The document summarizes several machine learning algorithms:
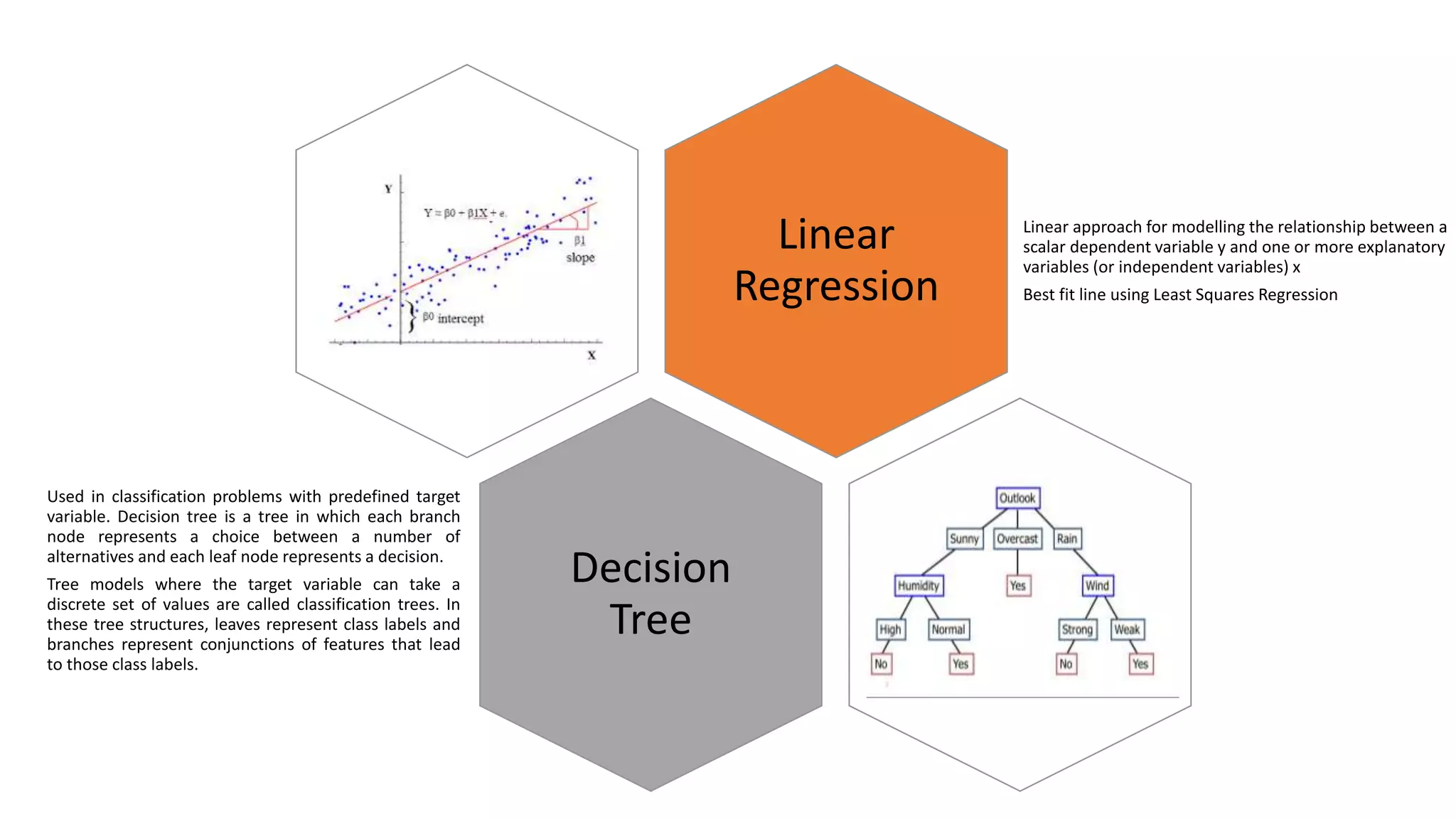
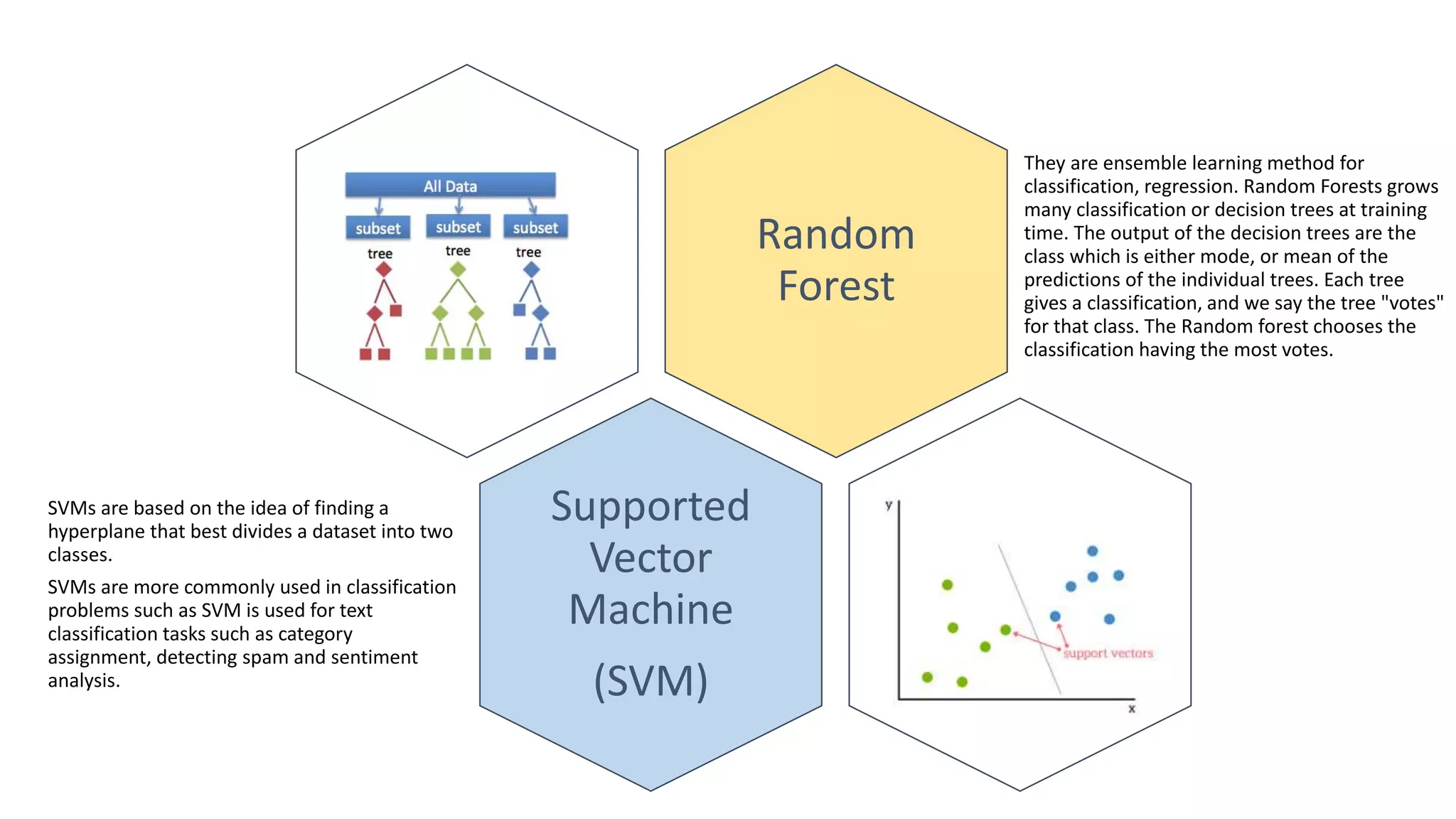
- Linear regression finds the best fit linear relationship between variables. Decision trees use branches to represent choices that lead to class labels. K-nearest neighbors approximates relationships locally using nearest instances.
