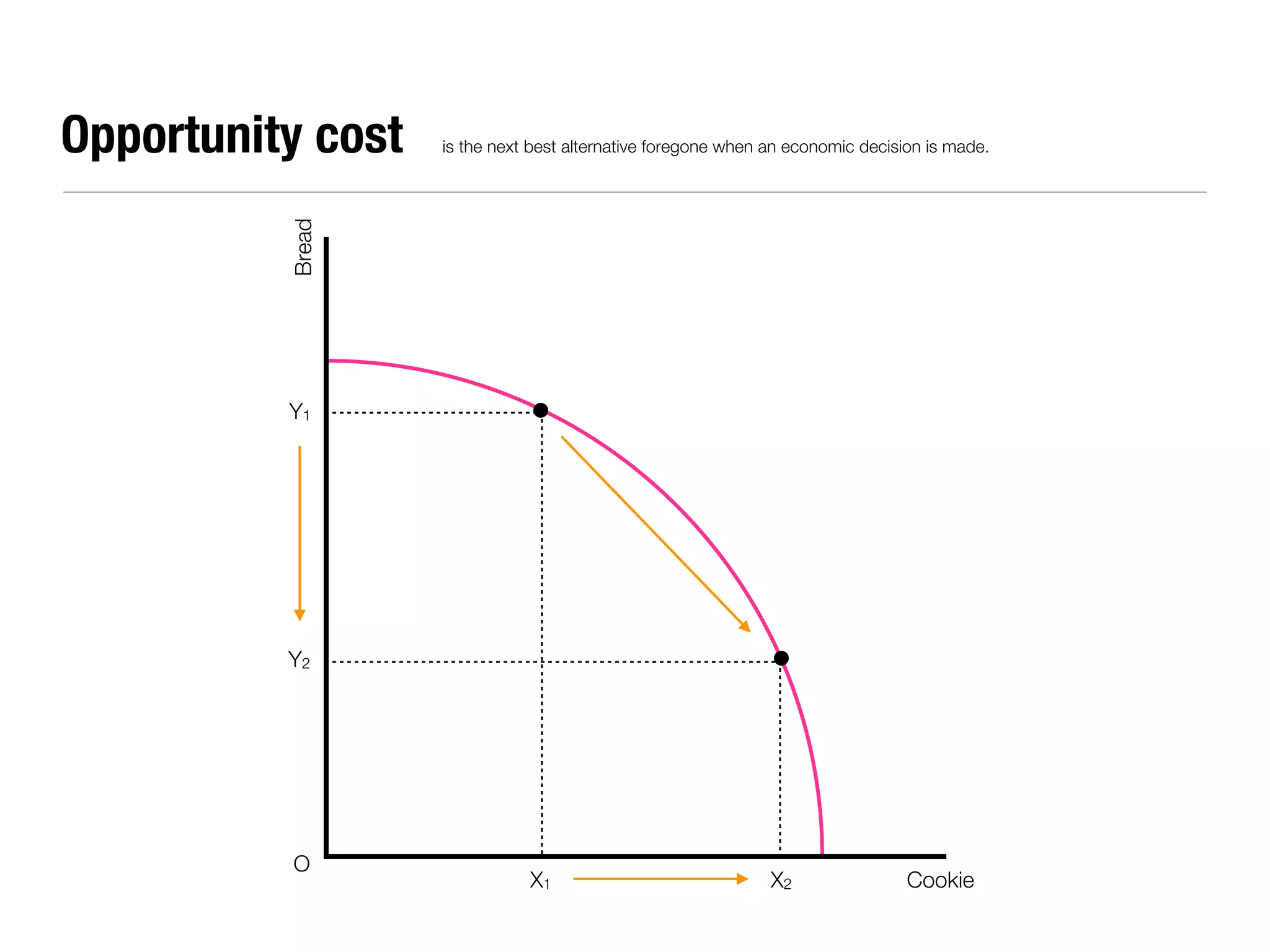
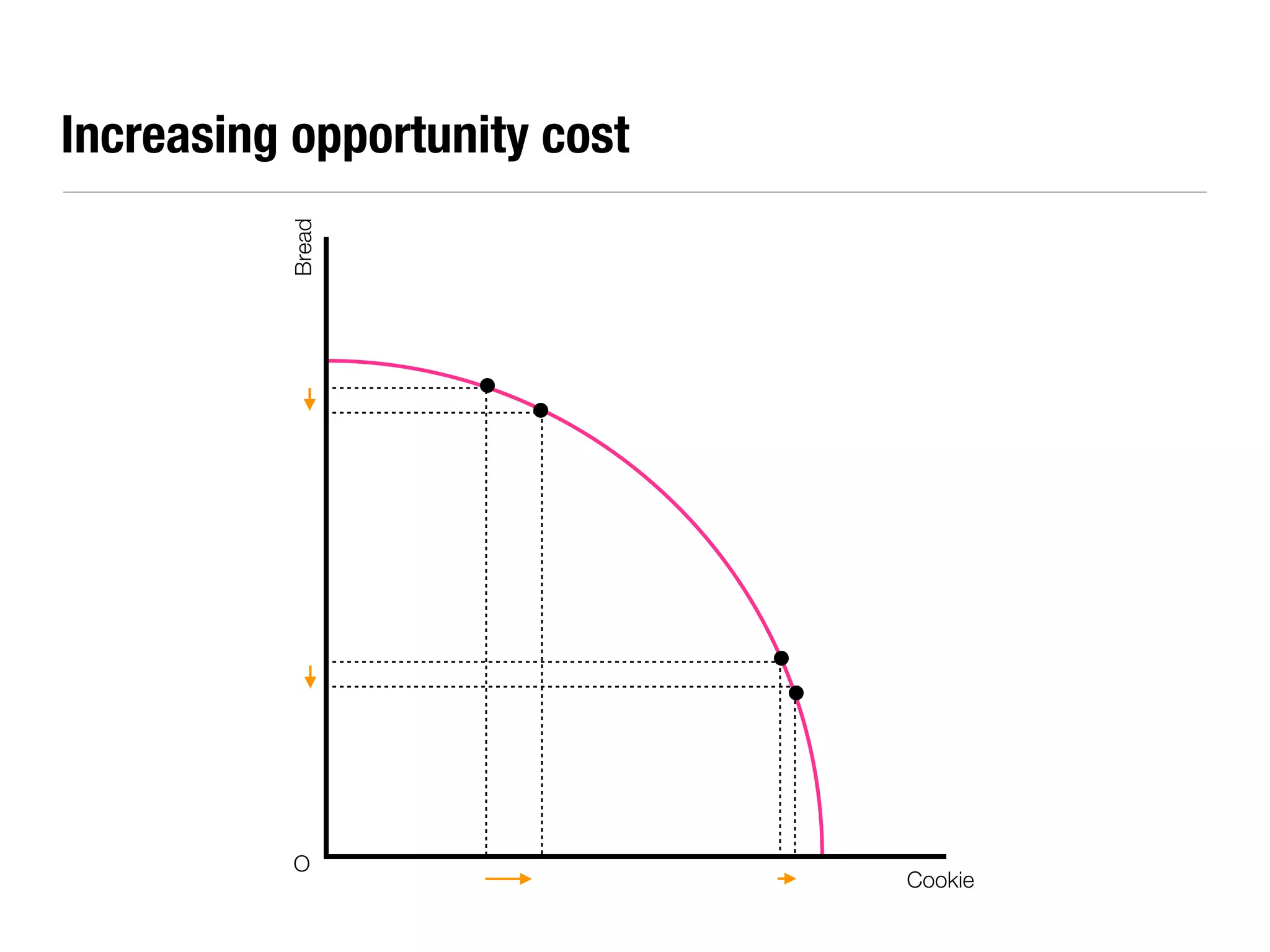
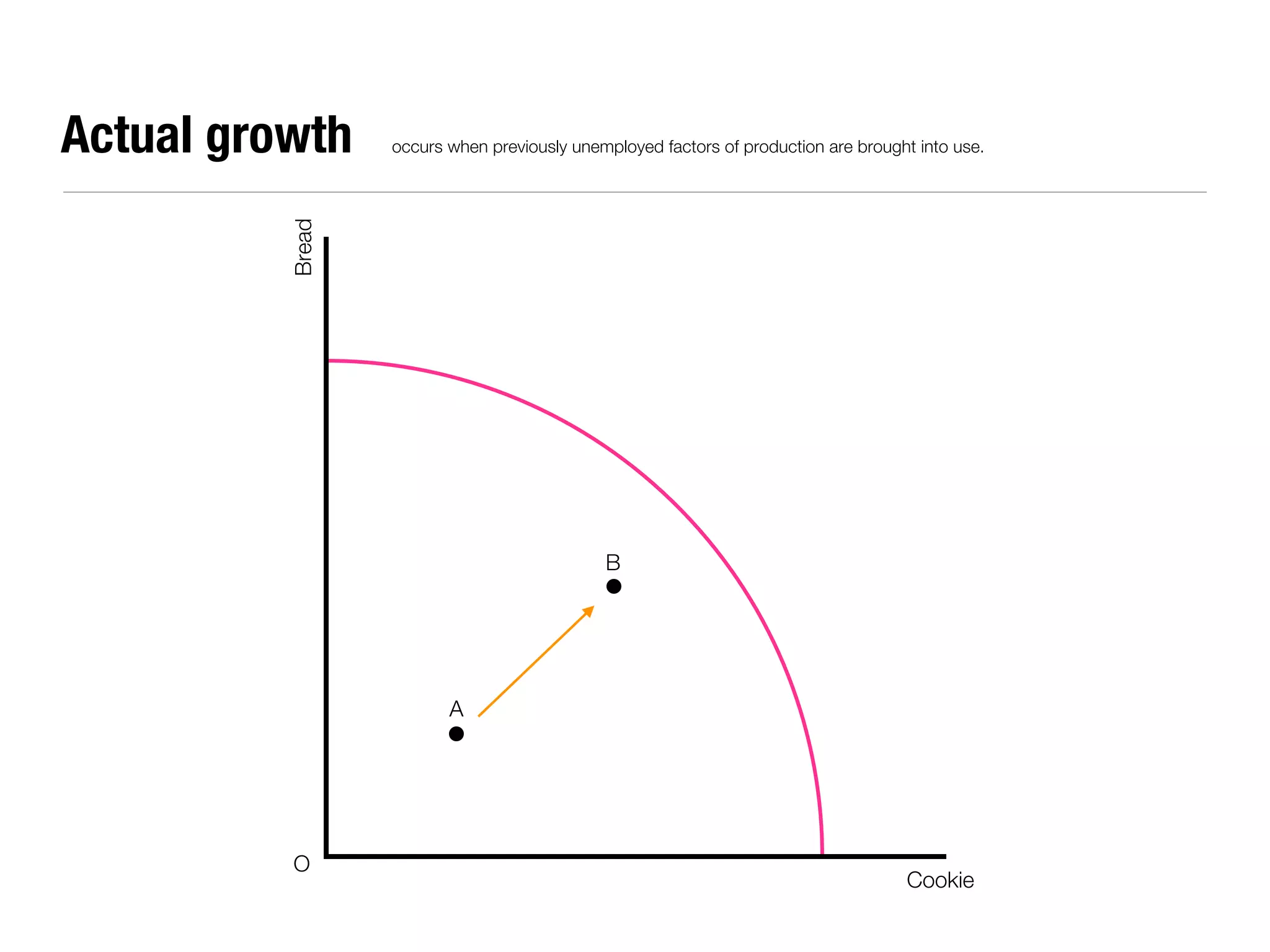
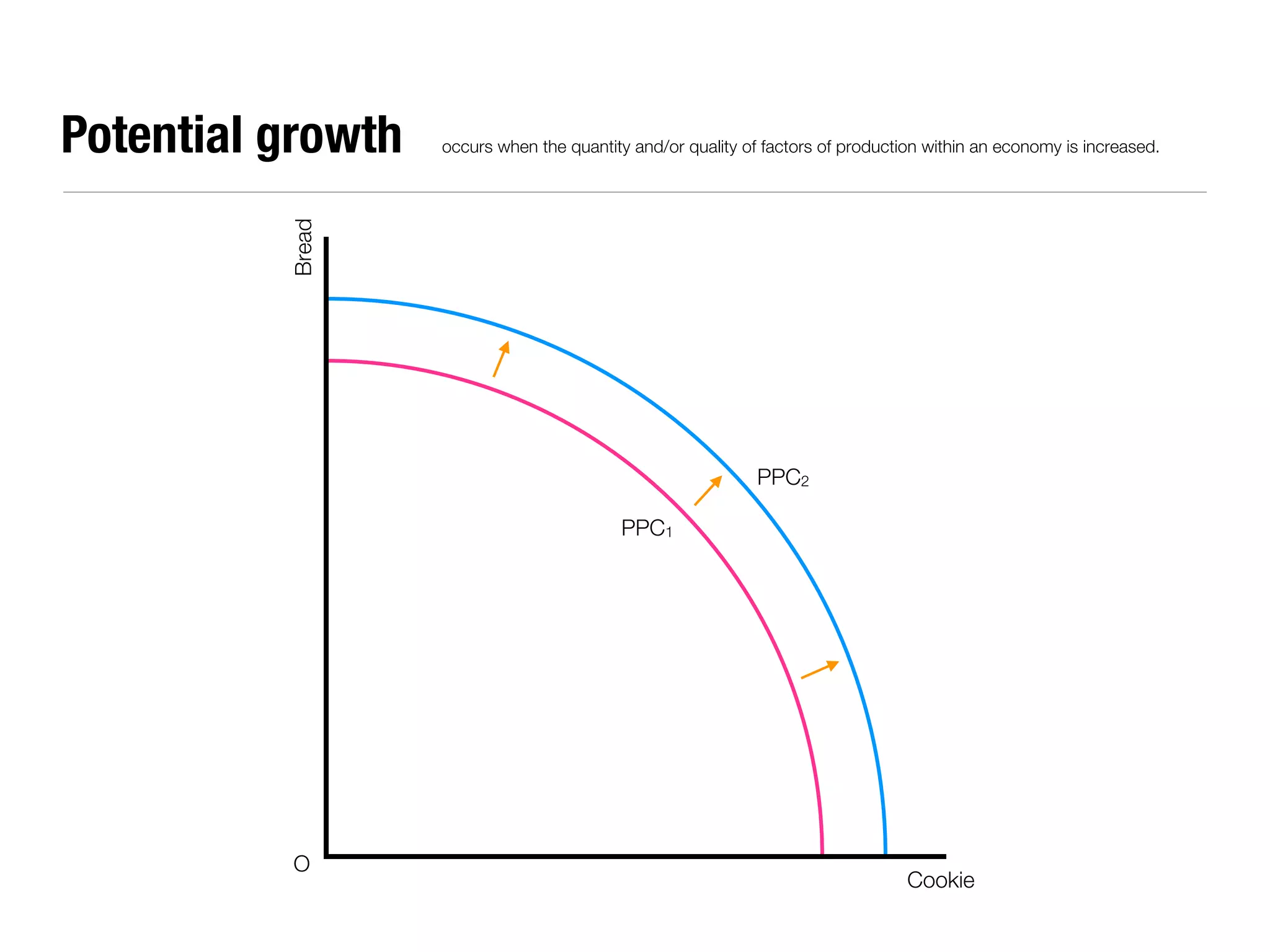
