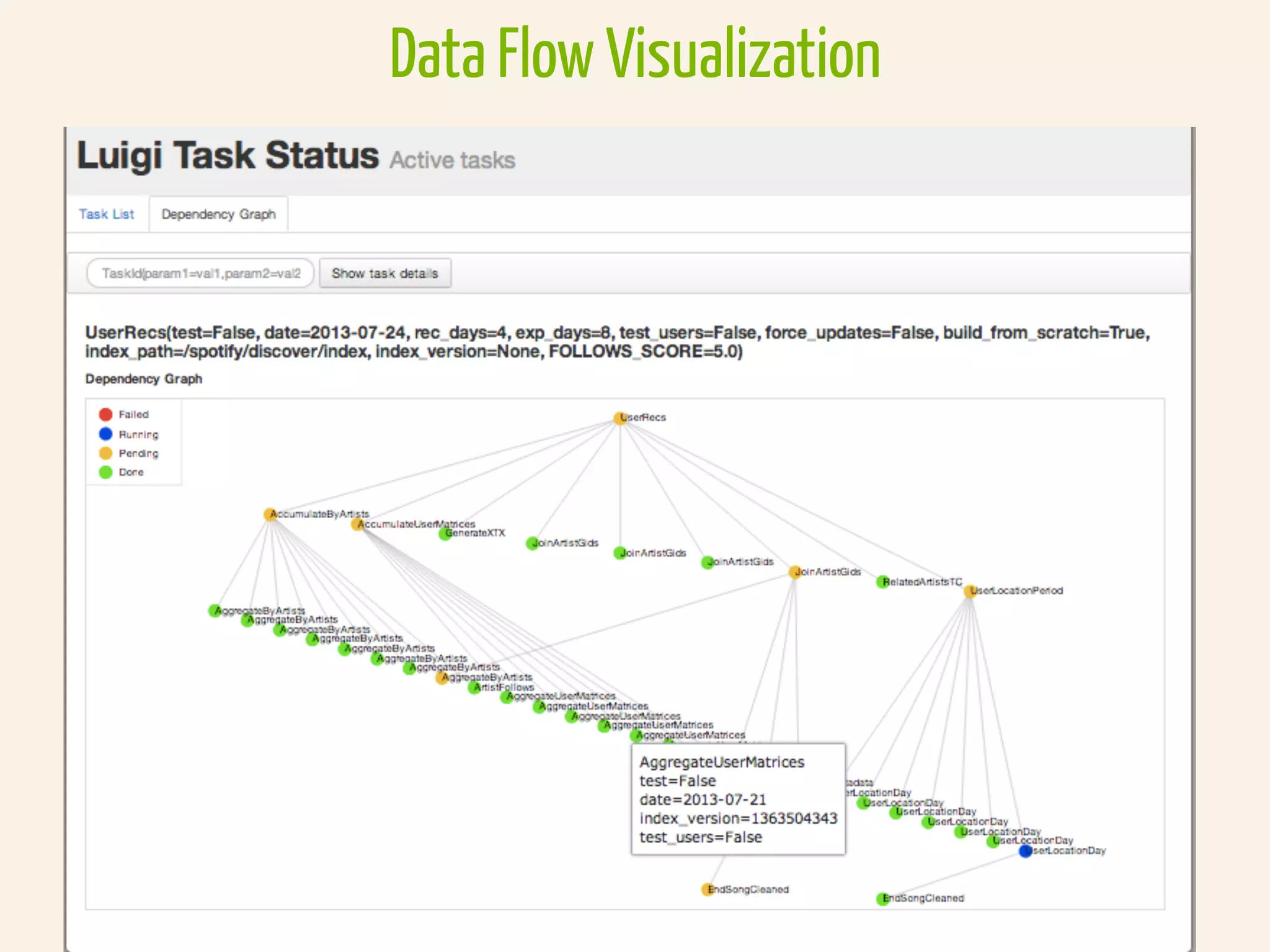
