1) An abstract data type (ADT) defines the operations that can be performed on a certain type of data but does not define how those operations are implemented.
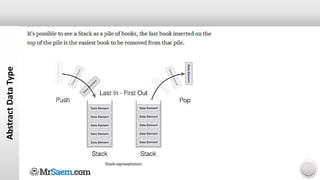
2) Common examples of ADTs include lists, stacks, queues, and trees. Each ADT has multiple possible concrete data type implementations.
3) To define an ADT, one identifies the essential data fields and operations without specifying how they are stored or computed. This provides an abstract model of the problem domain.