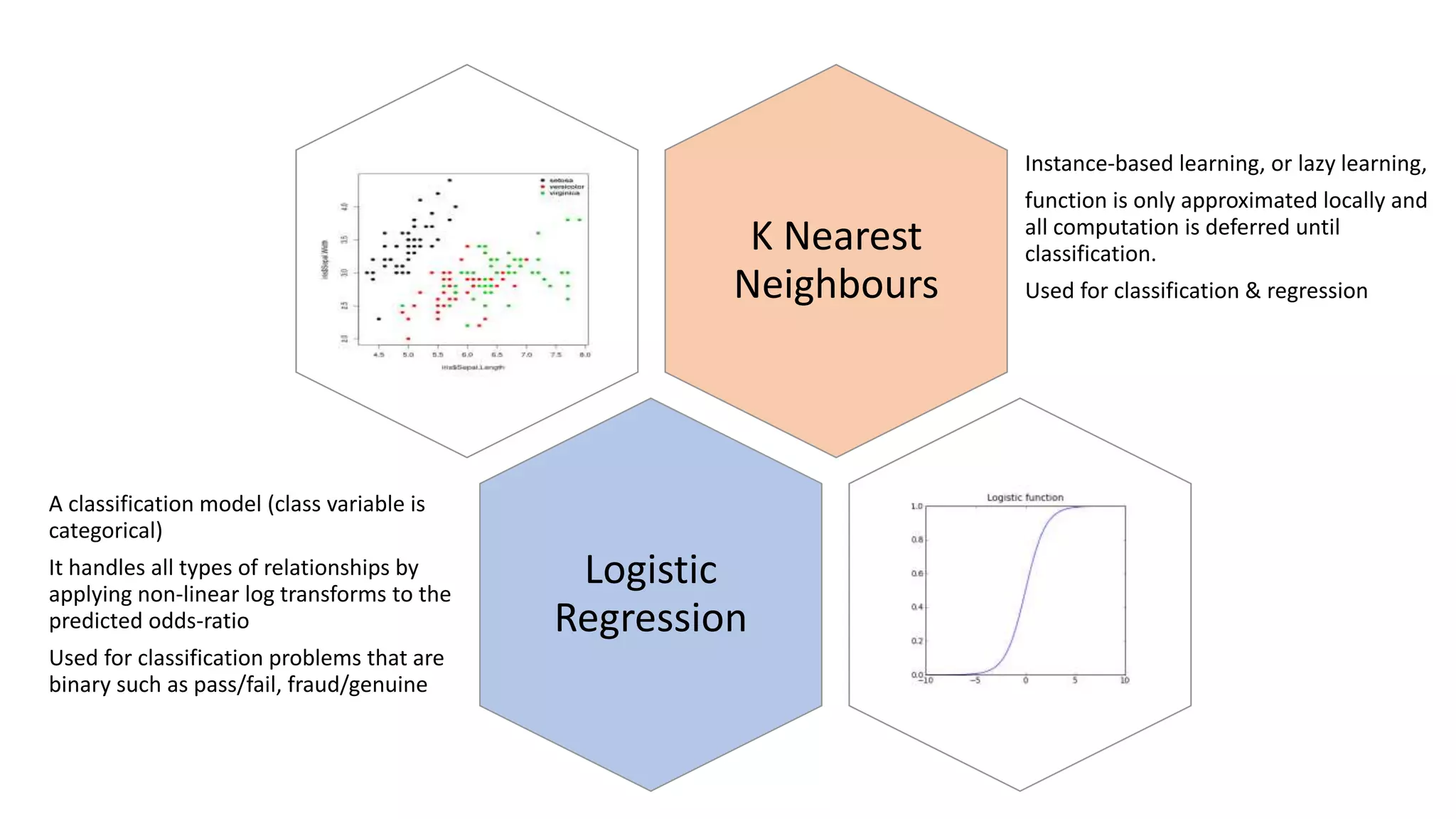
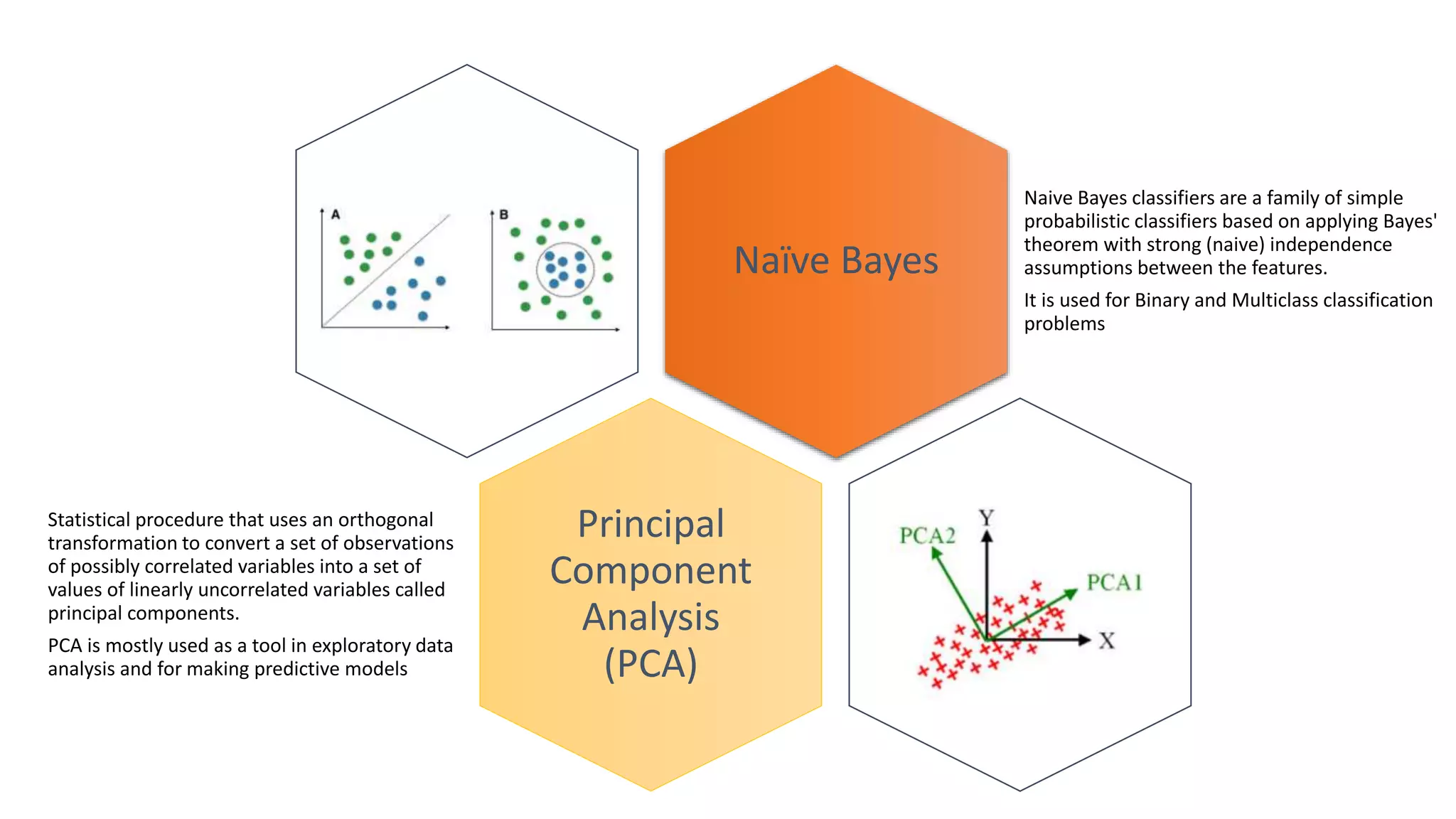
- Logistic regression handles nonlinear relationships for binary classification. Naive Bayes uses independence assumptions between features for classification. Principal component analysis transforms variables into uncorrelated components for analysis and models.
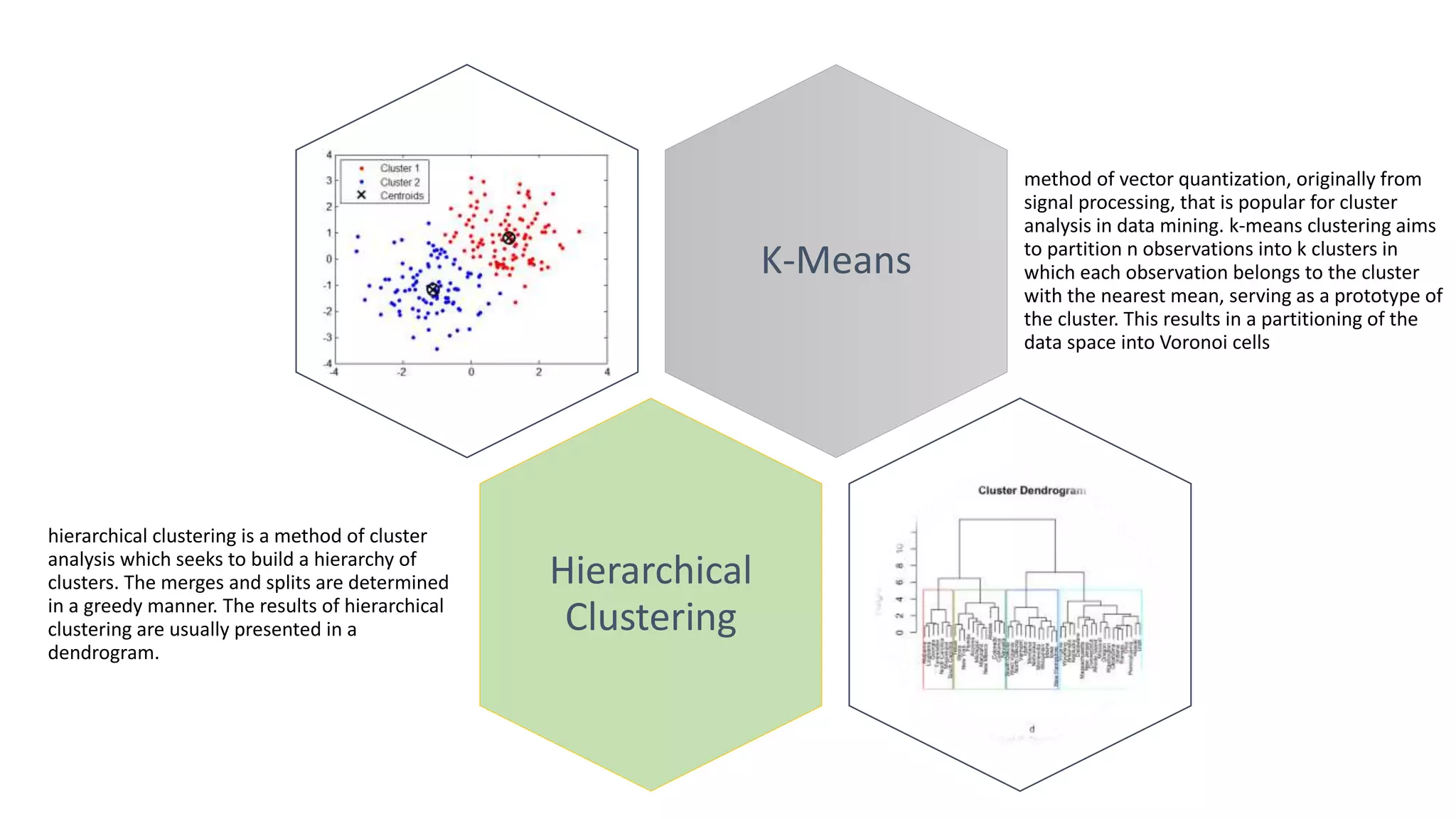
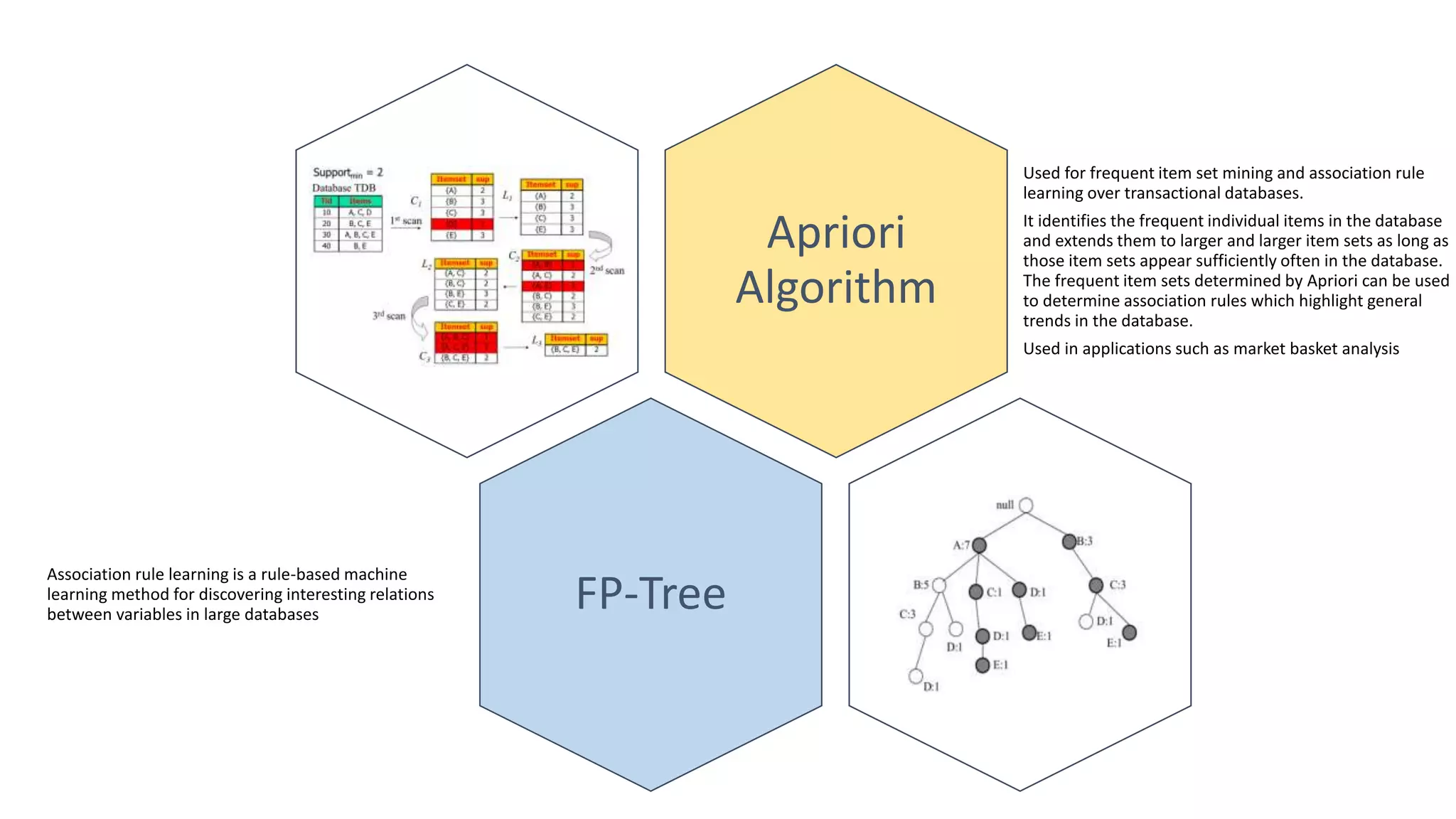
- K-means clustering partitions observations into clusters based on nearest cluster mean. Hierarchical clustering builds a hierarchy of clusters through successive merges and splits. Apriori identifies frequent item sets in transaction data to determine association rules.