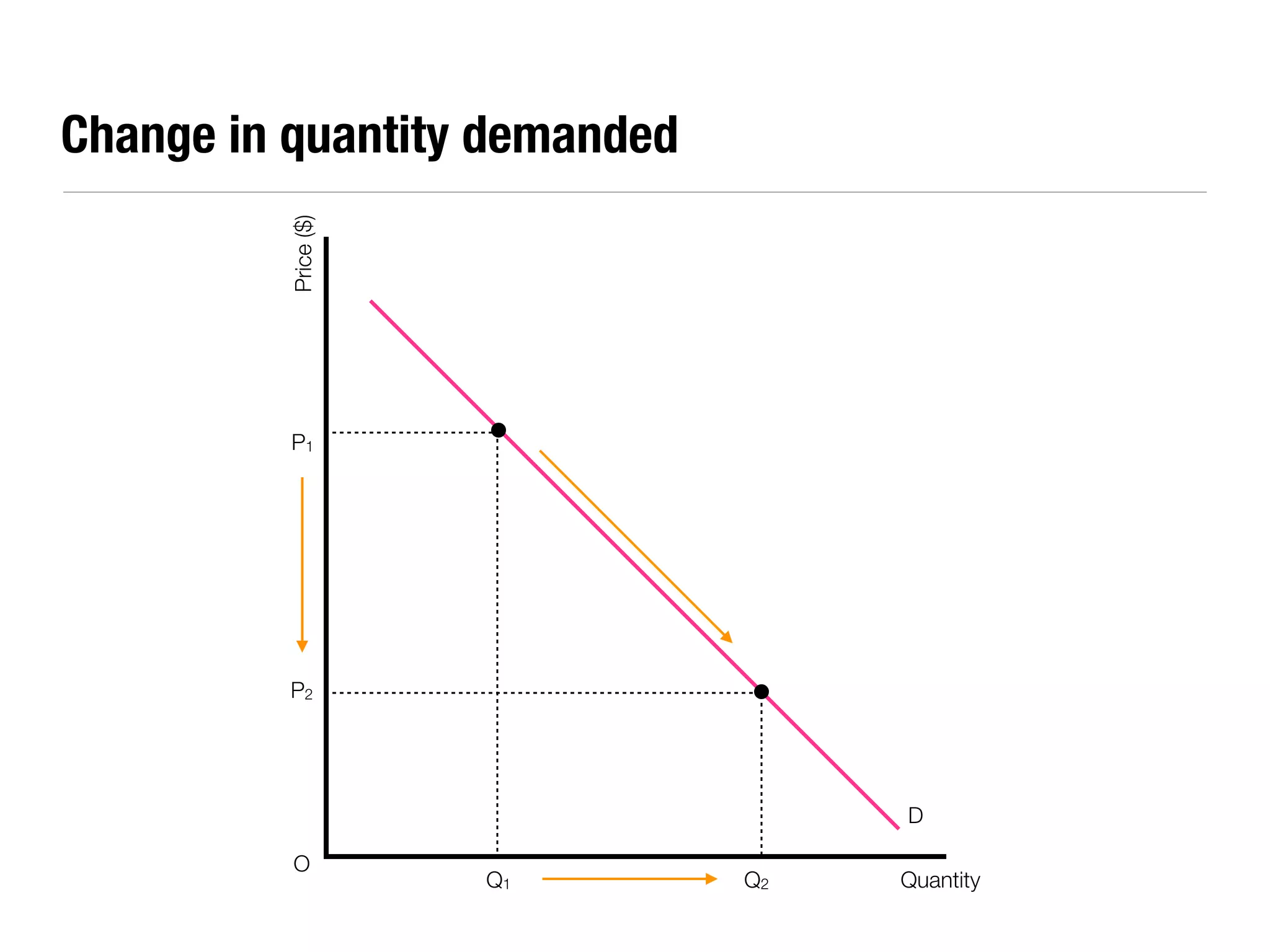
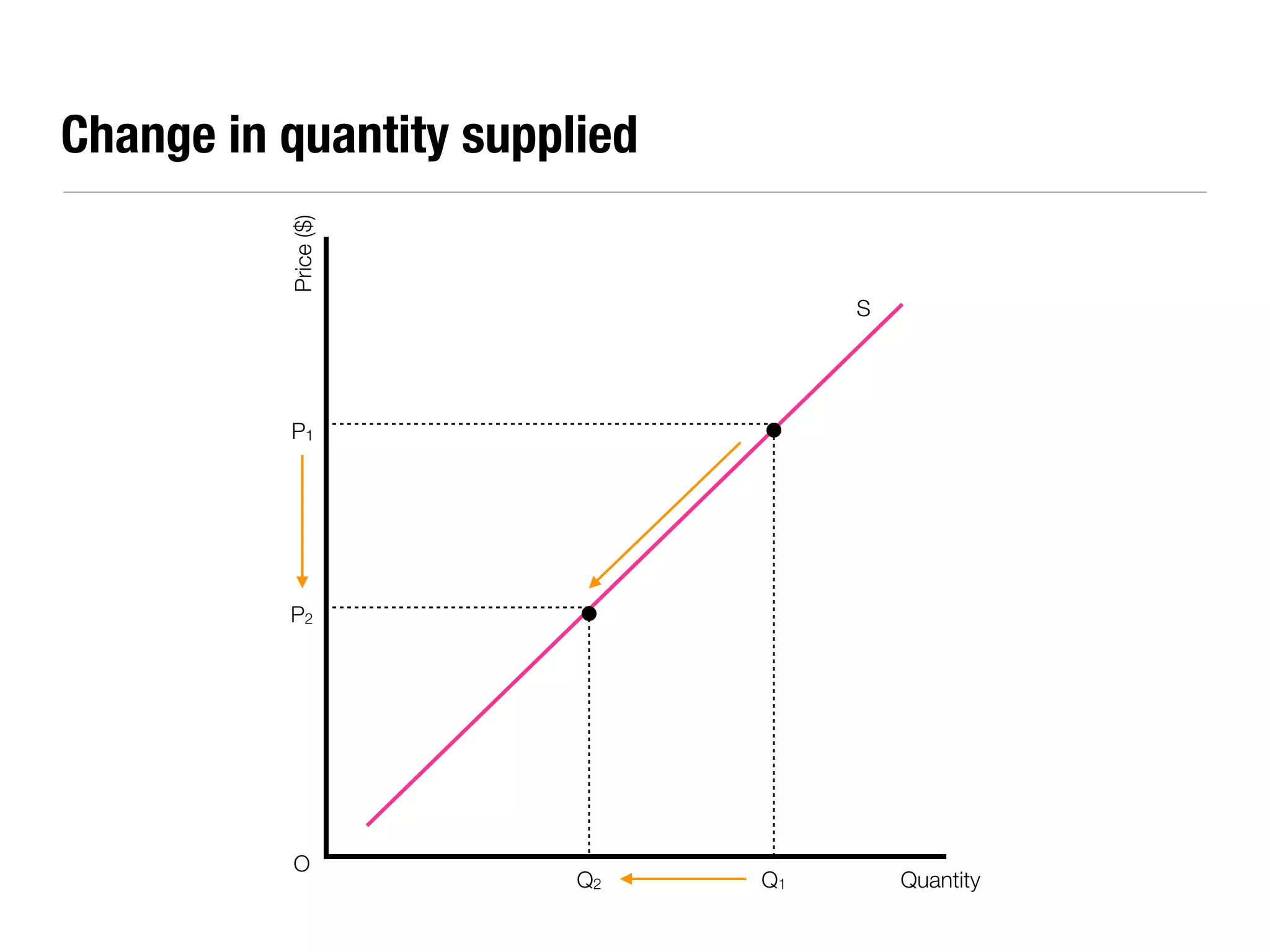
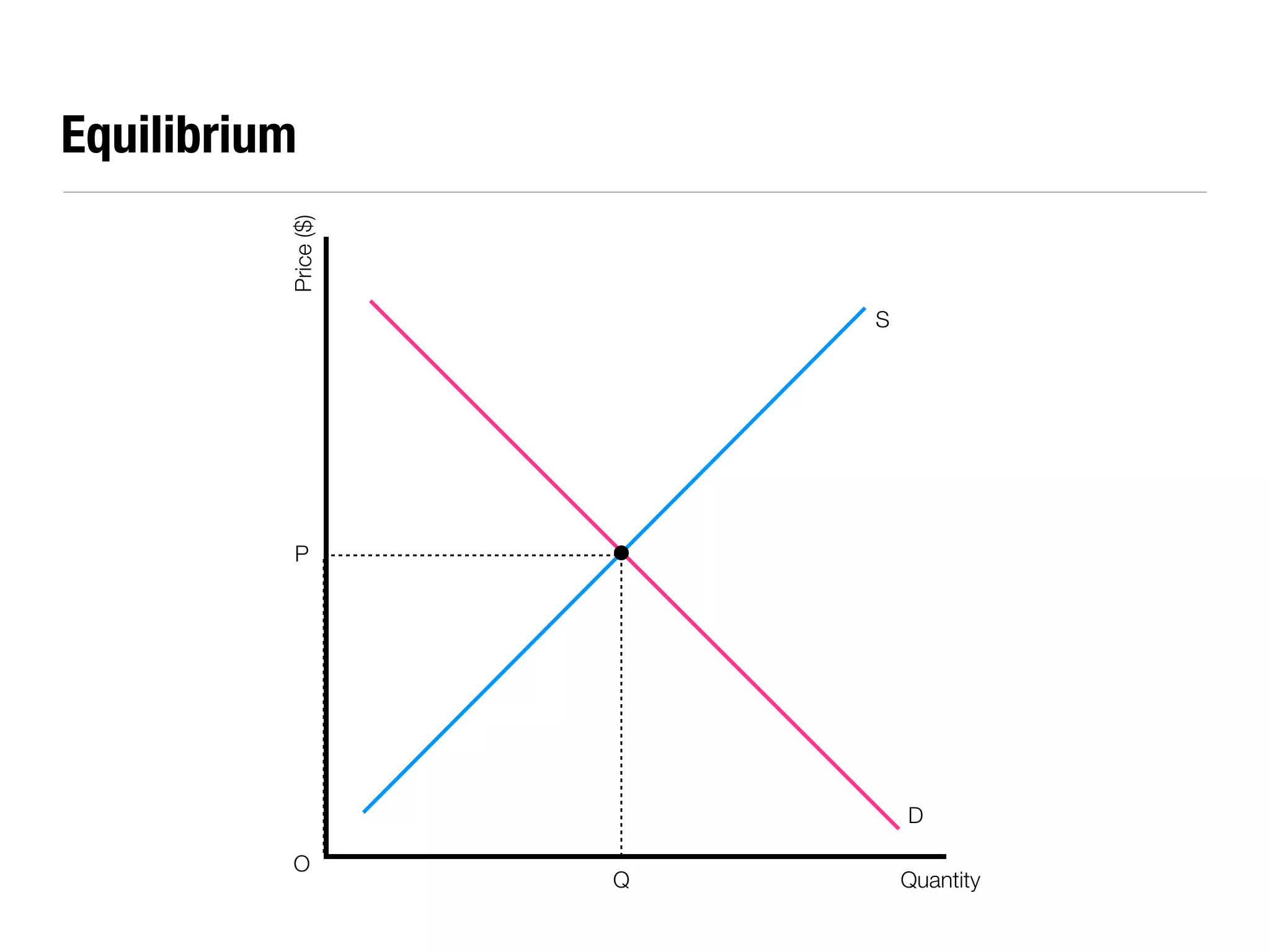
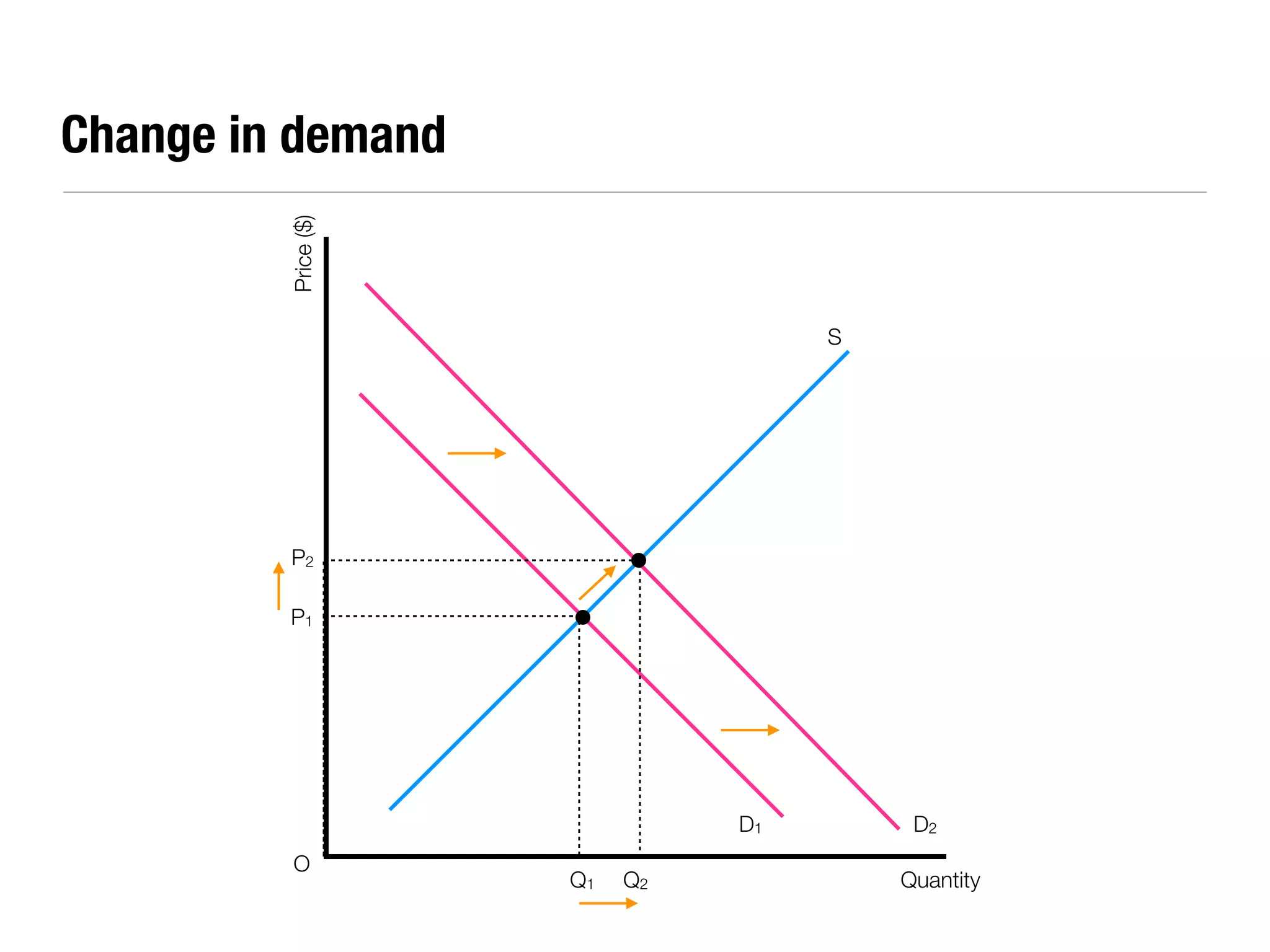
