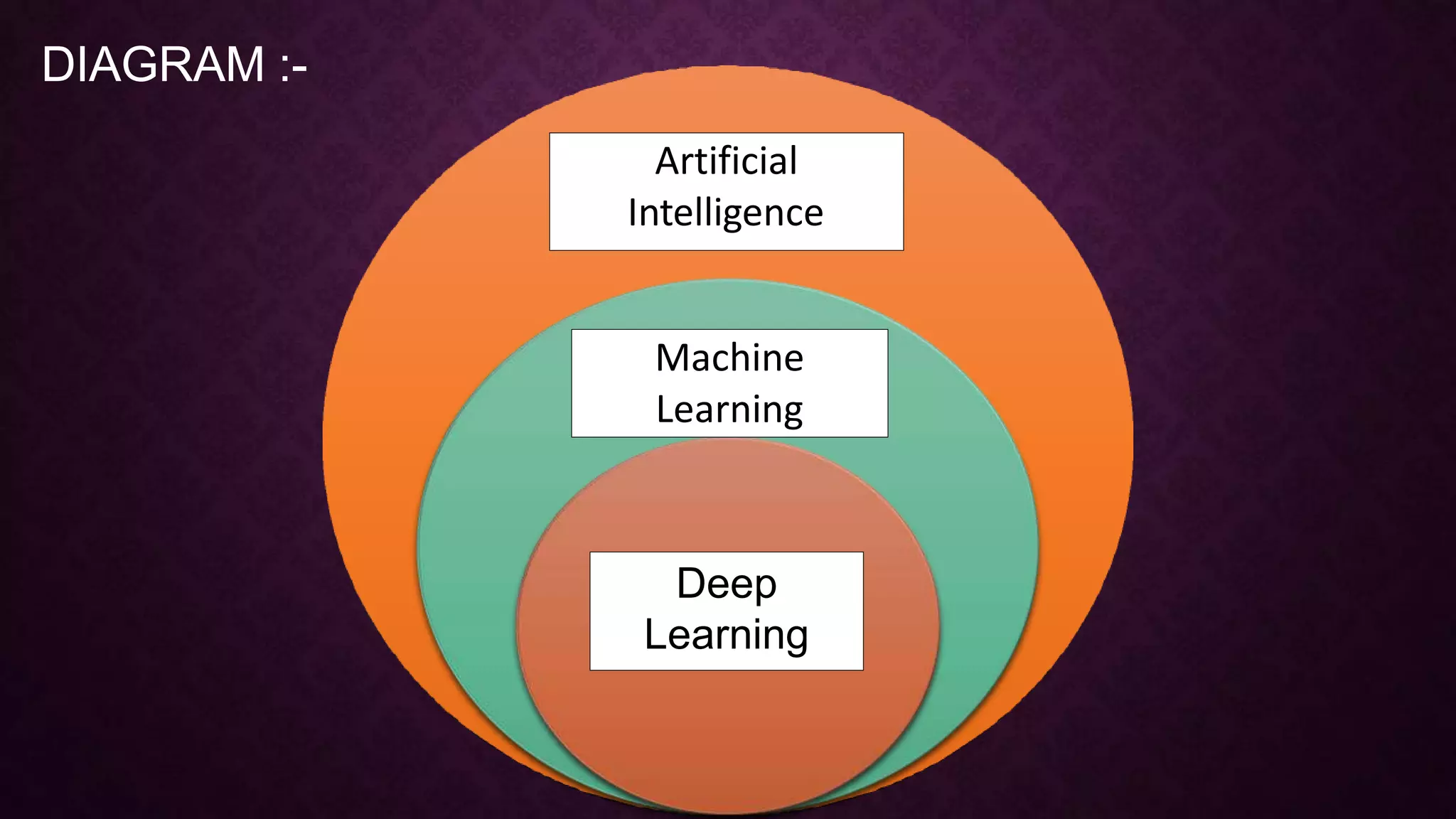
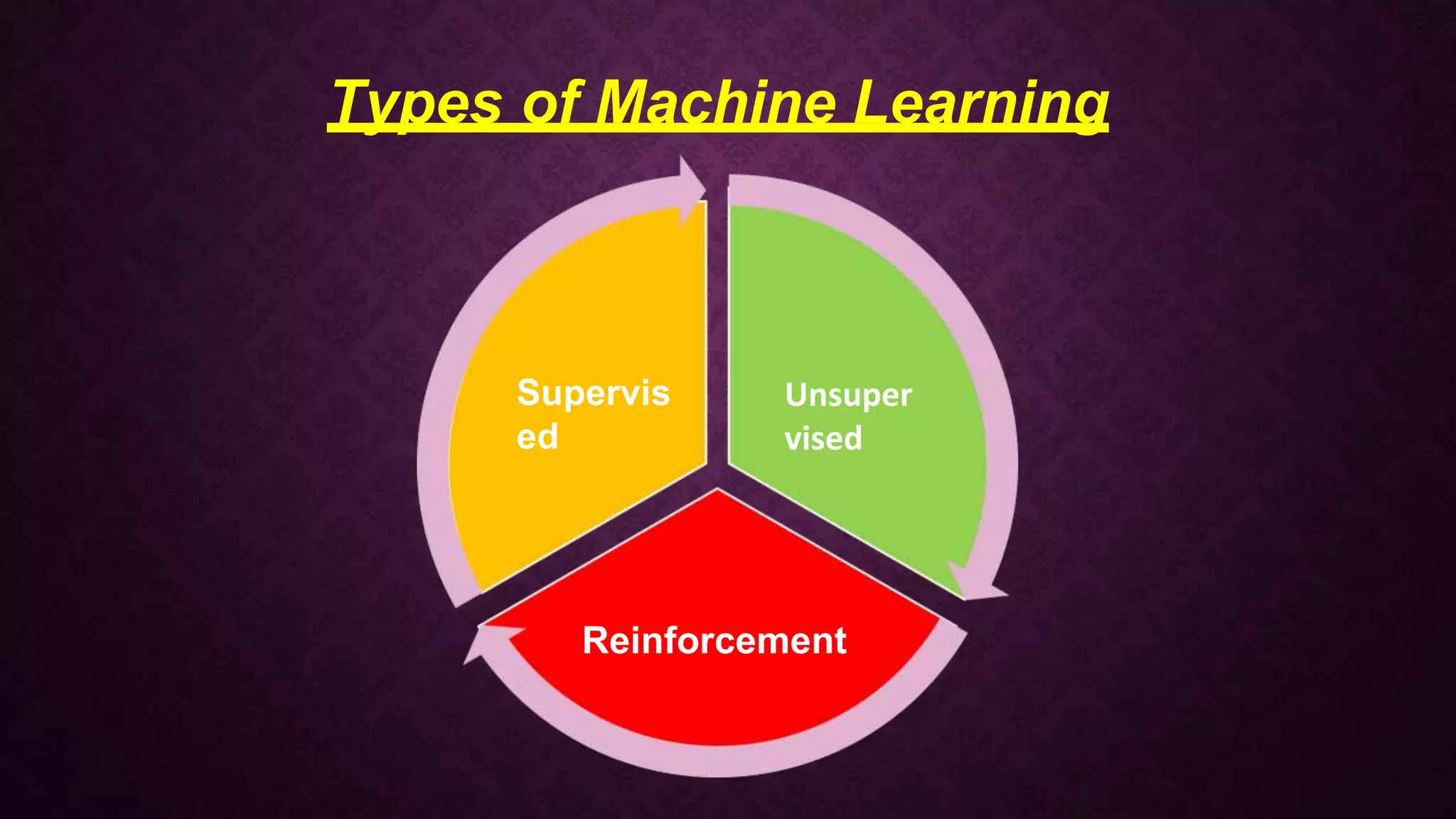
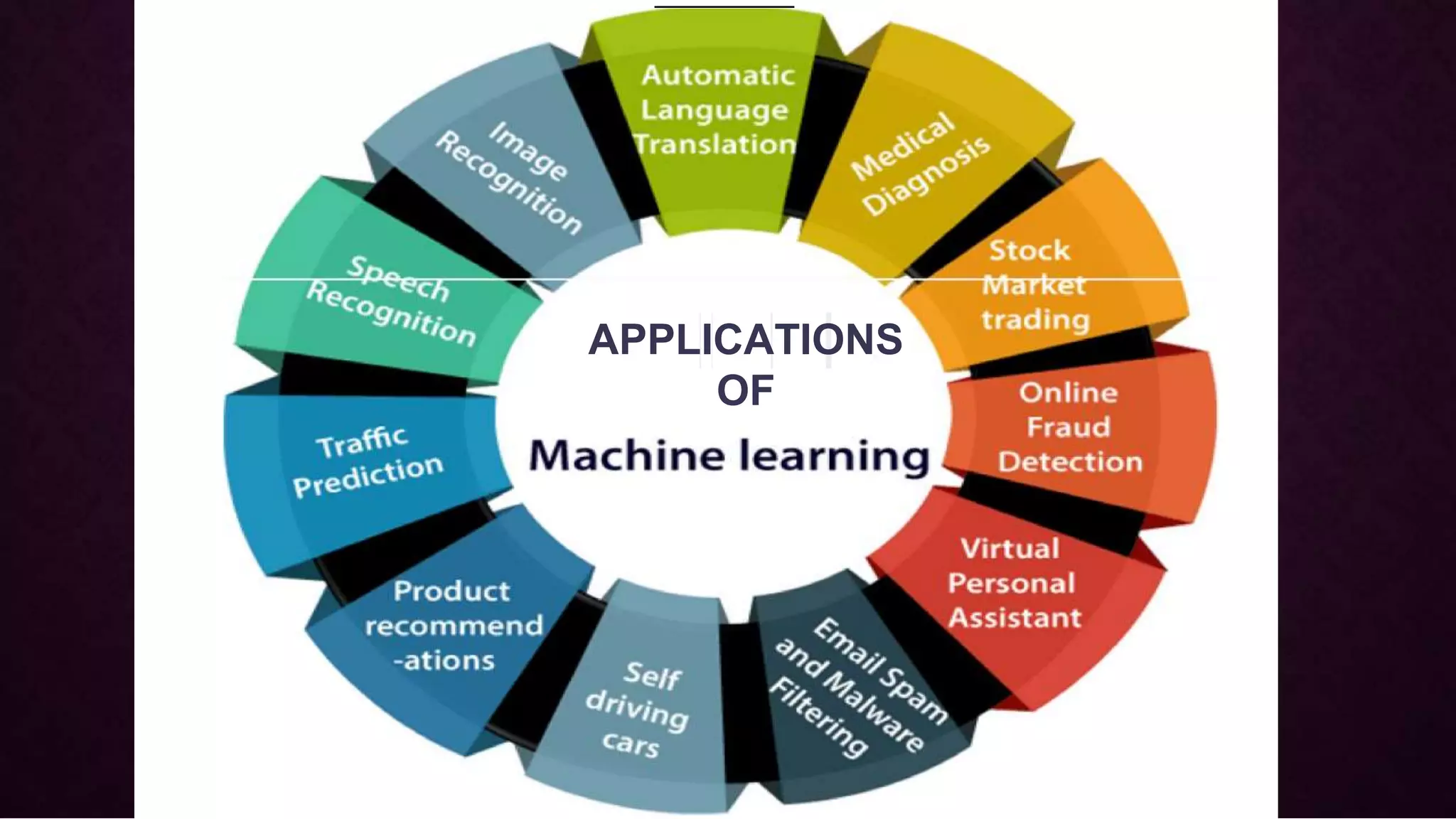
The presentation introduces machine learning as a subset of artificial intelligence, outlining its definition, processes, and types including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It details the seven steps of the machine learning process and highlights various applications such as image and speech recognition, traffic prediction, and self-driving cars. Key terms like algorithm, model, and the distinctions between different machine learning approaches are discussed.