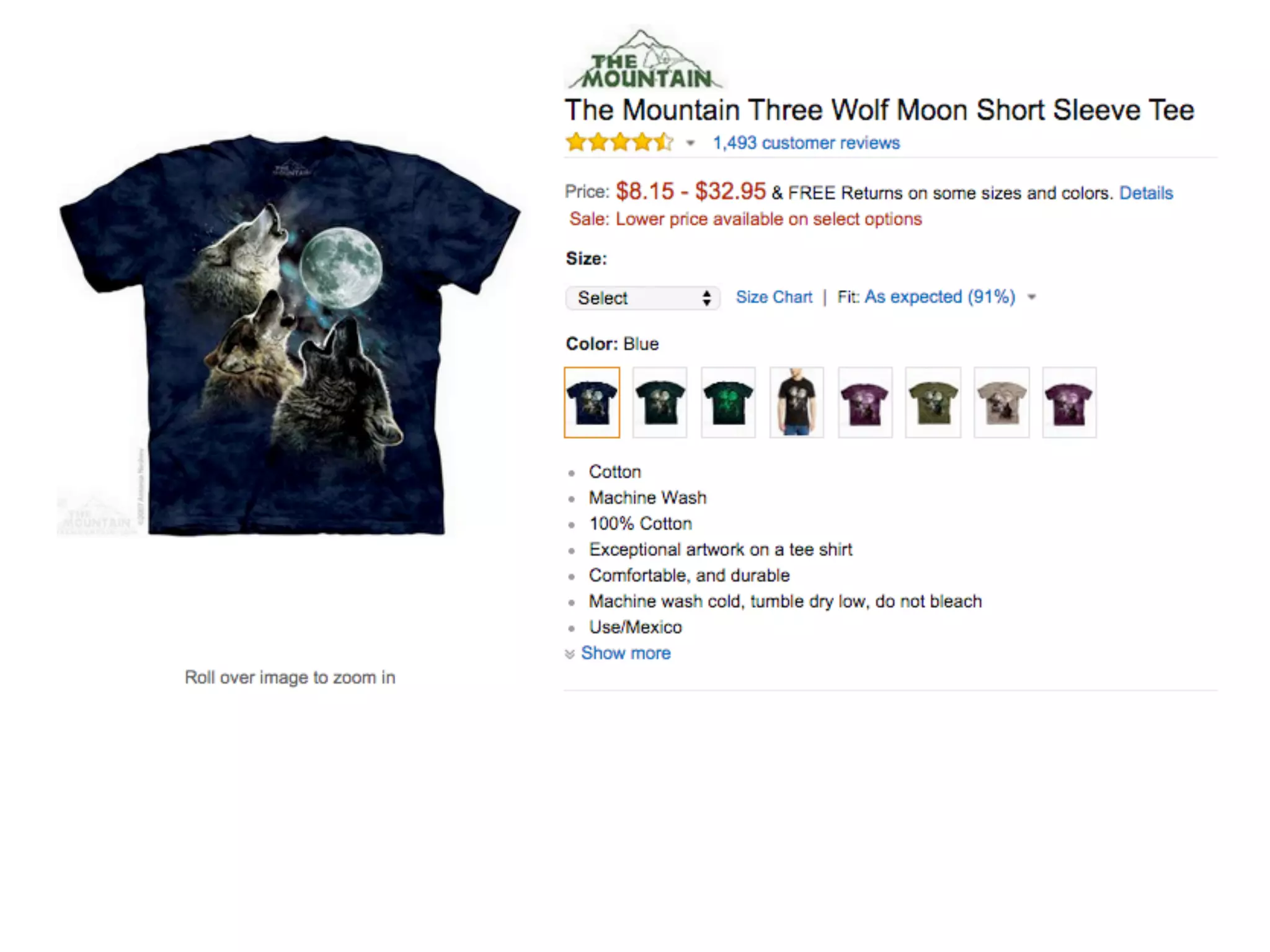