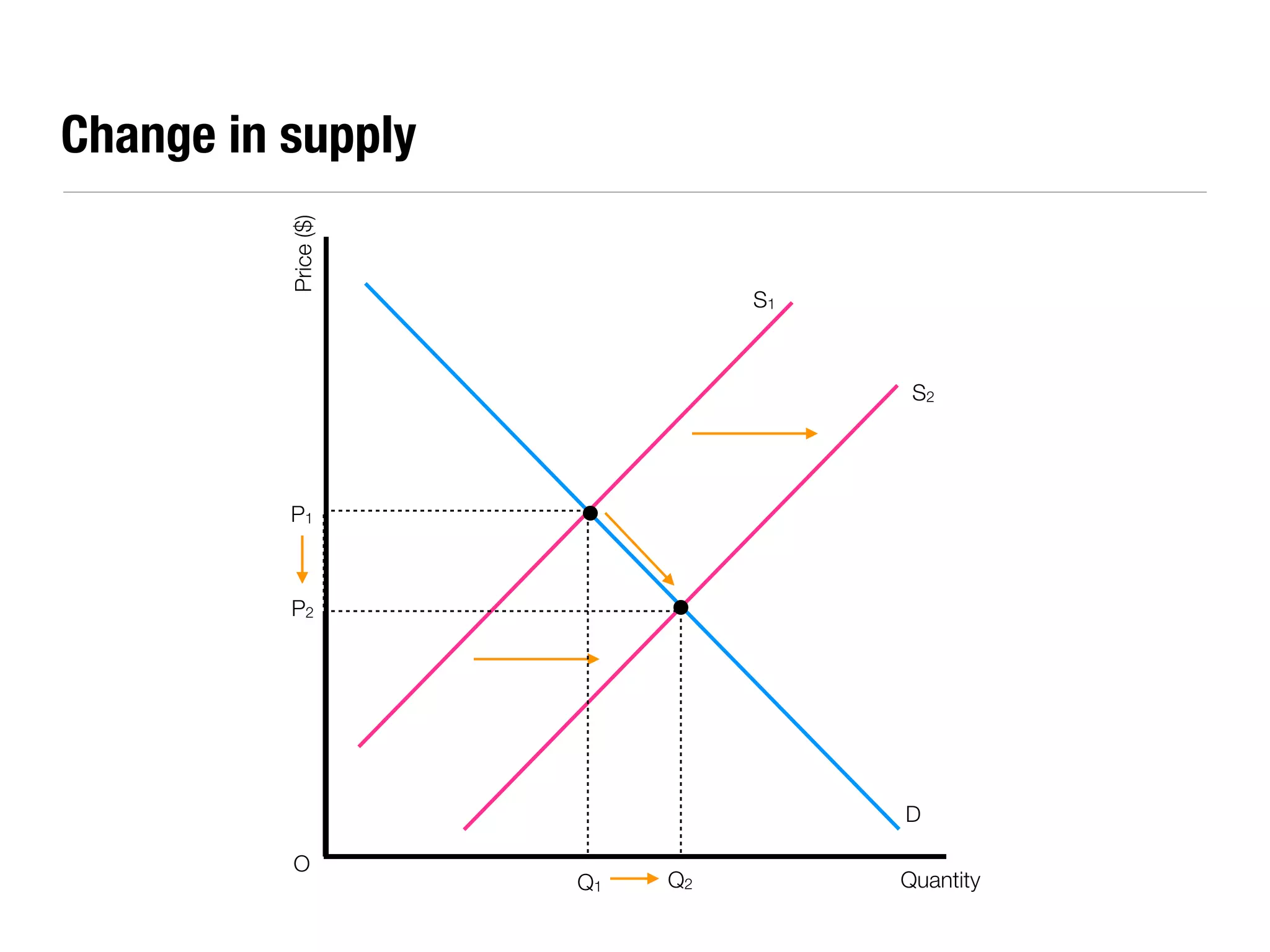
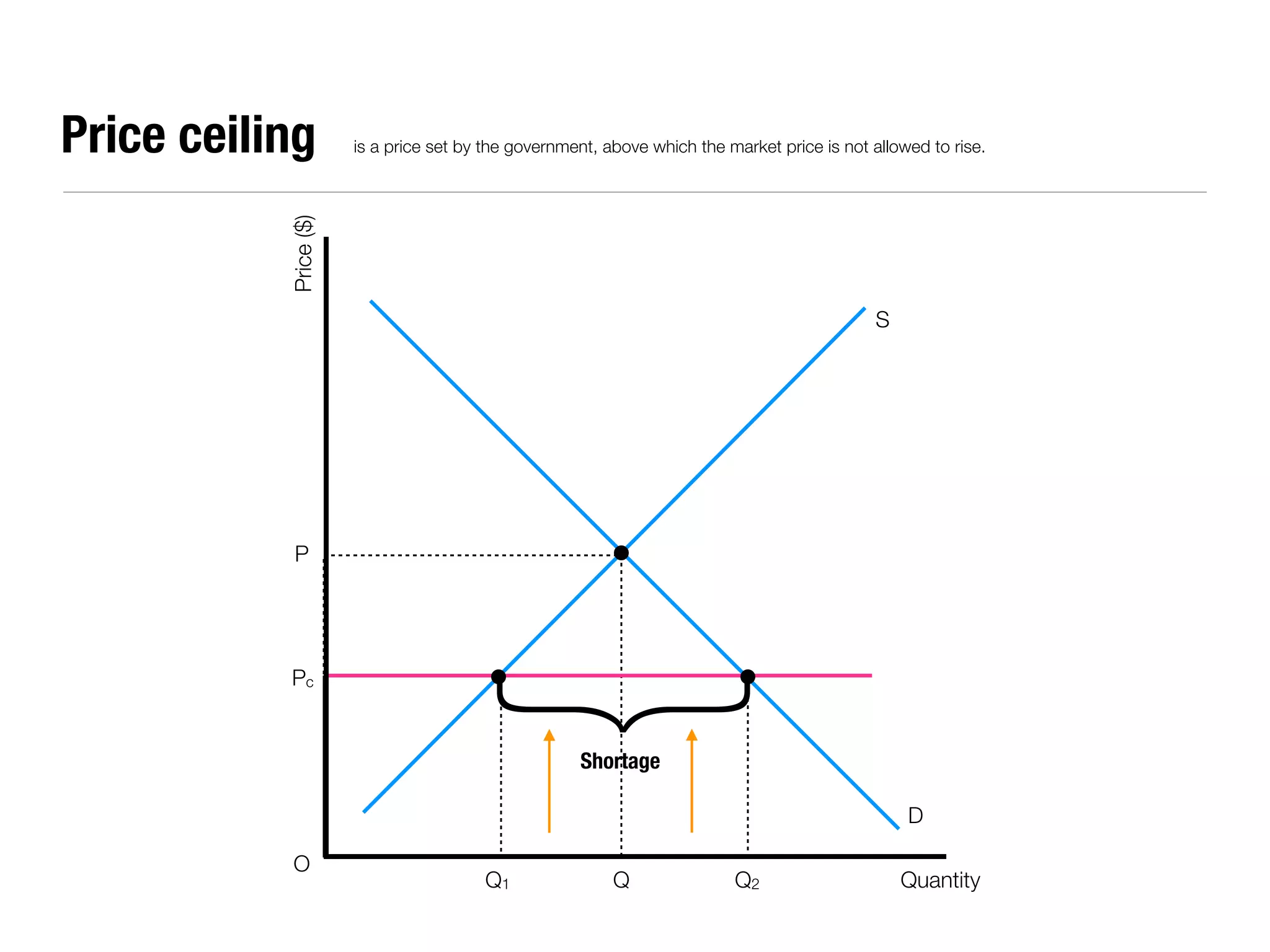
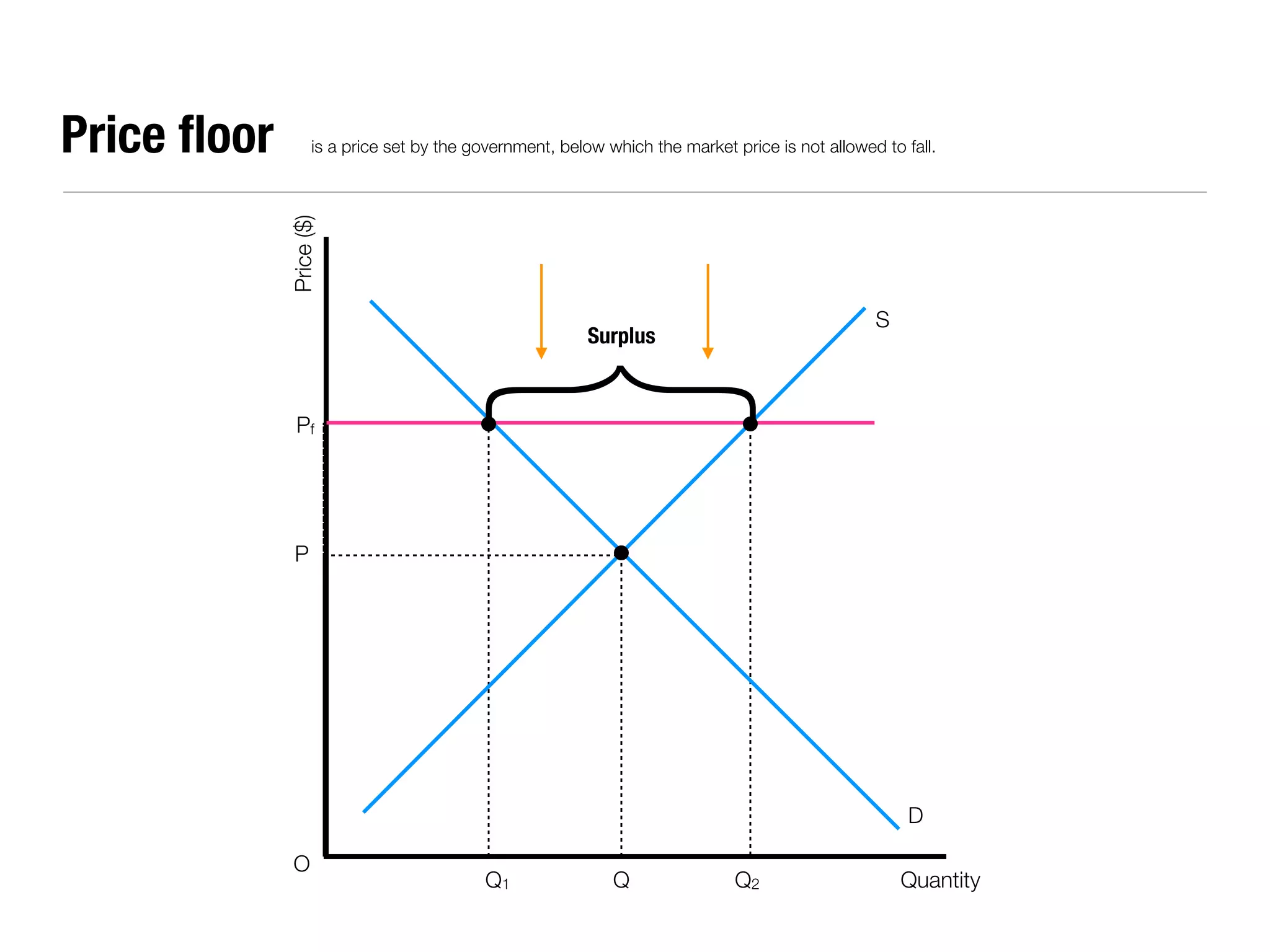
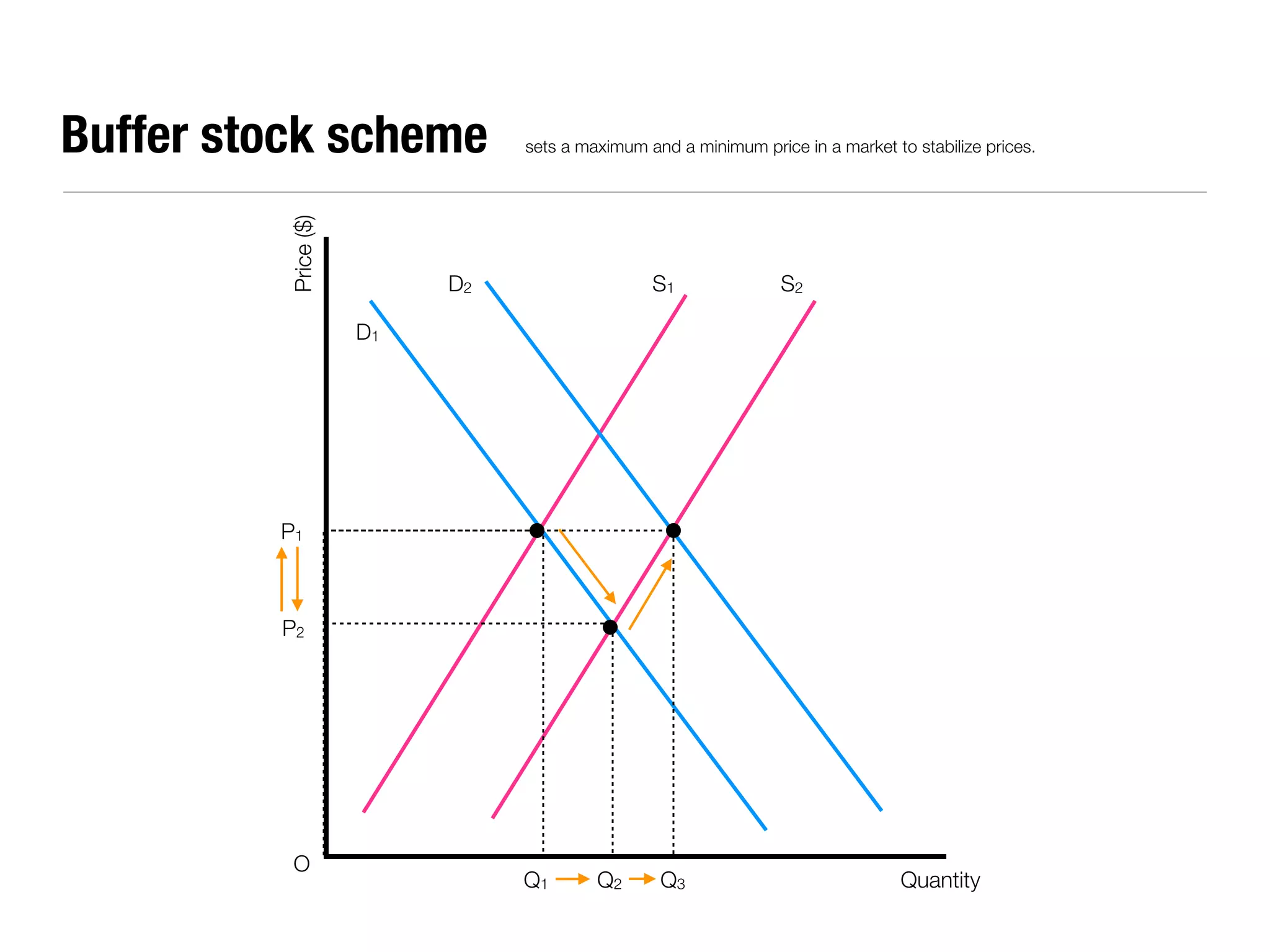
