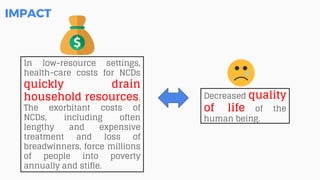
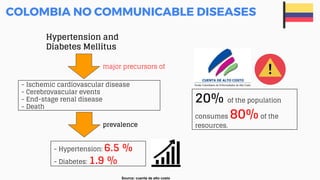
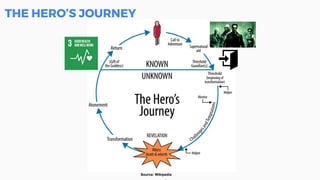
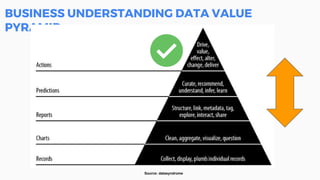
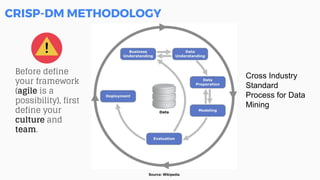
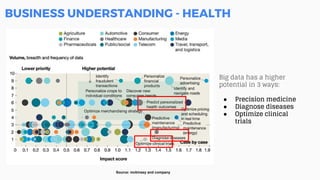
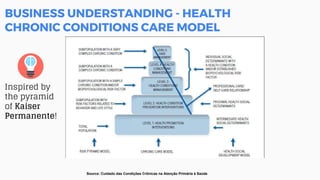
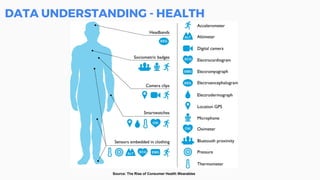
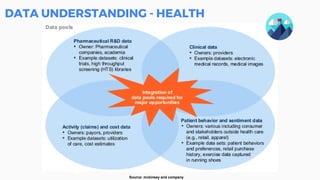
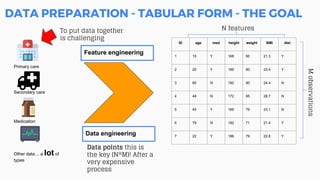
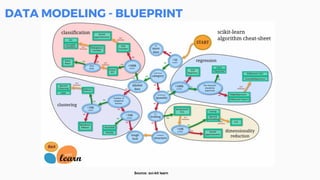
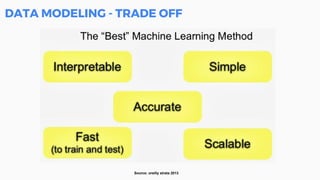
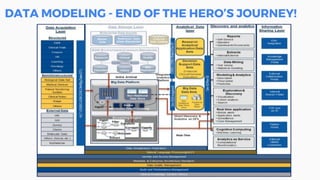
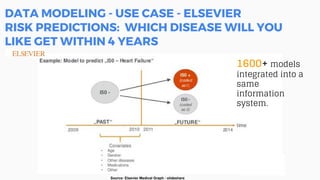
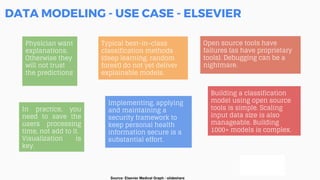
This document discusses the application of machine learning in healthcare. It provides an overview of machine learning and data science concepts and methodologies like the CRISP-DM process. It also discusses challenges with non-communicable diseases and opportunities for applying machine learning to areas like precision medicine, disease diagnosis, and clinical trials optimization using diverse healthcare data sources. Machine learning can help address issues like reducing healthcare costs and improving outcomes for conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease.