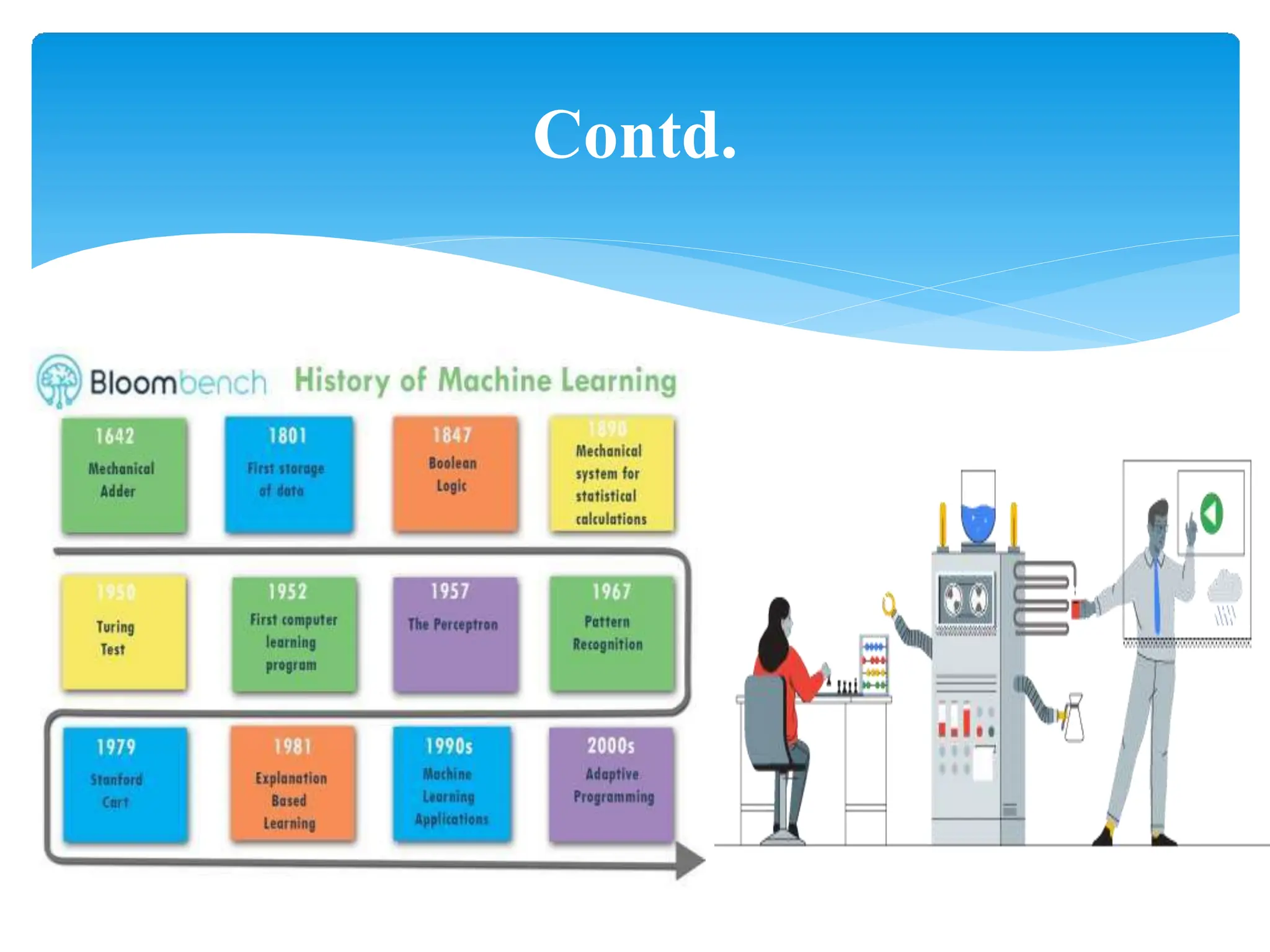
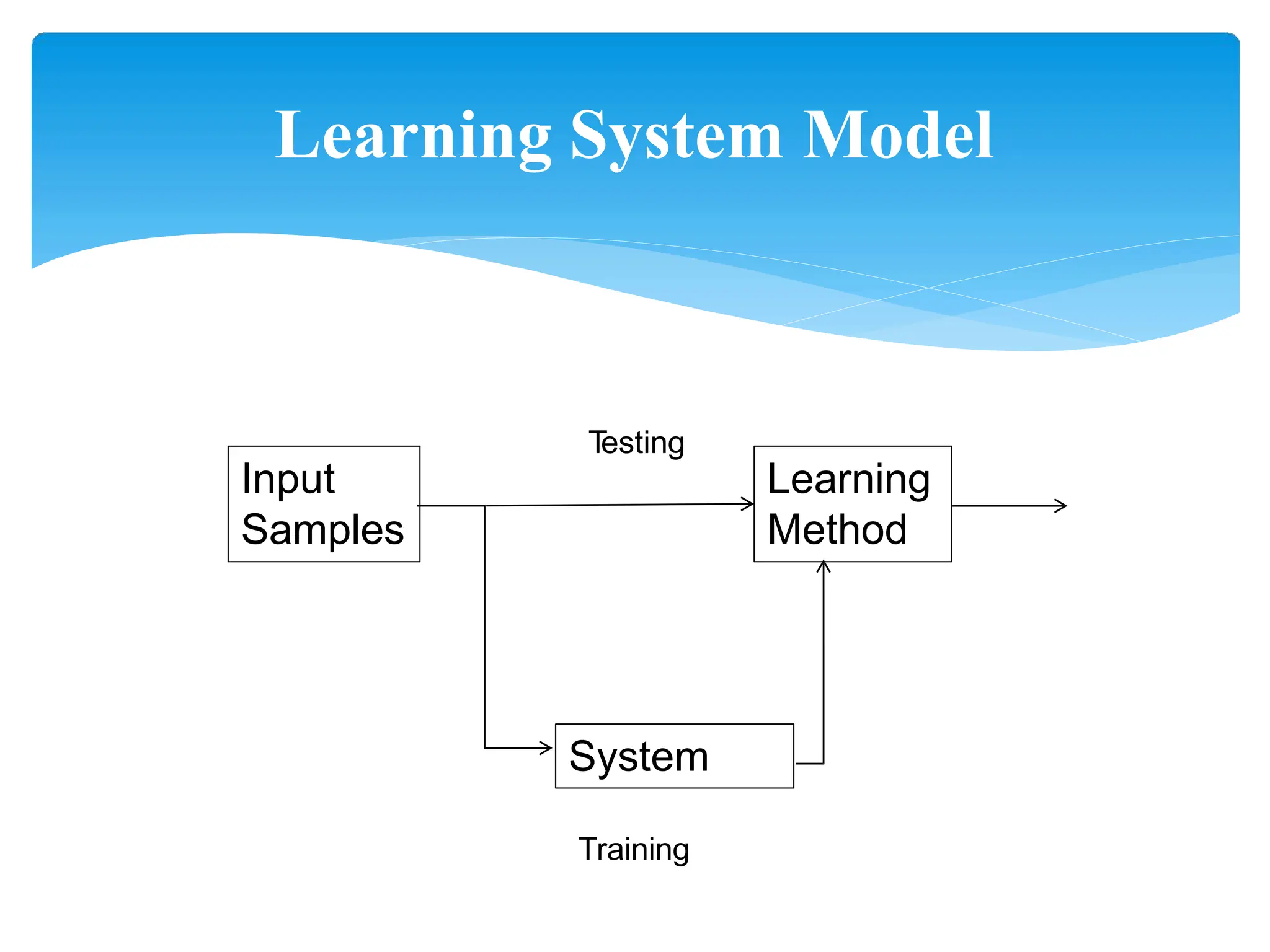
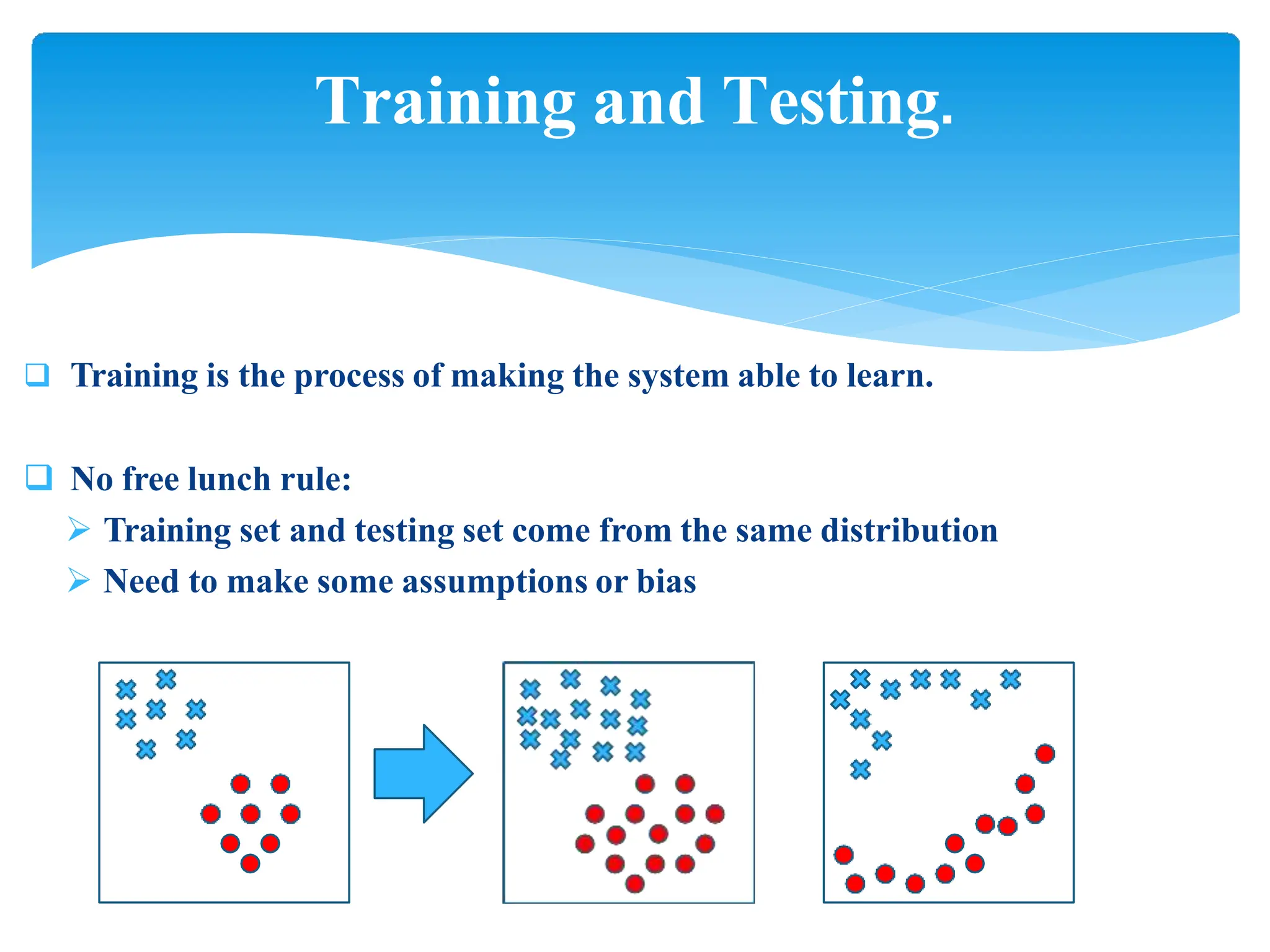