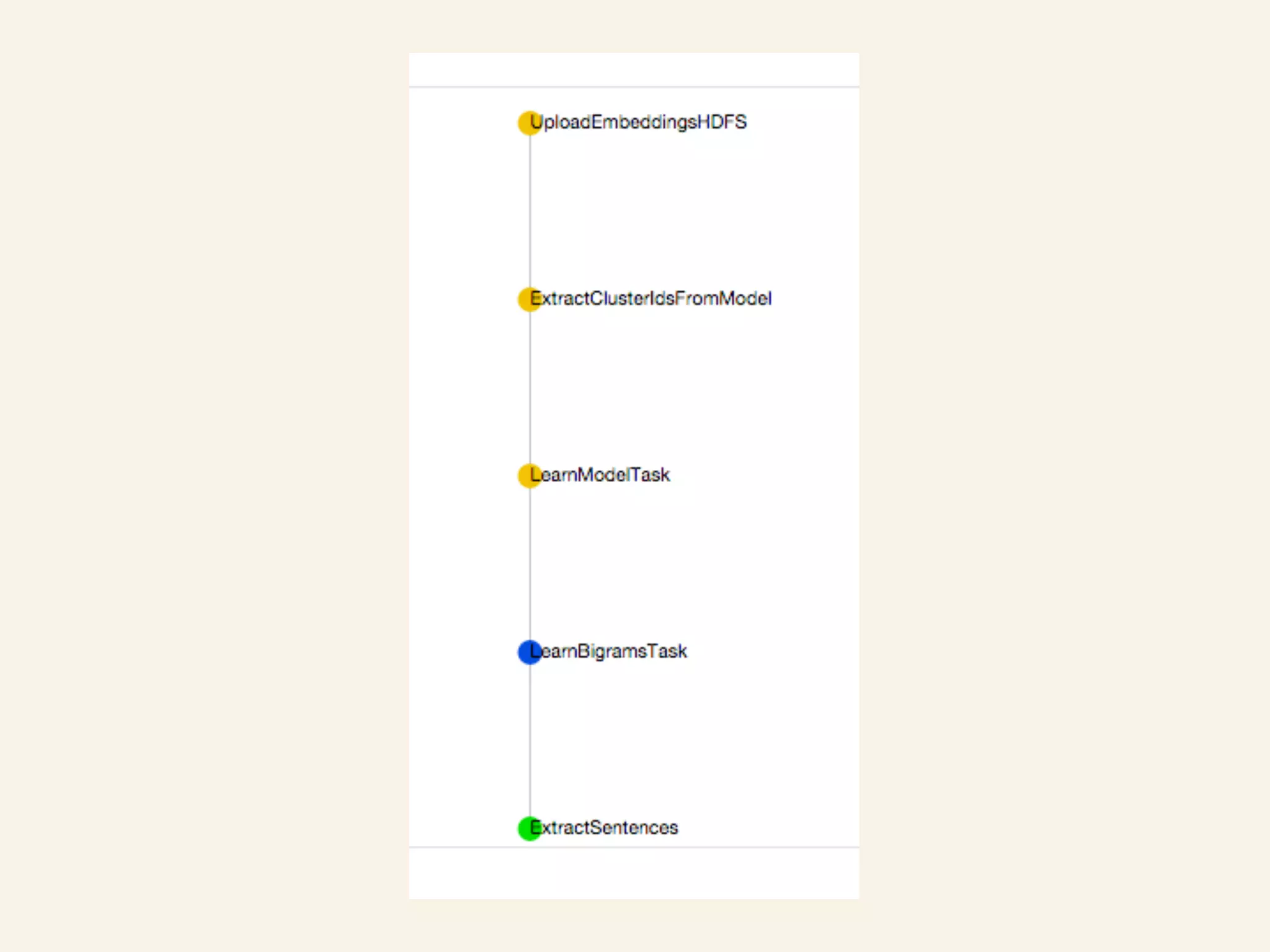
