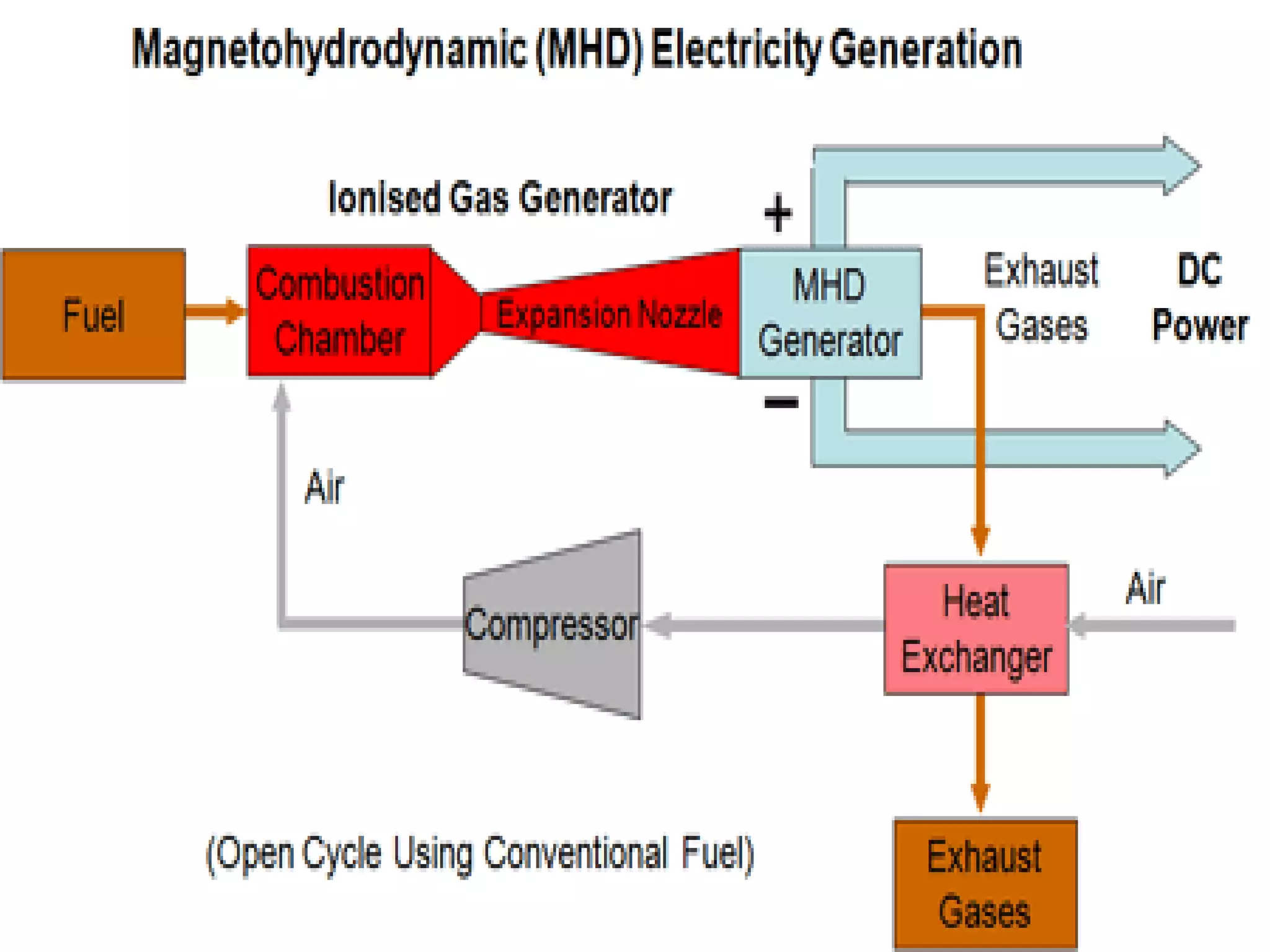
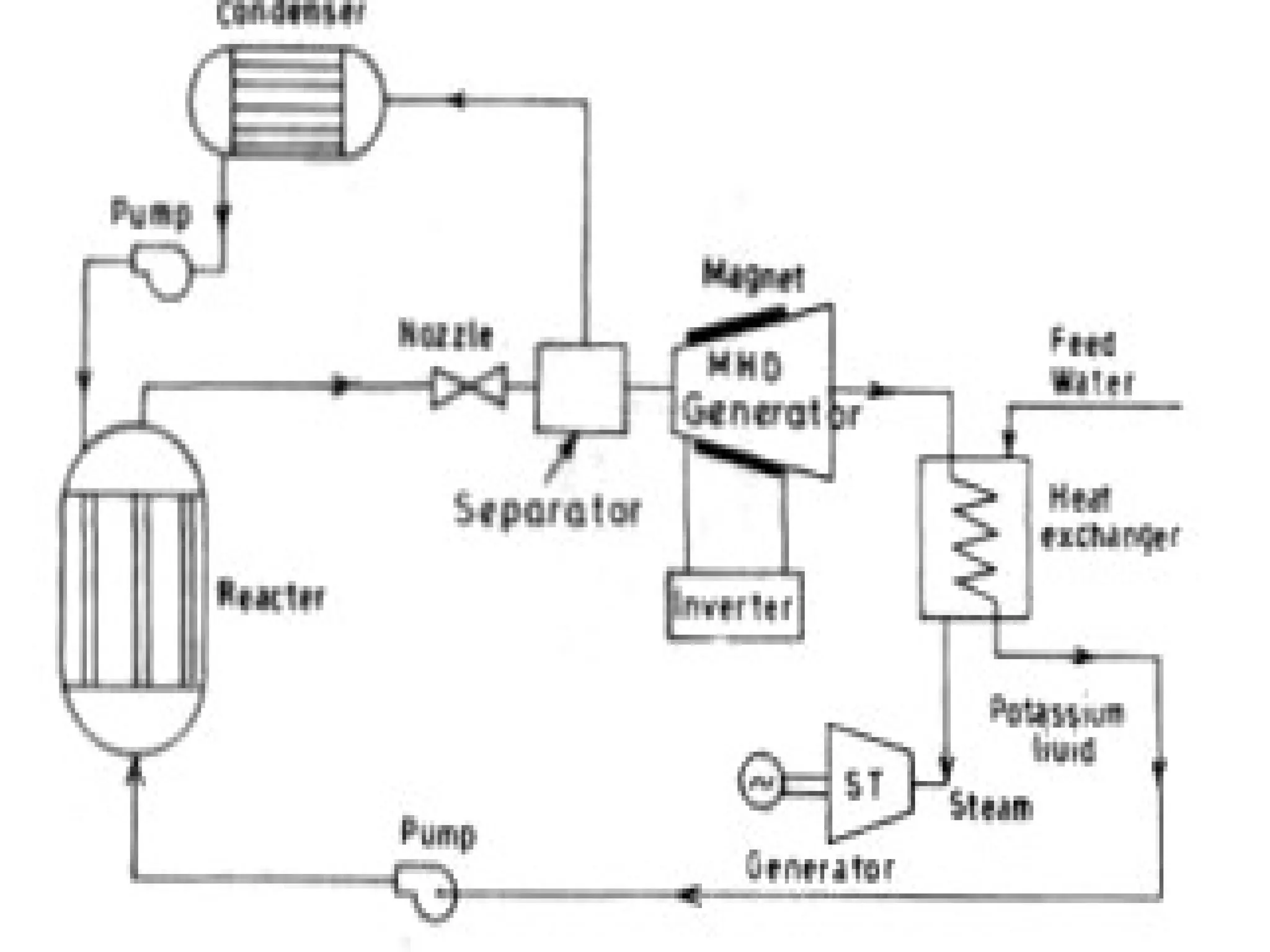
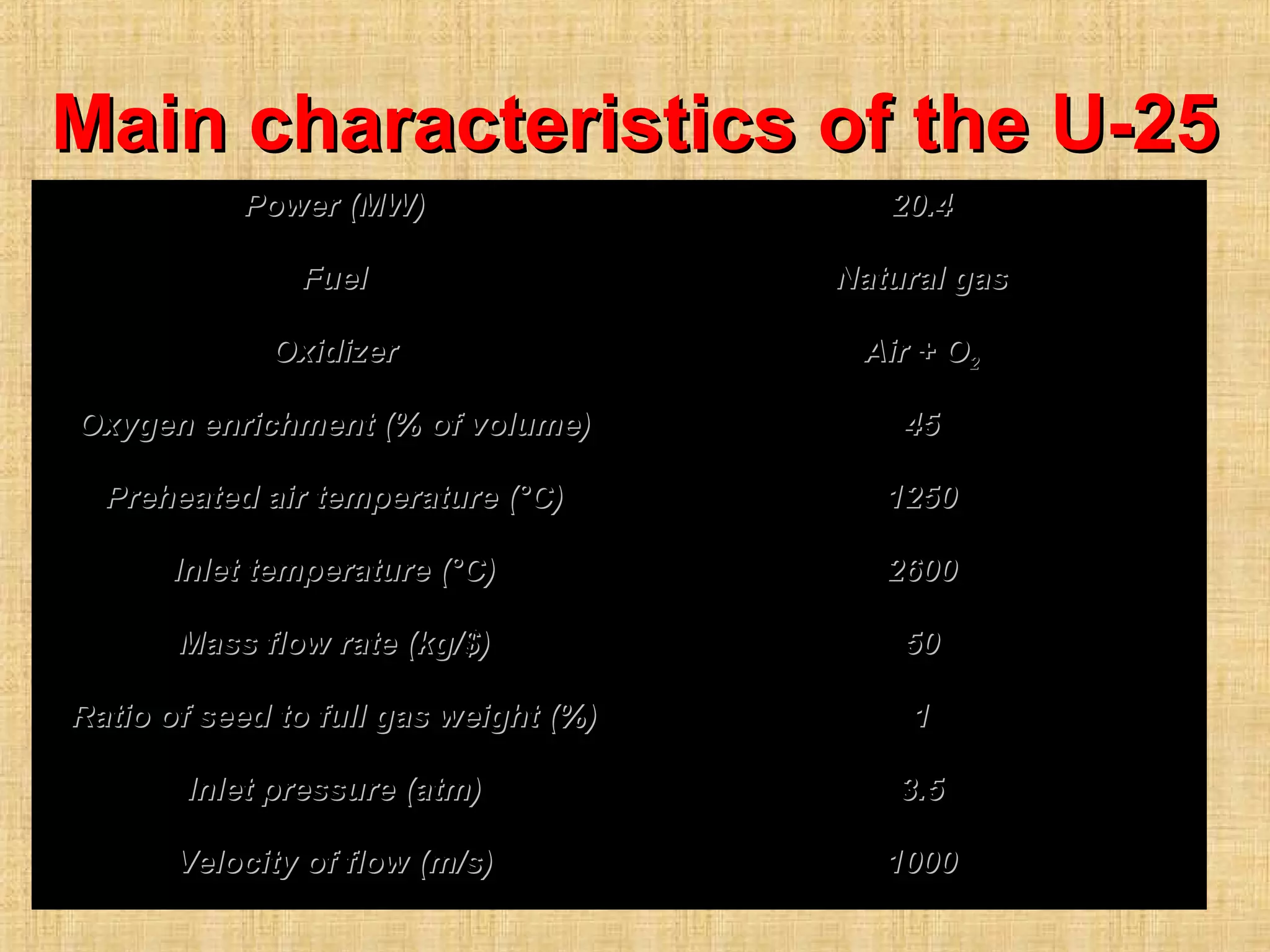
This document discusses magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) power generation. MHD uses electrically conducting fluids to directly convert heat into electricity in the presence of magnetic fields. It has the potential for higher efficiencies than traditional steam plants. There are two main types of MHD systems - open cycle systems which exhaust hot gases directly and closed cycle systems which recirculate the working fluid. MHD systems avoid moving parts but developing the high temperature fluids and magnetic fields presents design challenges. The technology could allow more efficient, pollution-free large-scale power generation if these problems are addressed.