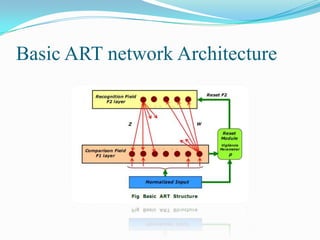
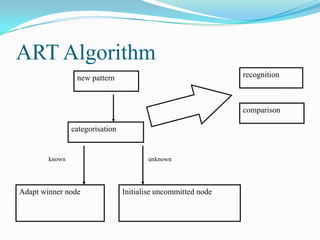
The document outlines Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART), a type of neural network invented by Stephen Grossberg in 1976. ART networks aim to solve the stability-plasticity dilemma by allowing plasticity to learn new patterns while maintaining stability of previously learned patterns. The basic ART system consists of a comparison field, recognition field, vigilance parameter, and reset module. The ART algorithm matches input patterns to stored cluster templates, either joining the closest matching cluster or initializing a new one. [/SUMMARY]