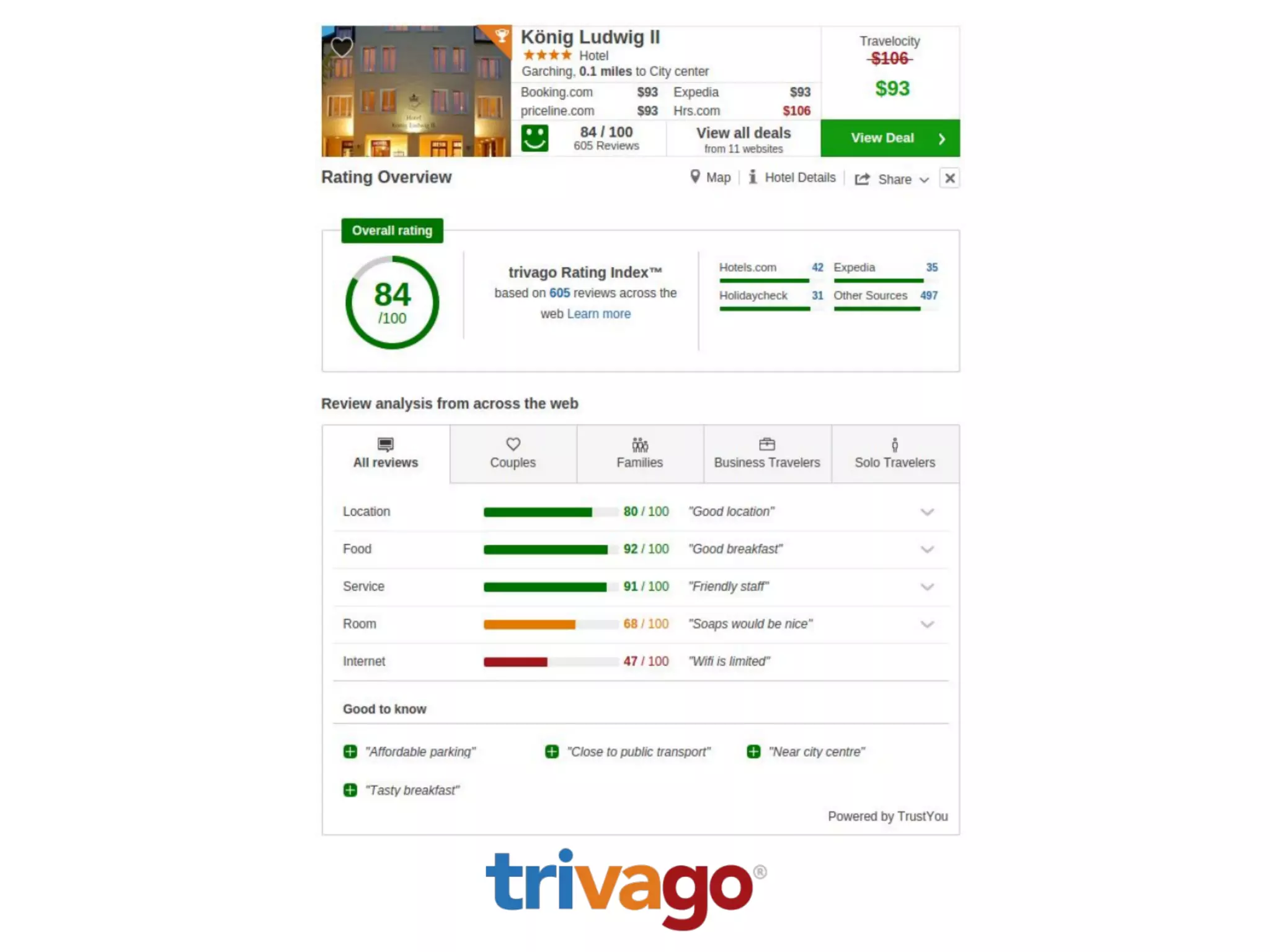