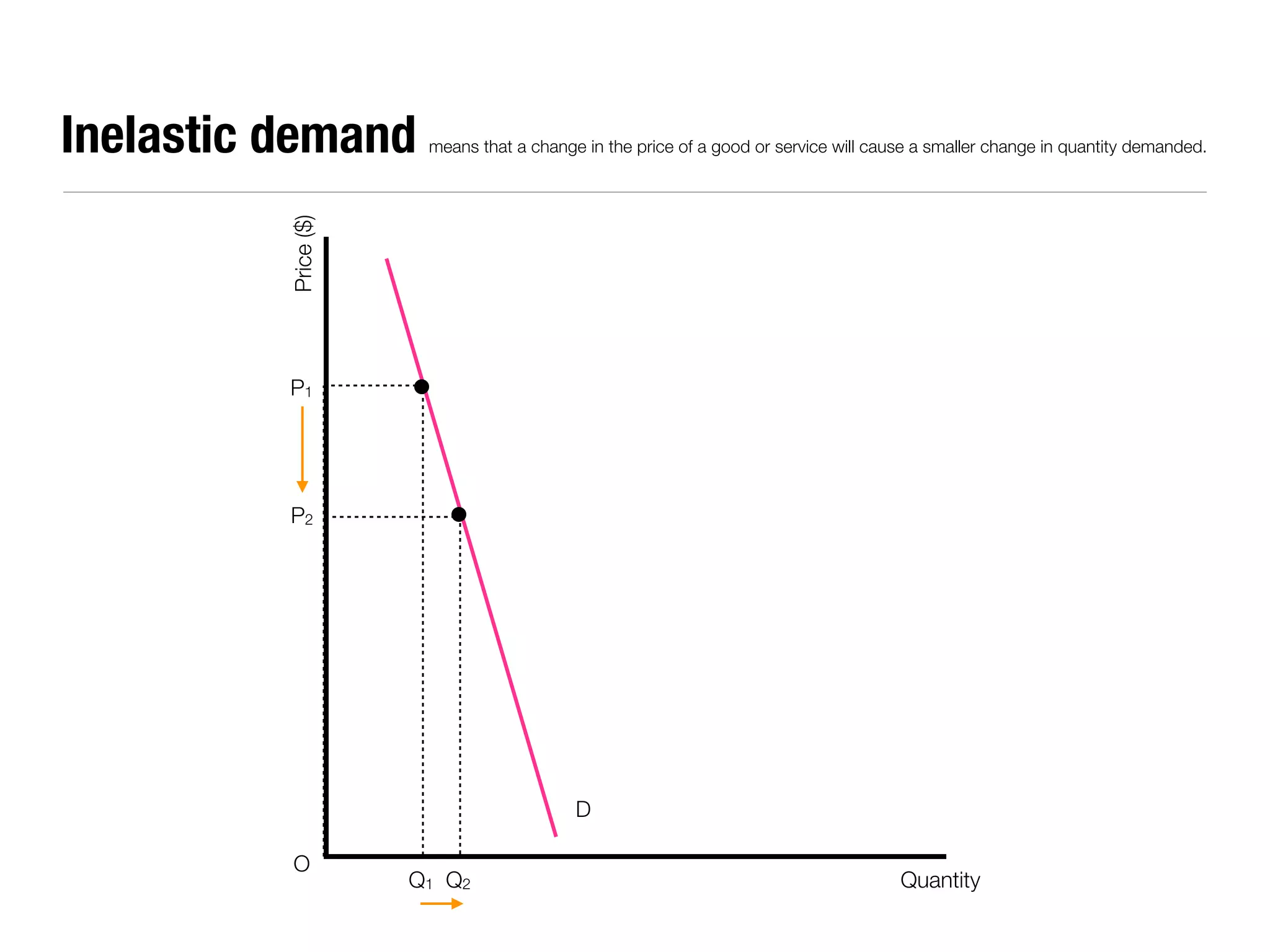
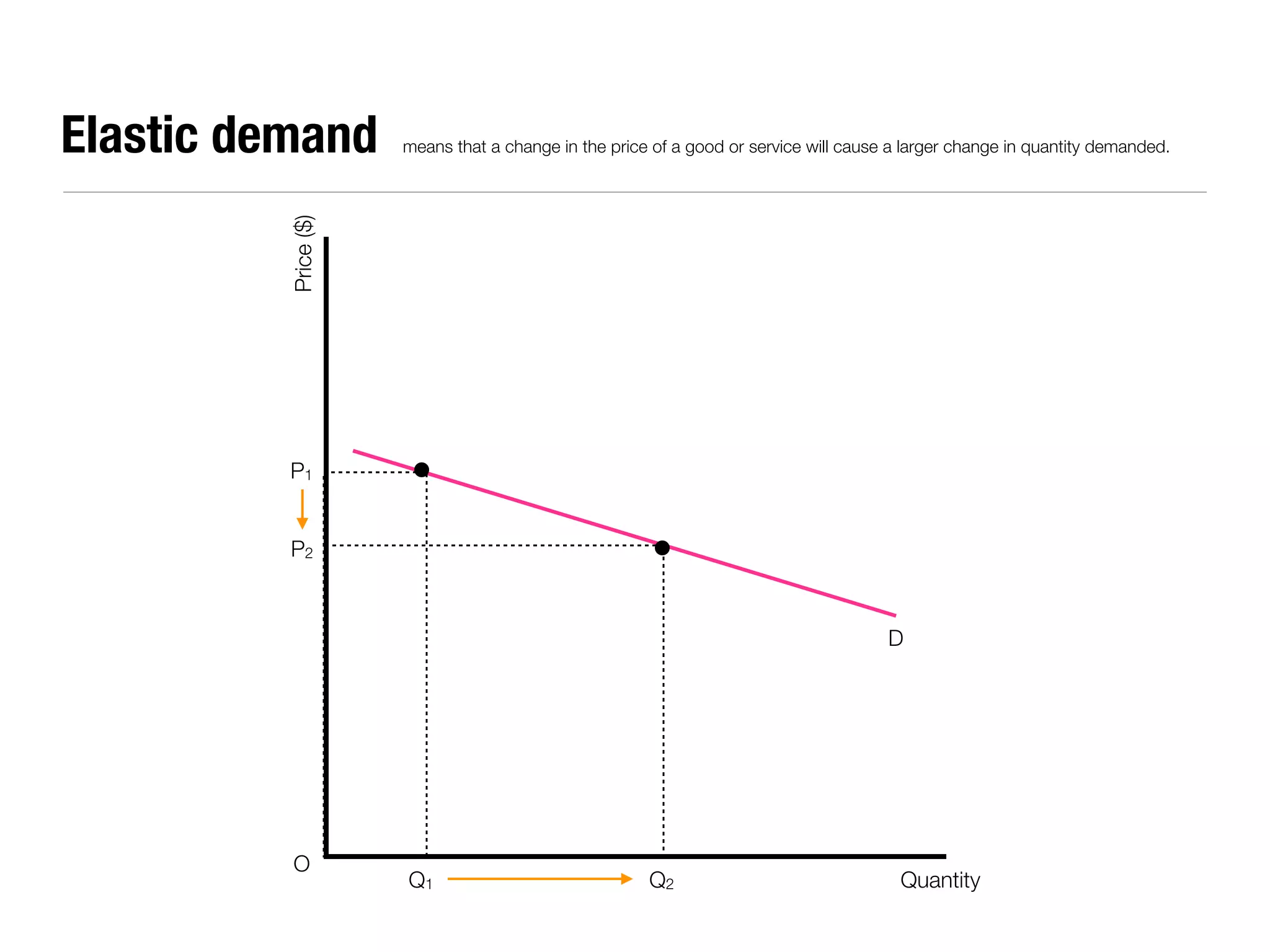
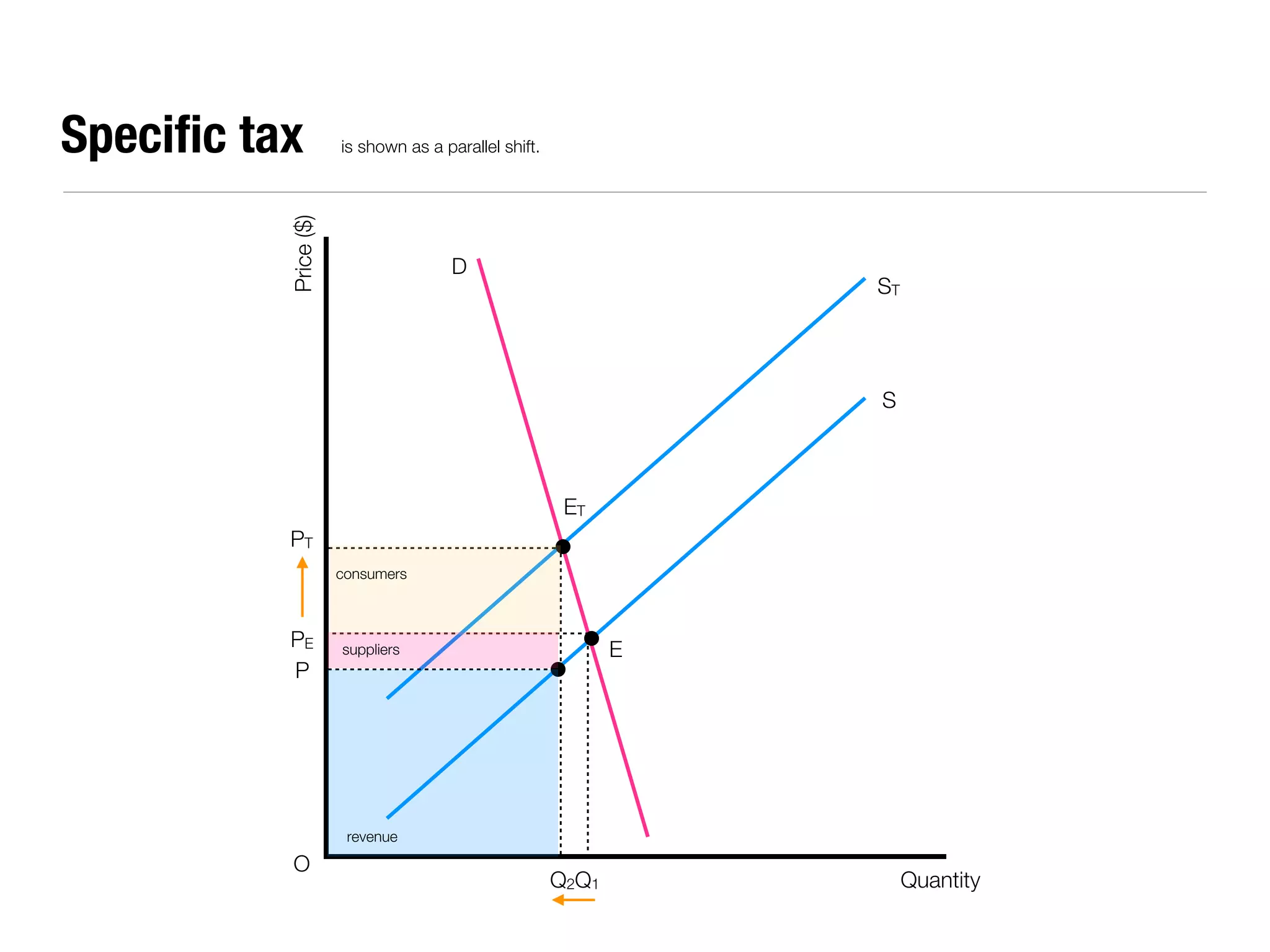
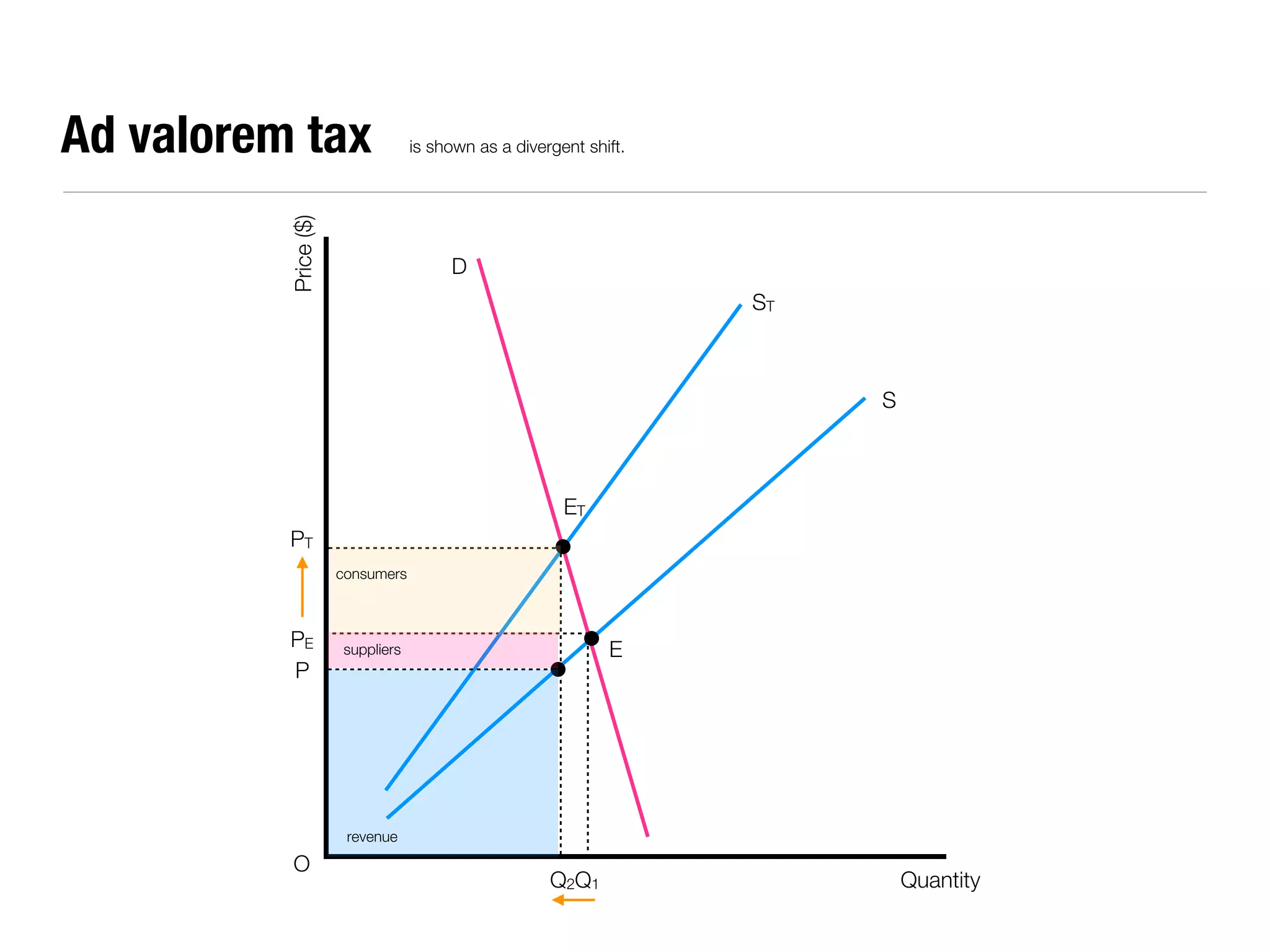
