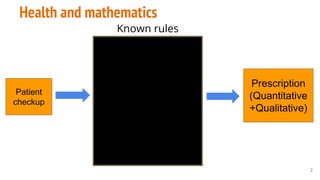
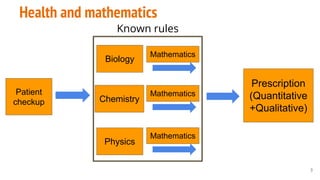
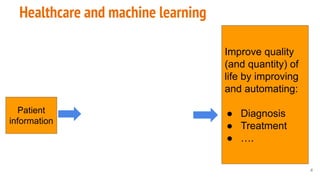
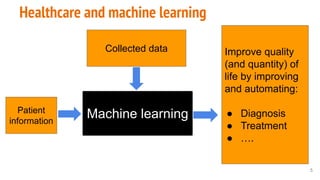
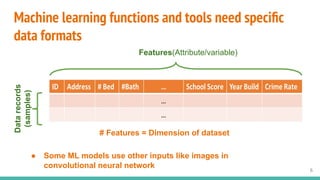
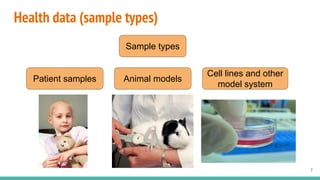
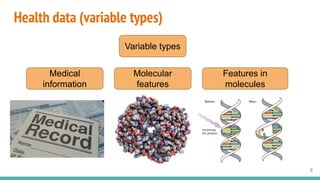
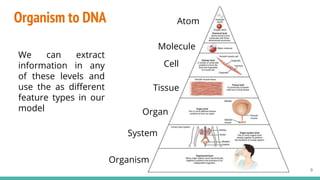
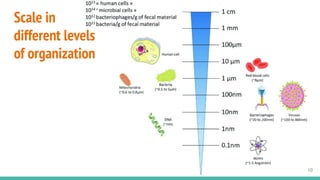
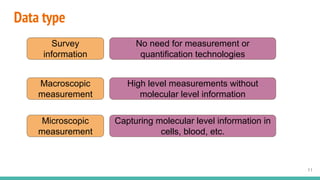
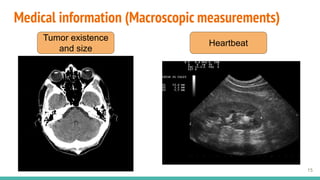
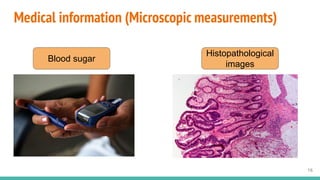
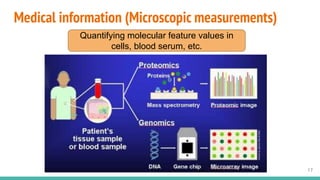
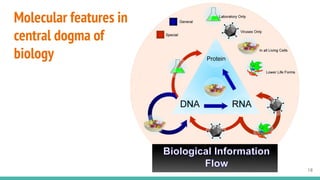
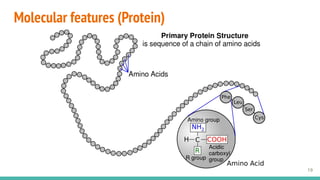
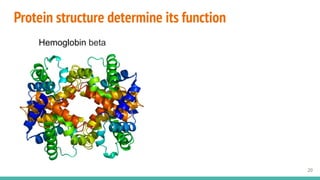
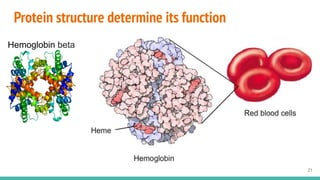
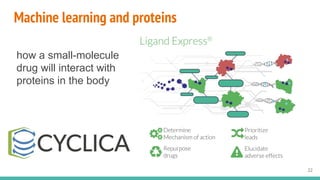
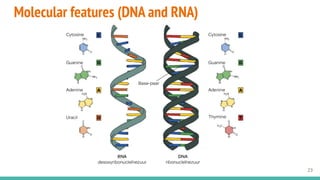
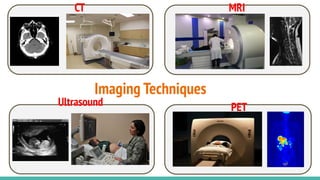
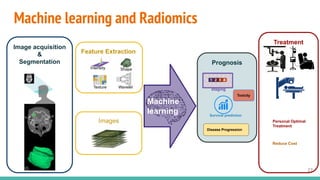
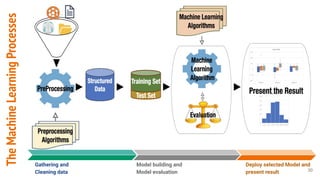
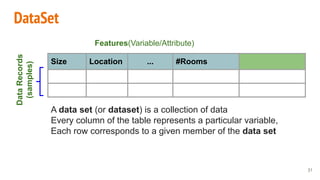
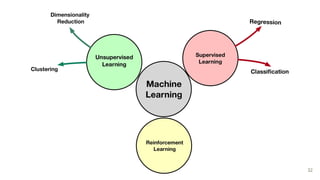
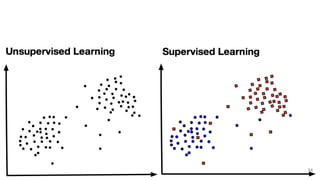
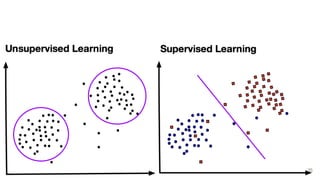
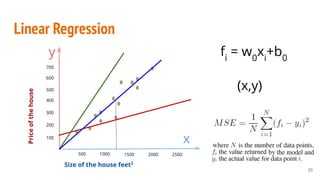
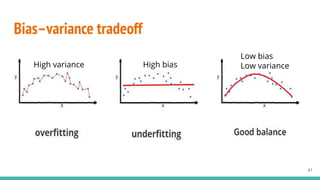
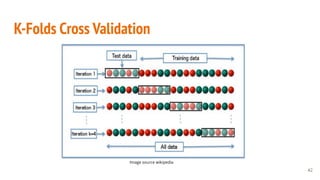
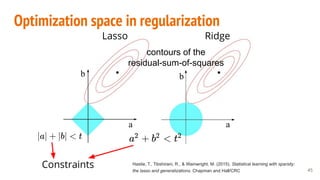
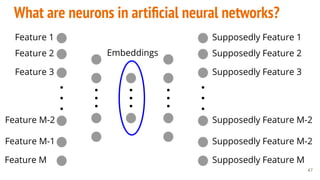
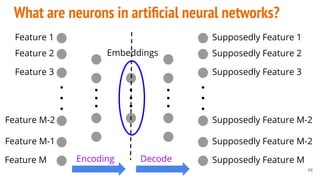