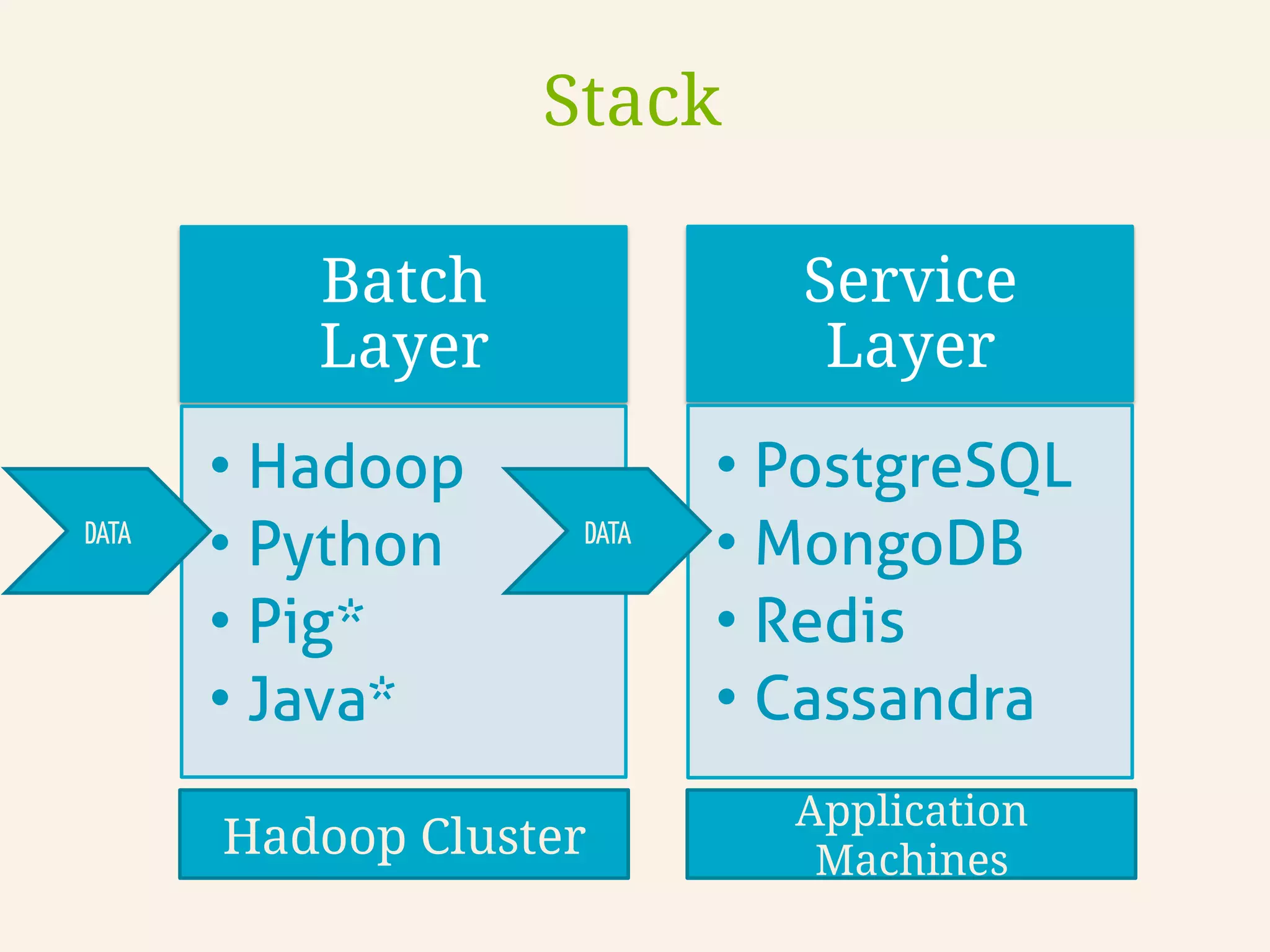