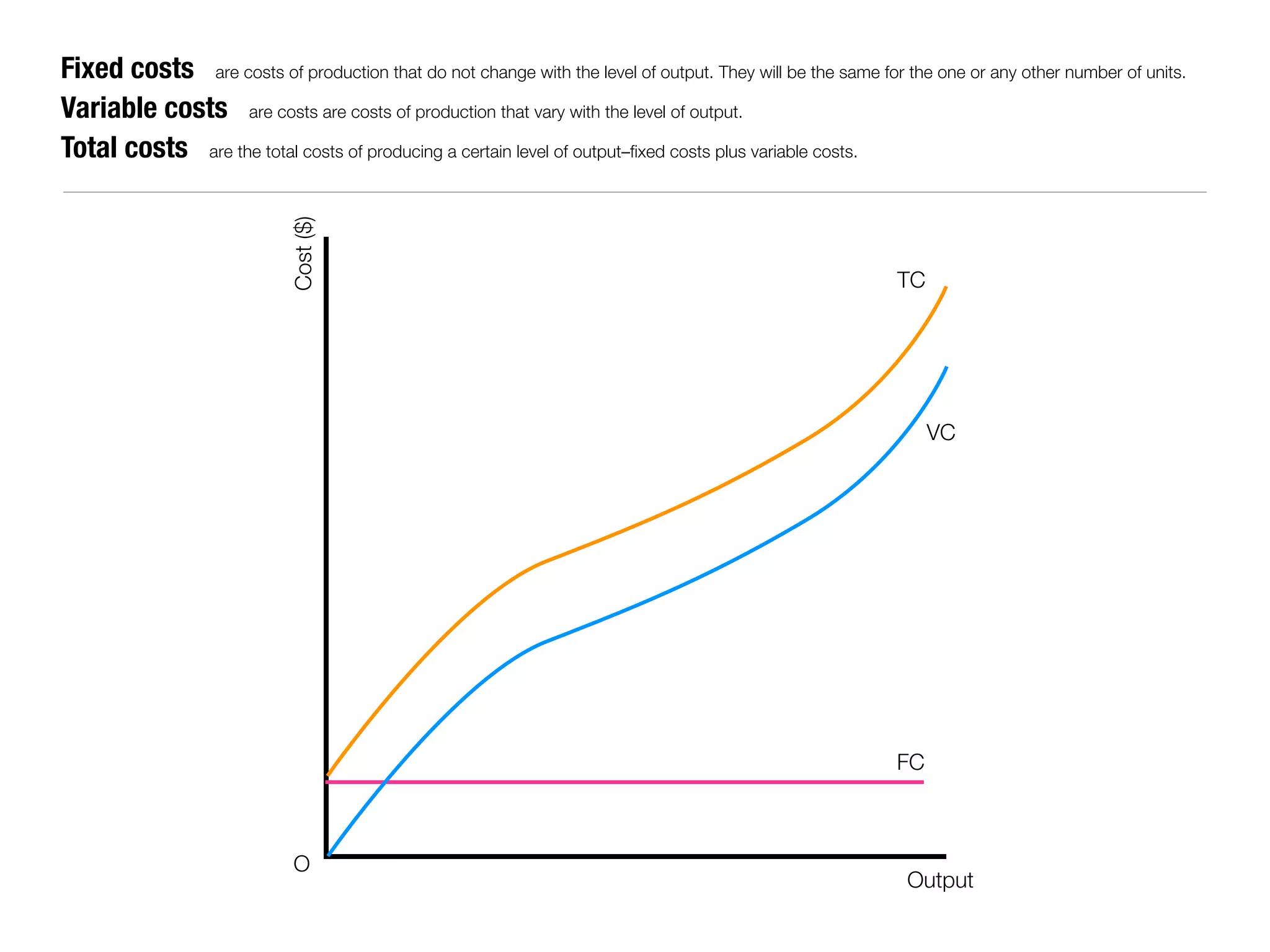
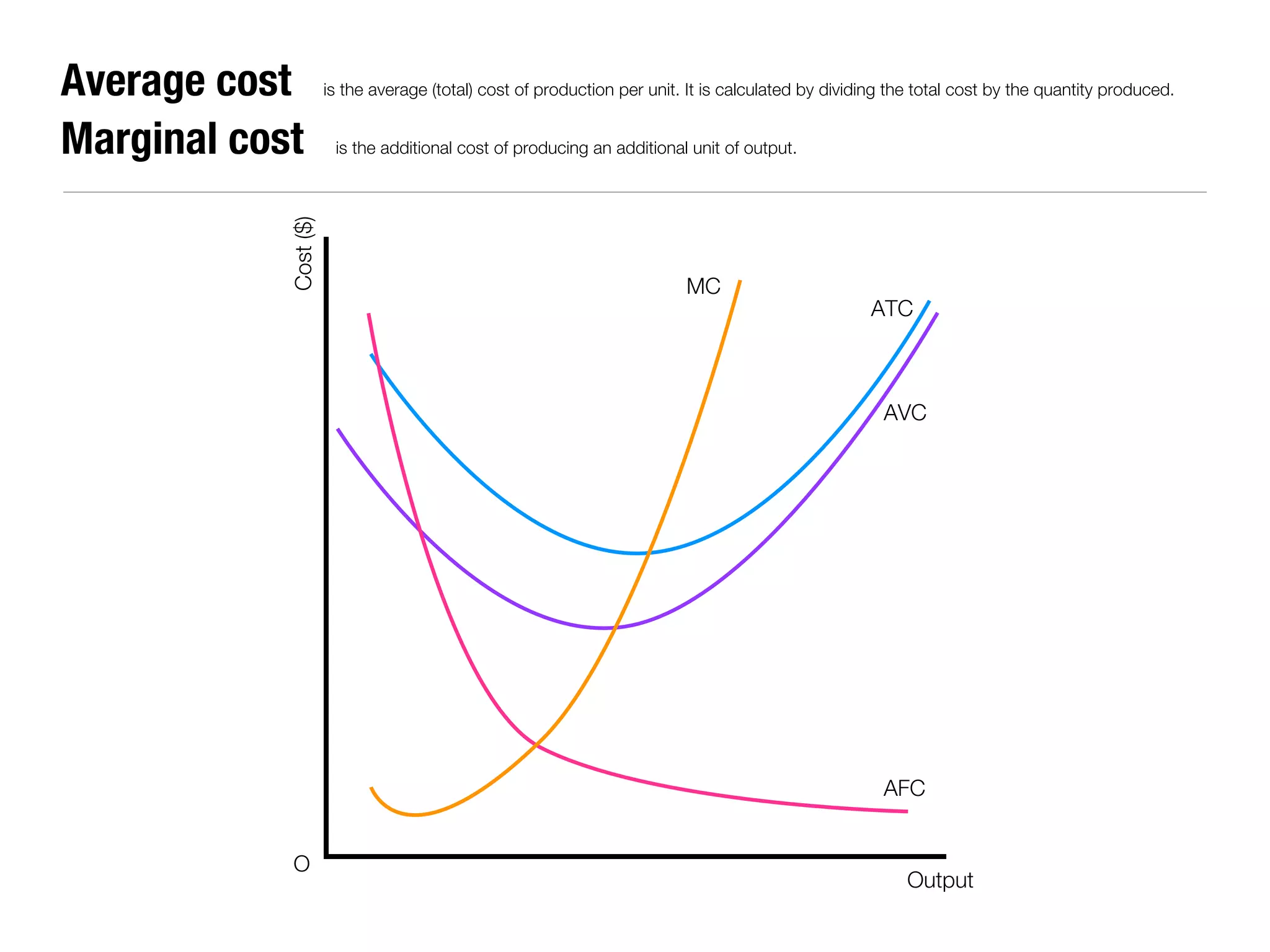
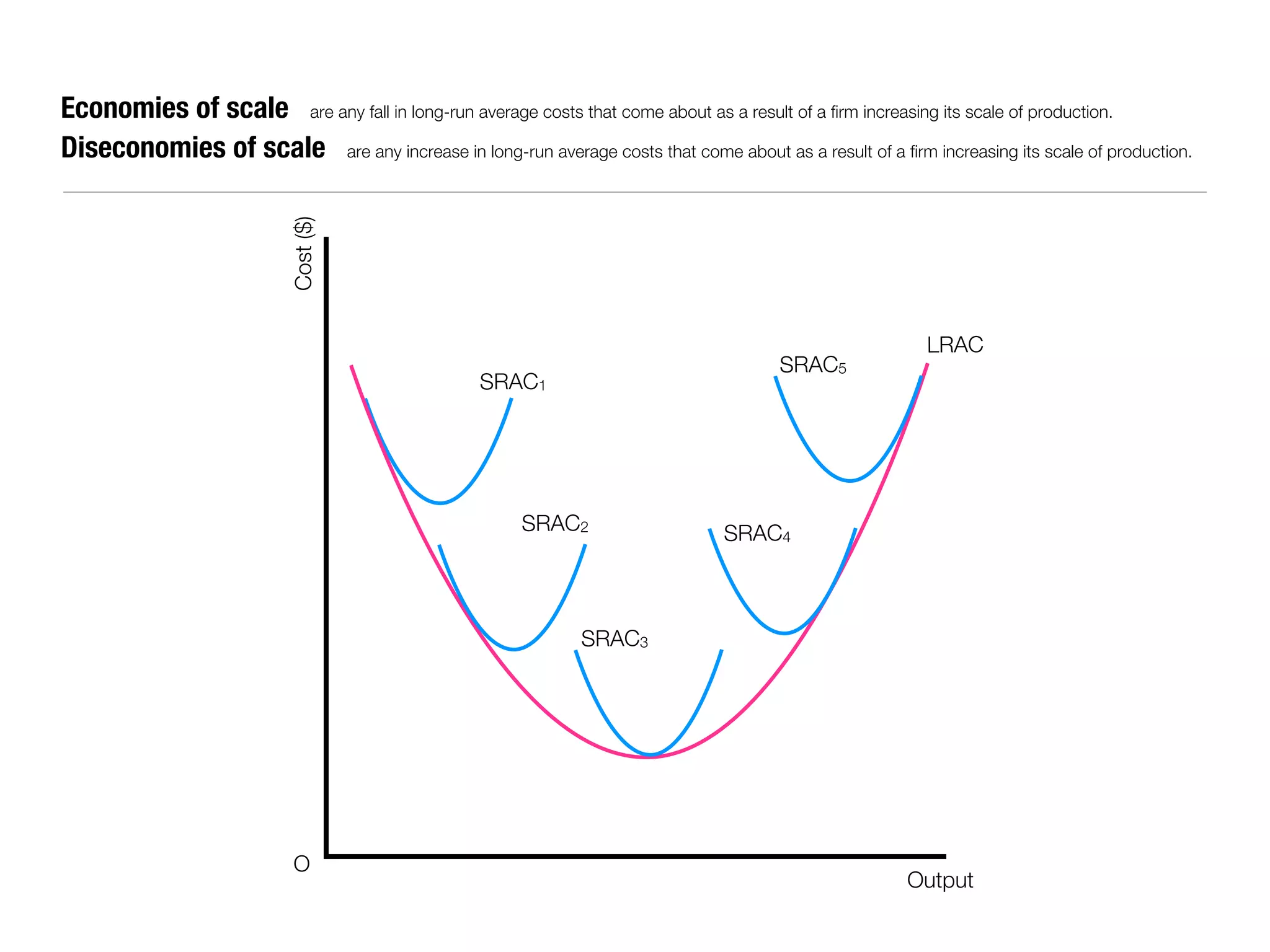
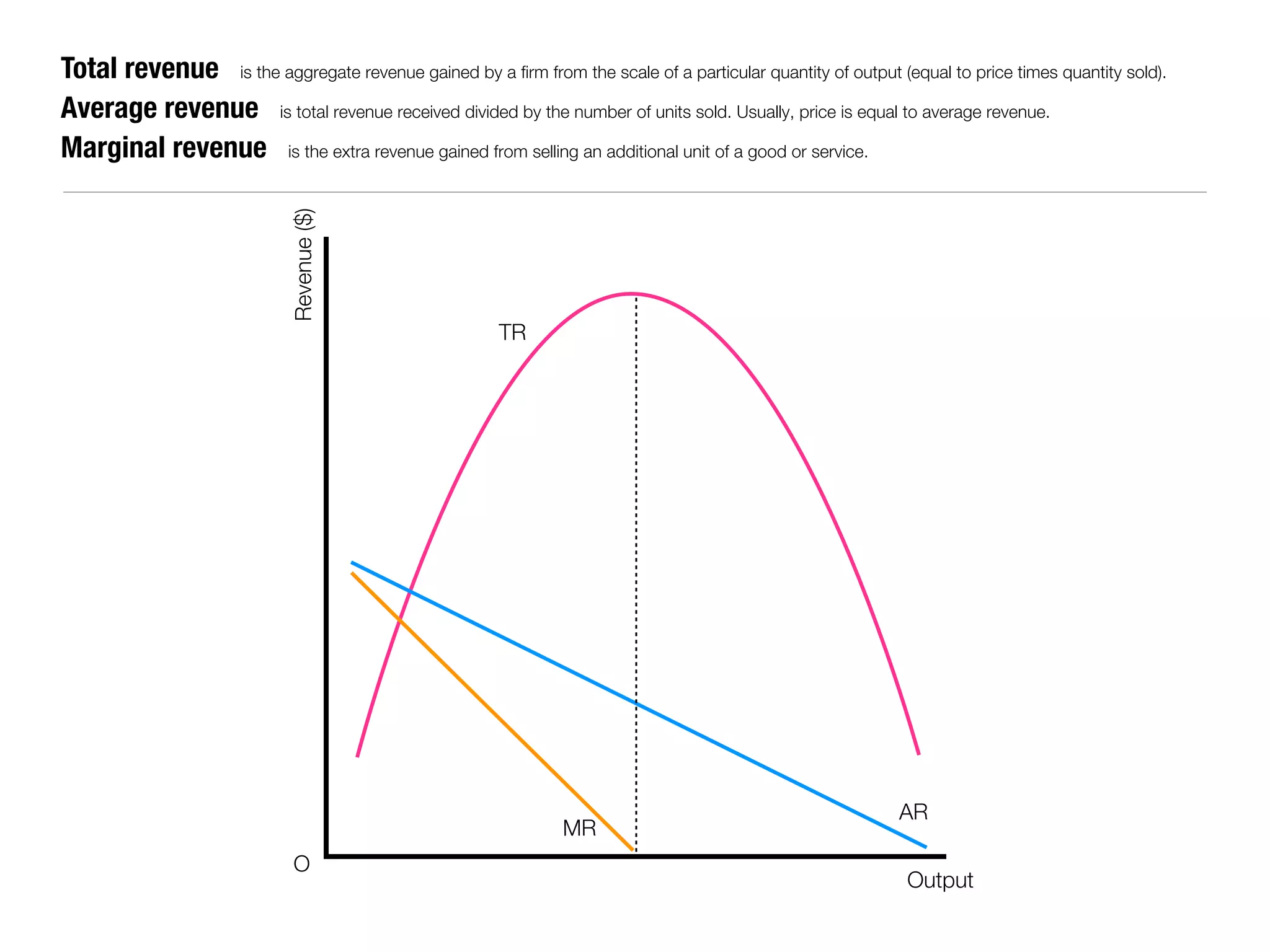