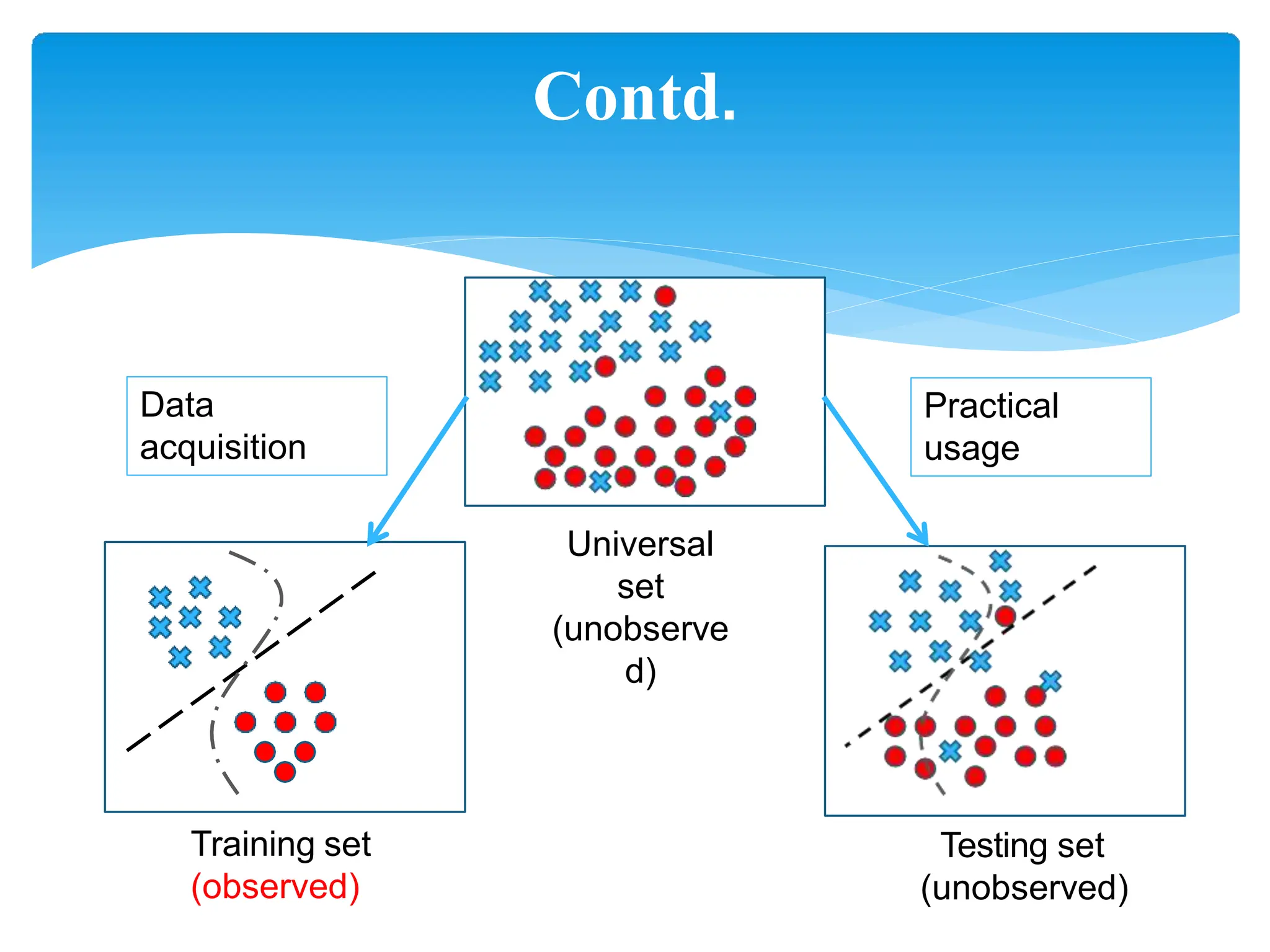
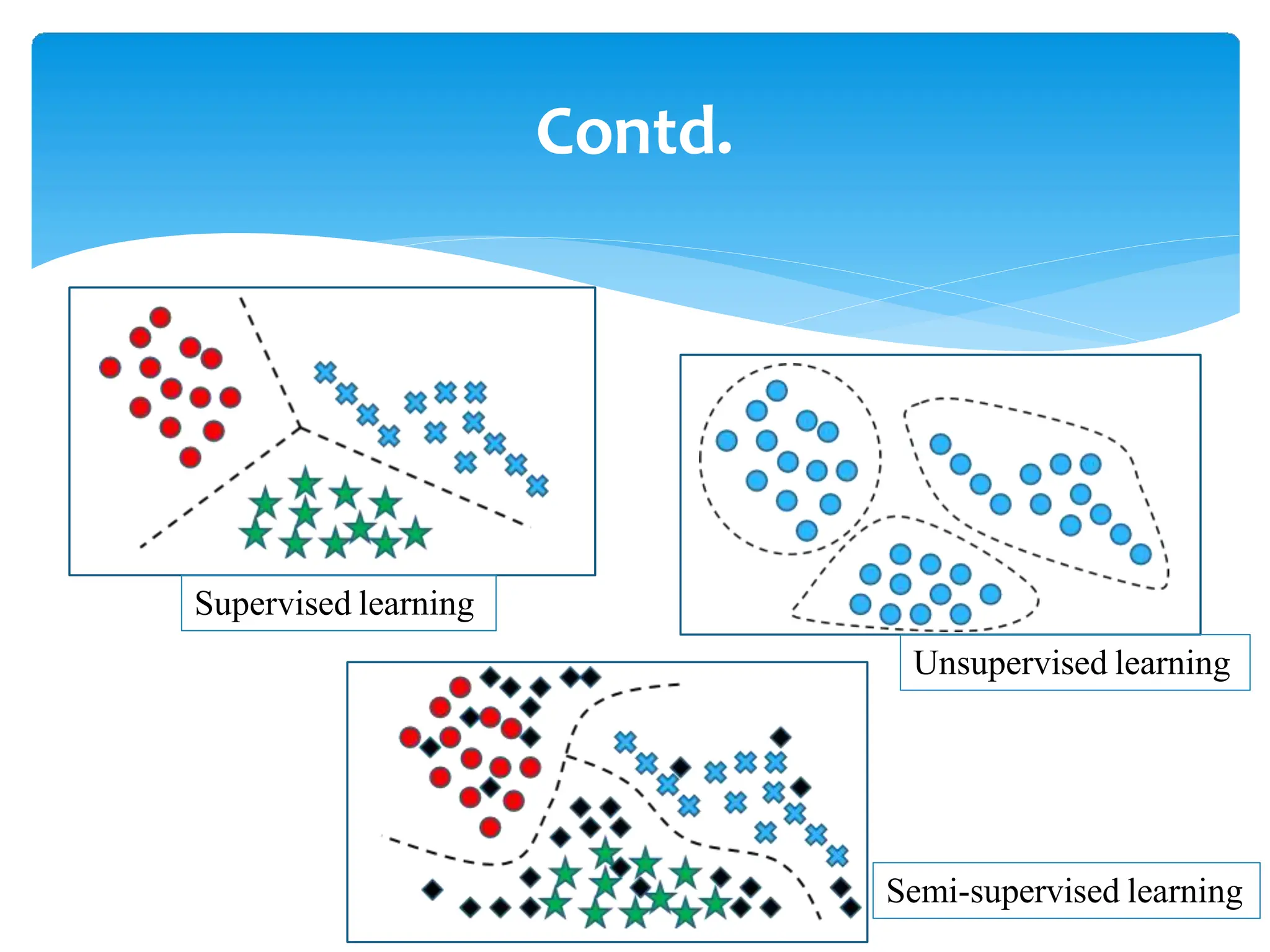
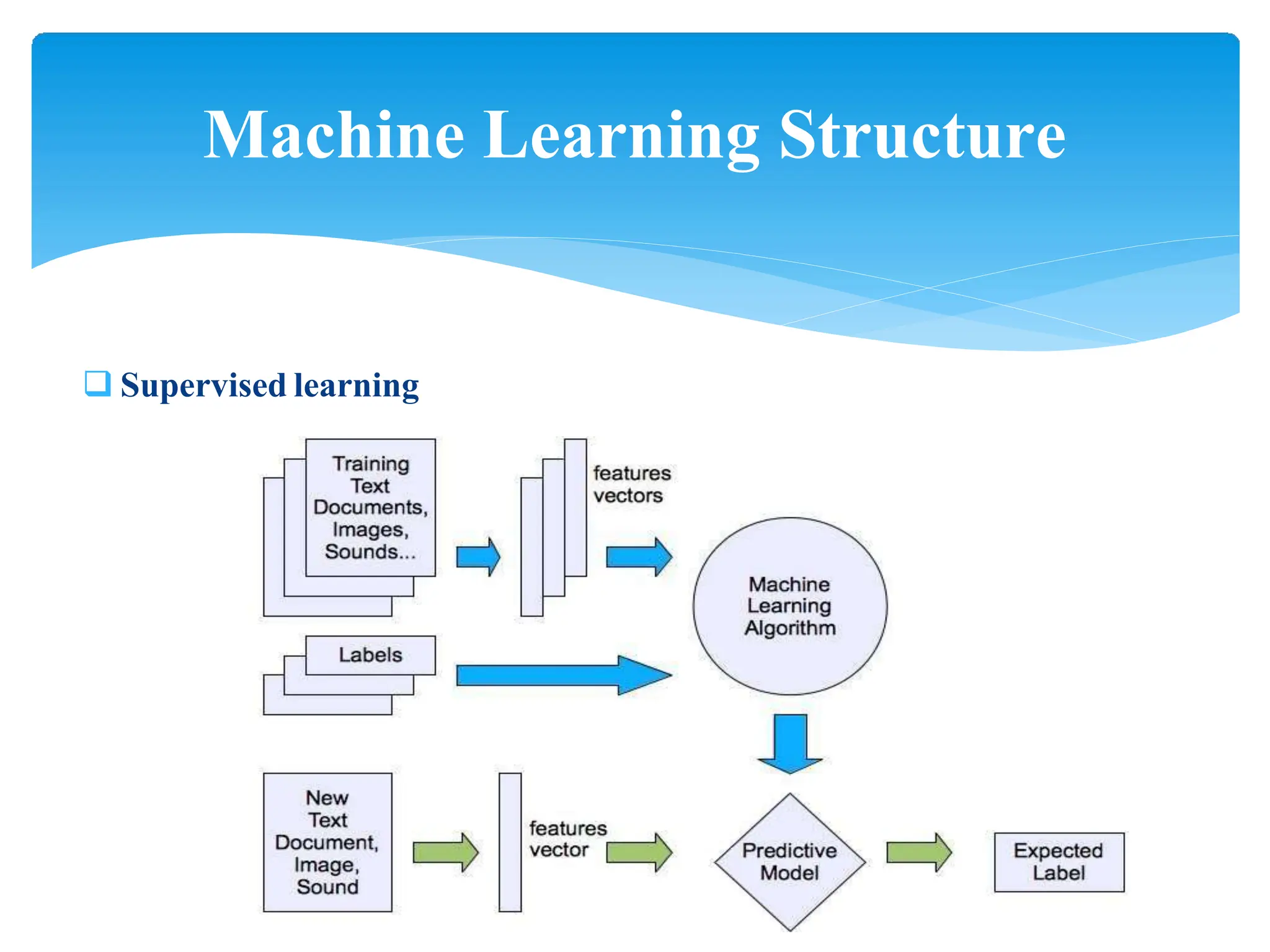
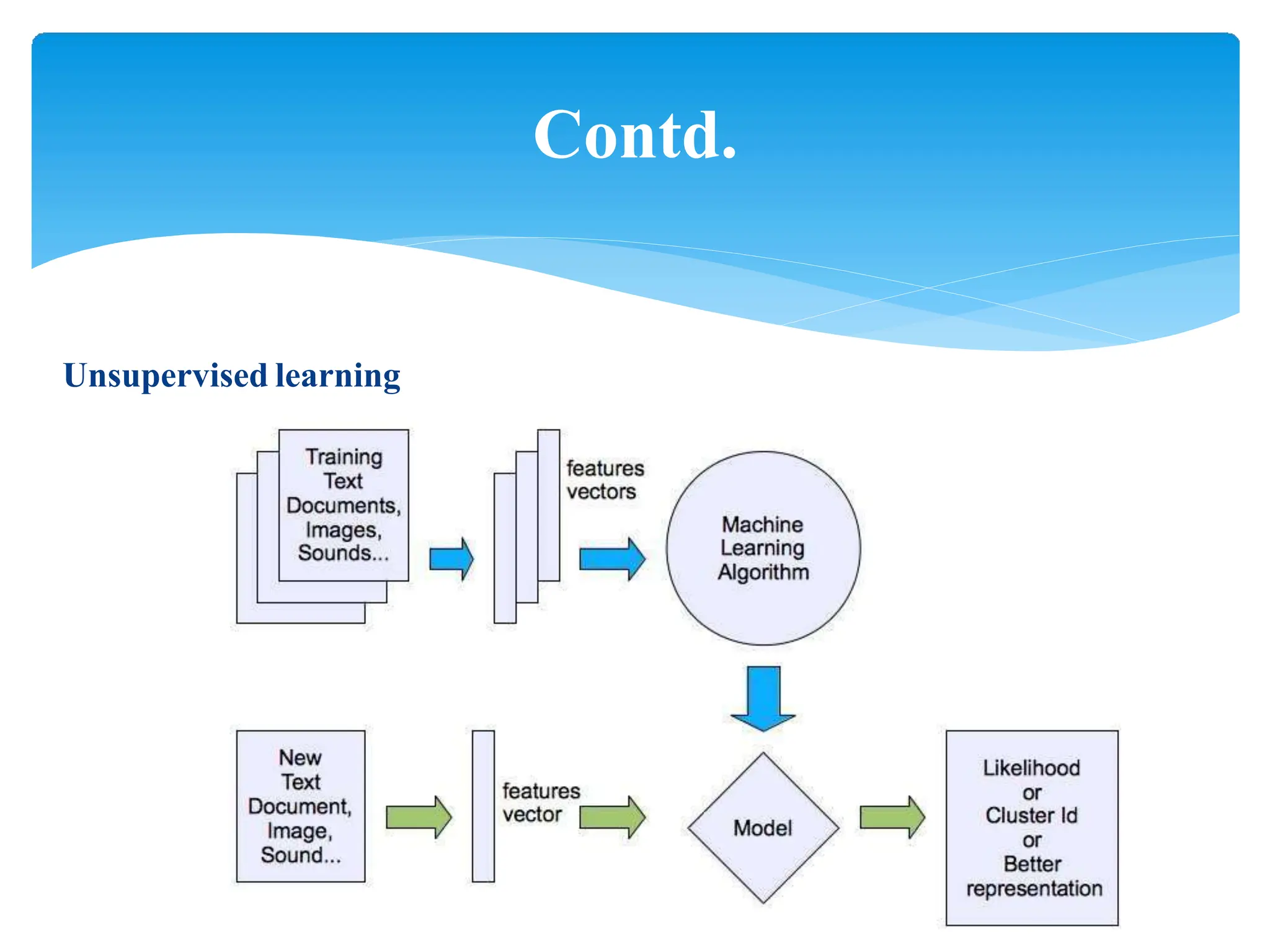
This presentation provides an overview of machine learning, including its history, definitions, applications and algorithms. It begins with early work in the 1950s and discusses modern definitions of machine learning as systems that improve with experience. The presentation outlines key concepts like training and testing data, performance factors and common algorithm types for supervised, unsupervised and semi-supervised learning. It concludes that machine learning will become increasingly important in many domains from multimedia to economics.