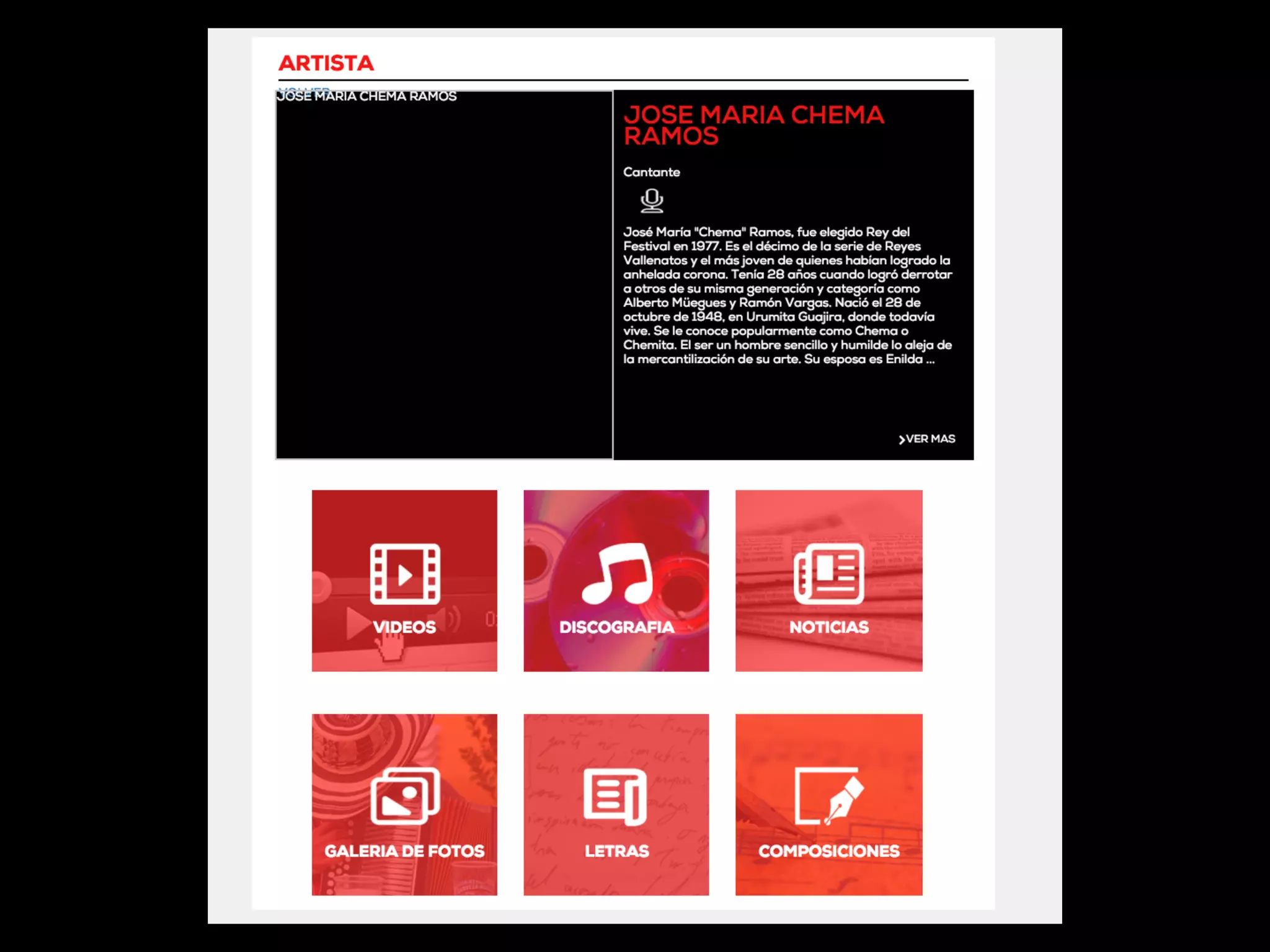