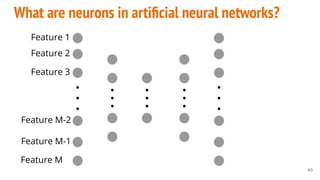
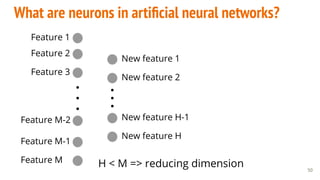
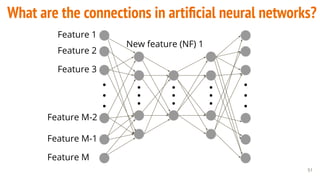
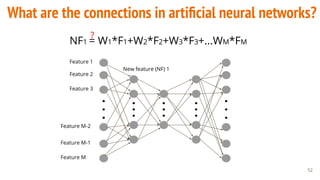
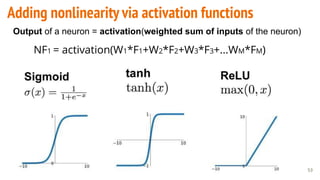
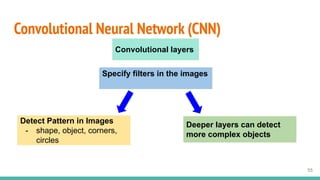
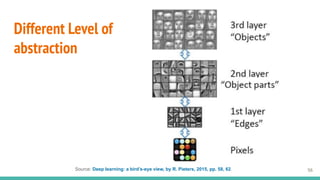
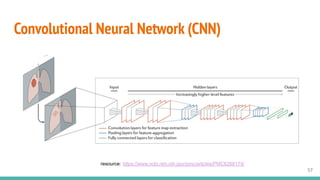
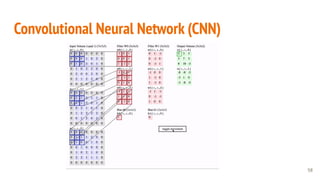
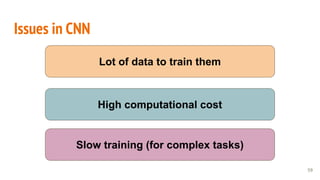
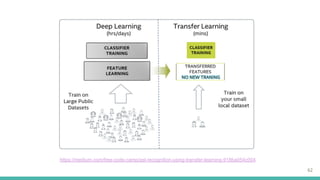
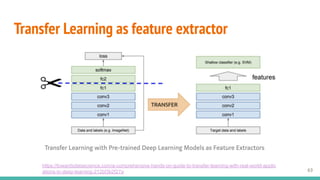
This document provides an overview of machine learning applications in healthcare. It discusses how machine learning can be used to improve diagnosis, treatment, and other areas by automating processes and analyzing patient information. Different types of health data that can be used as inputs for machine learning models are described, including medical information, molecular features, and medical images. Common machine learning tasks for images like detection, segmentation, and diagnosis are also outlined. The document then explains the basic machine learning process of gathering and cleaning data, building and evaluating models, and deploying selected models. Common machine learning algorithms like linear regression, regularization techniques, and deep learning approaches like convolutional neural networks are briefly introduced.