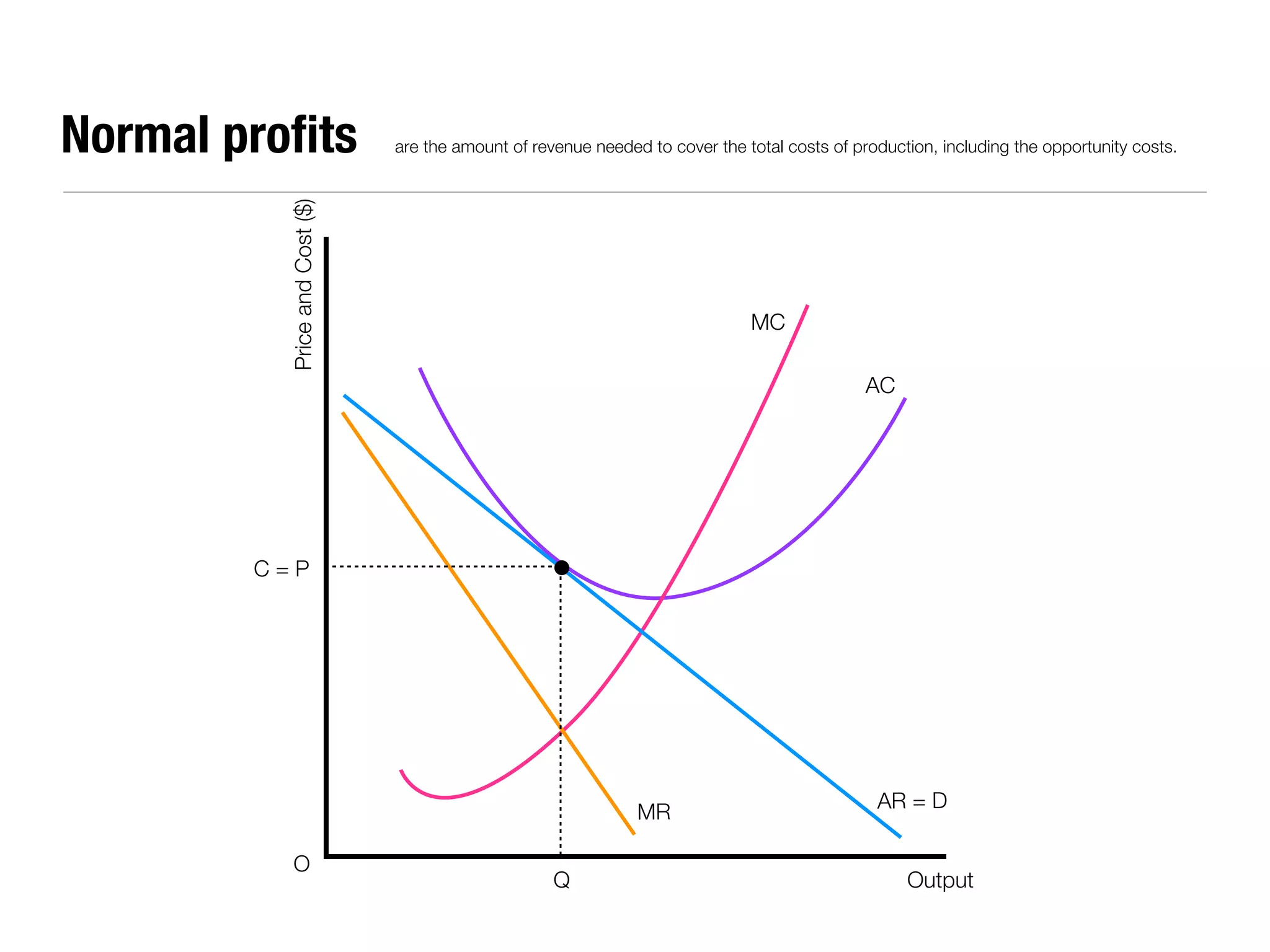
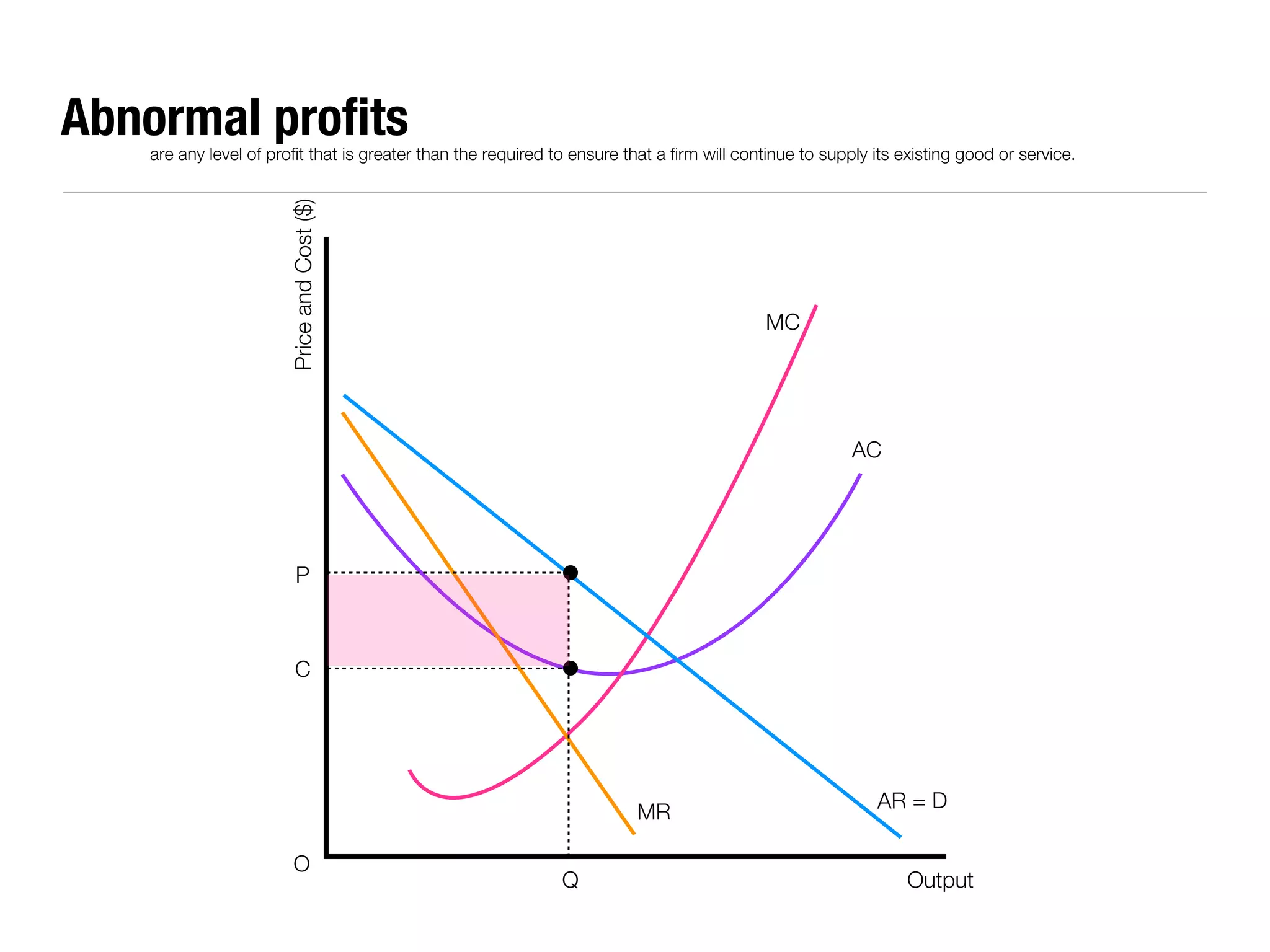
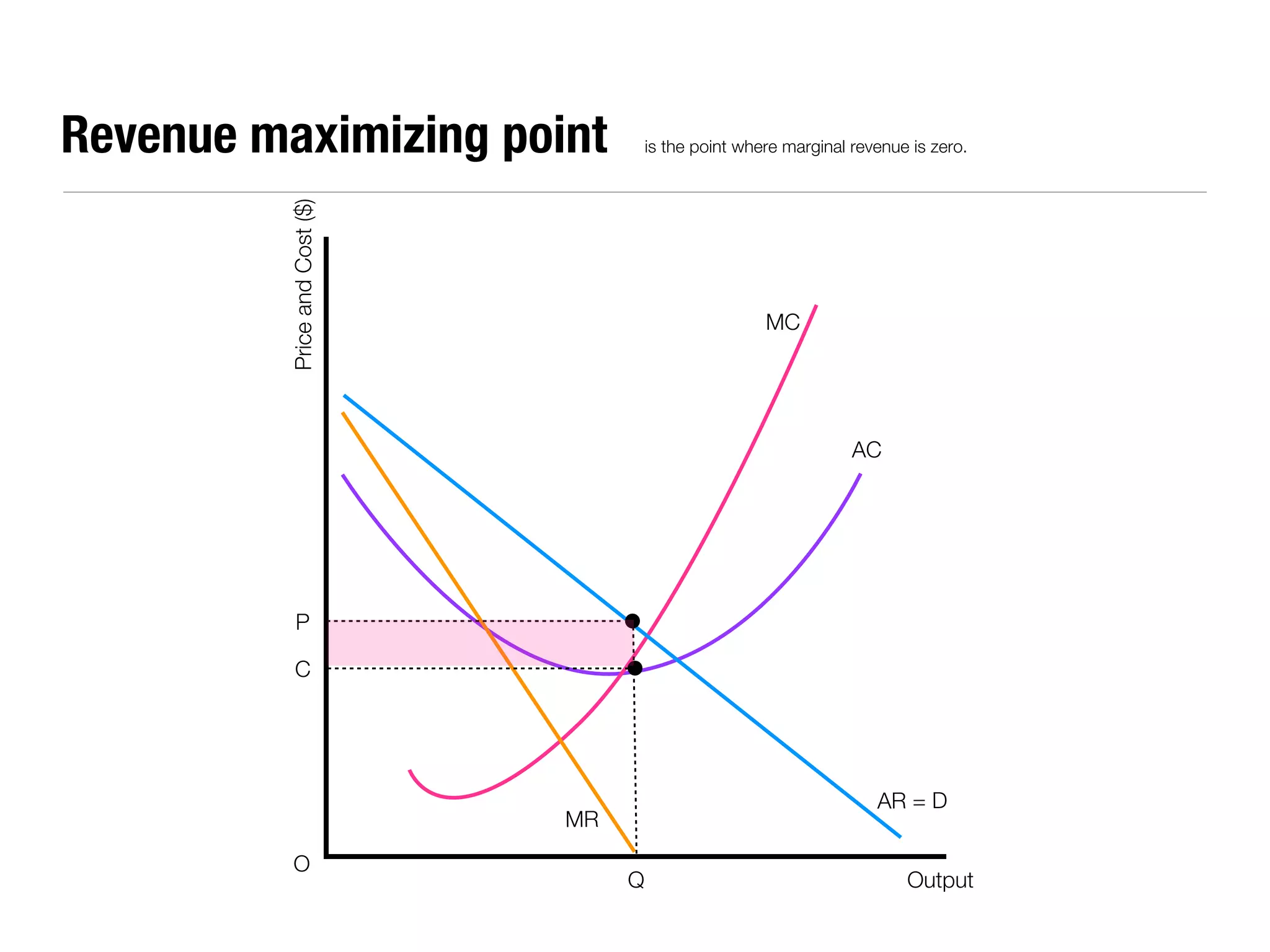
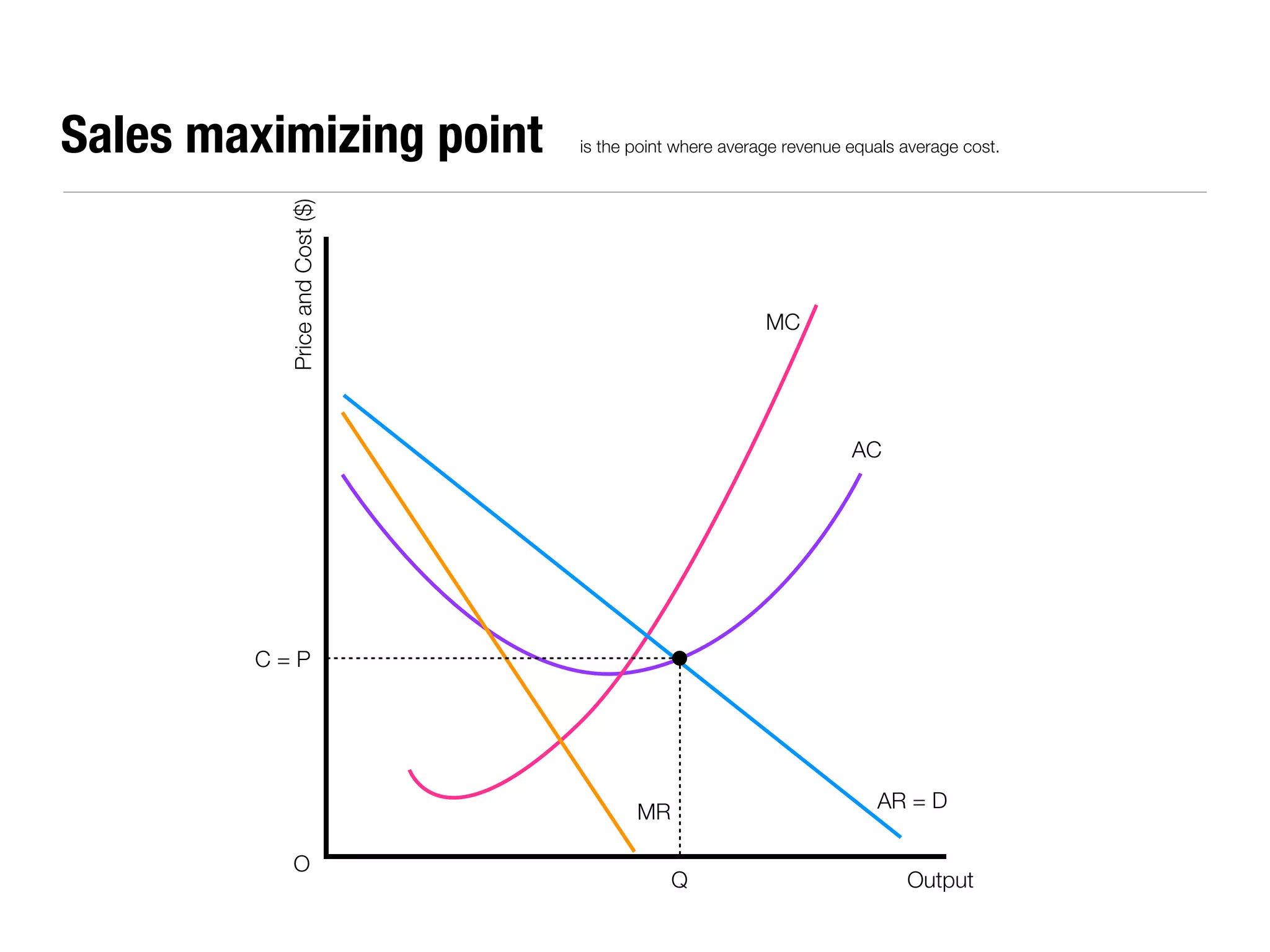
The document summarizes key economic concepts related to production possibilities curves, opportunity cost, actual and potential growth, demand and supply, equilibrium price and quantity, changes in demand and supply, price controls, taxes, costs of production, revenues, profits, and price discrimination. It provides graphs and explanations for each concept.