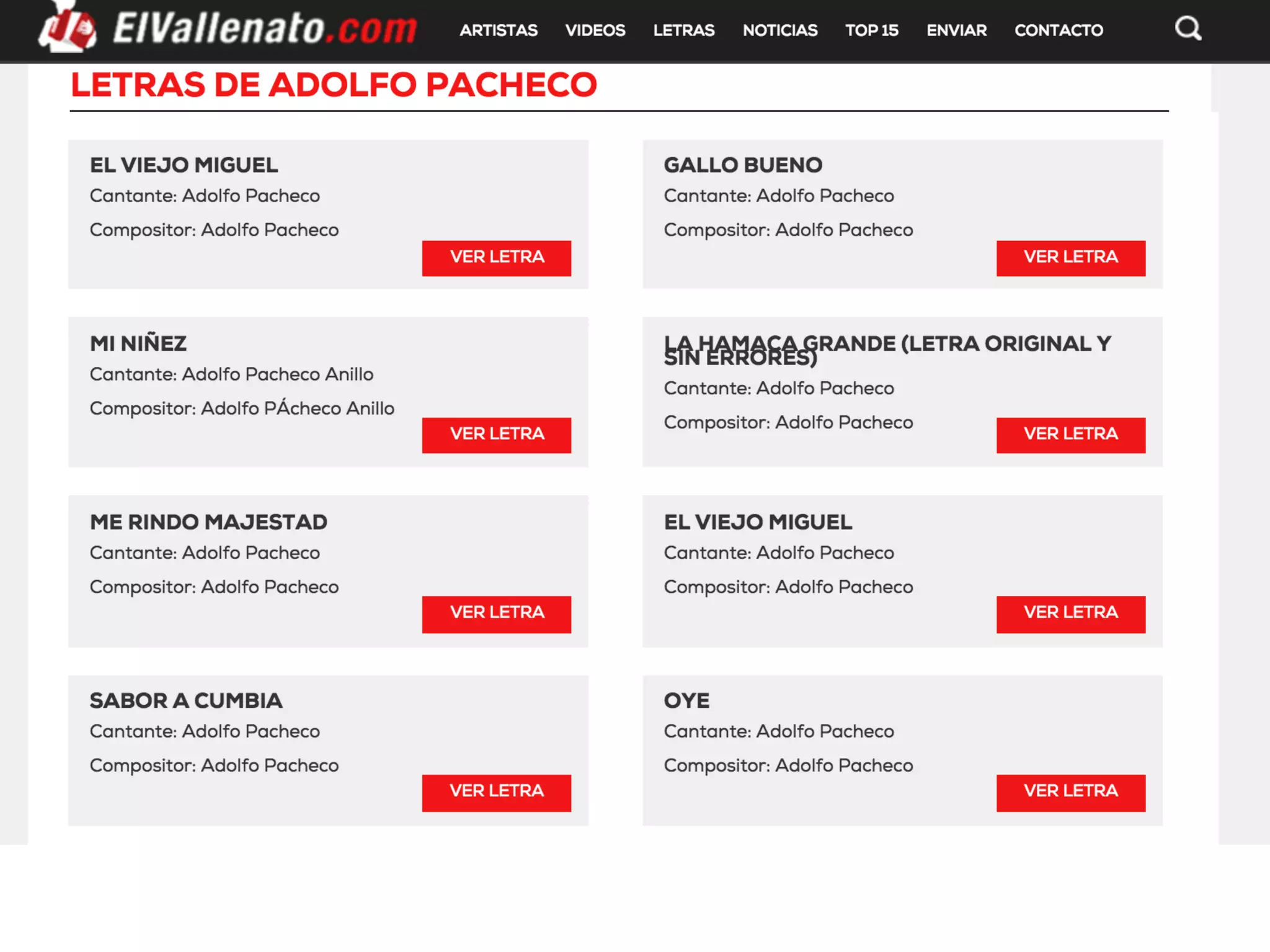
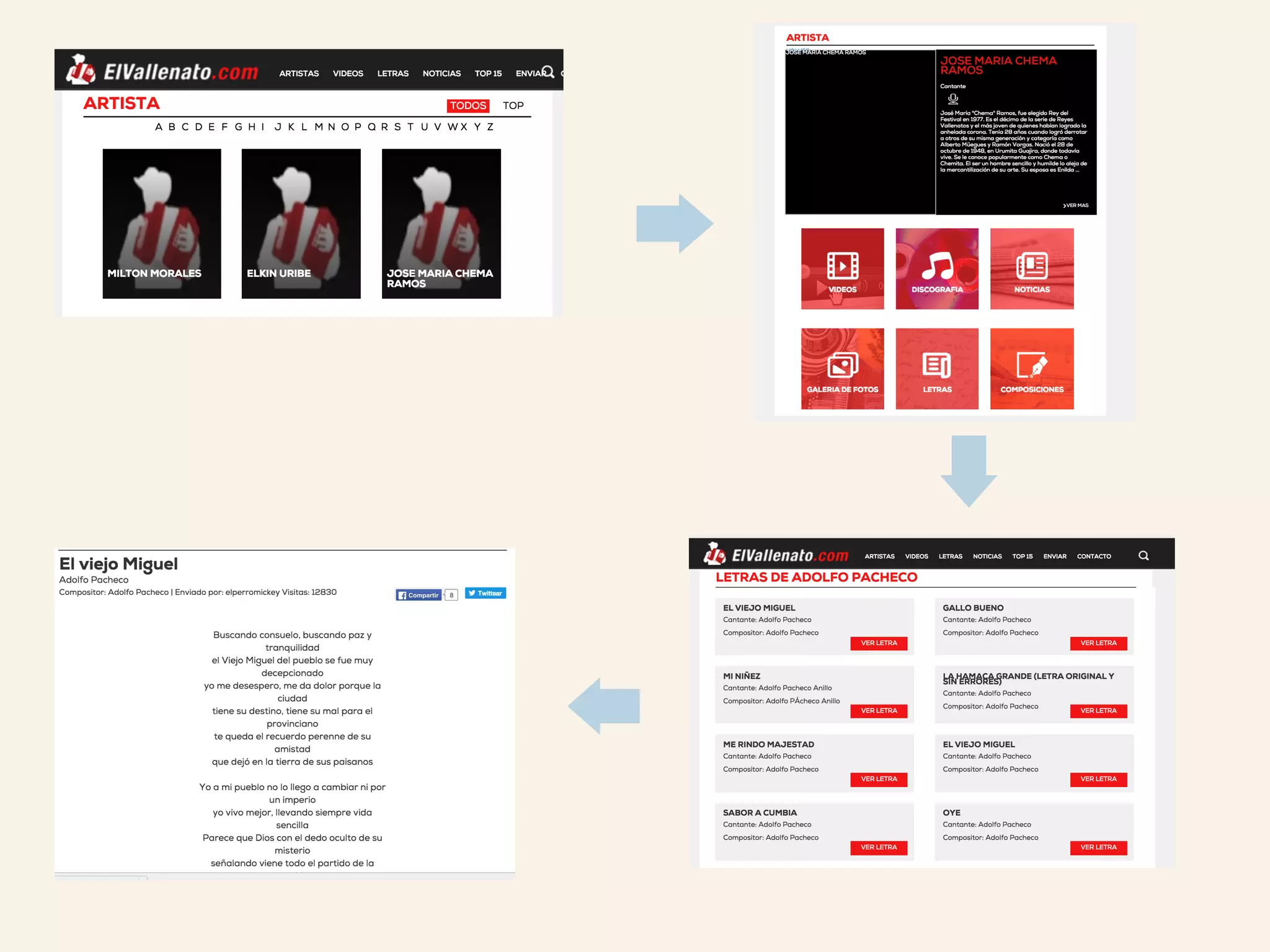
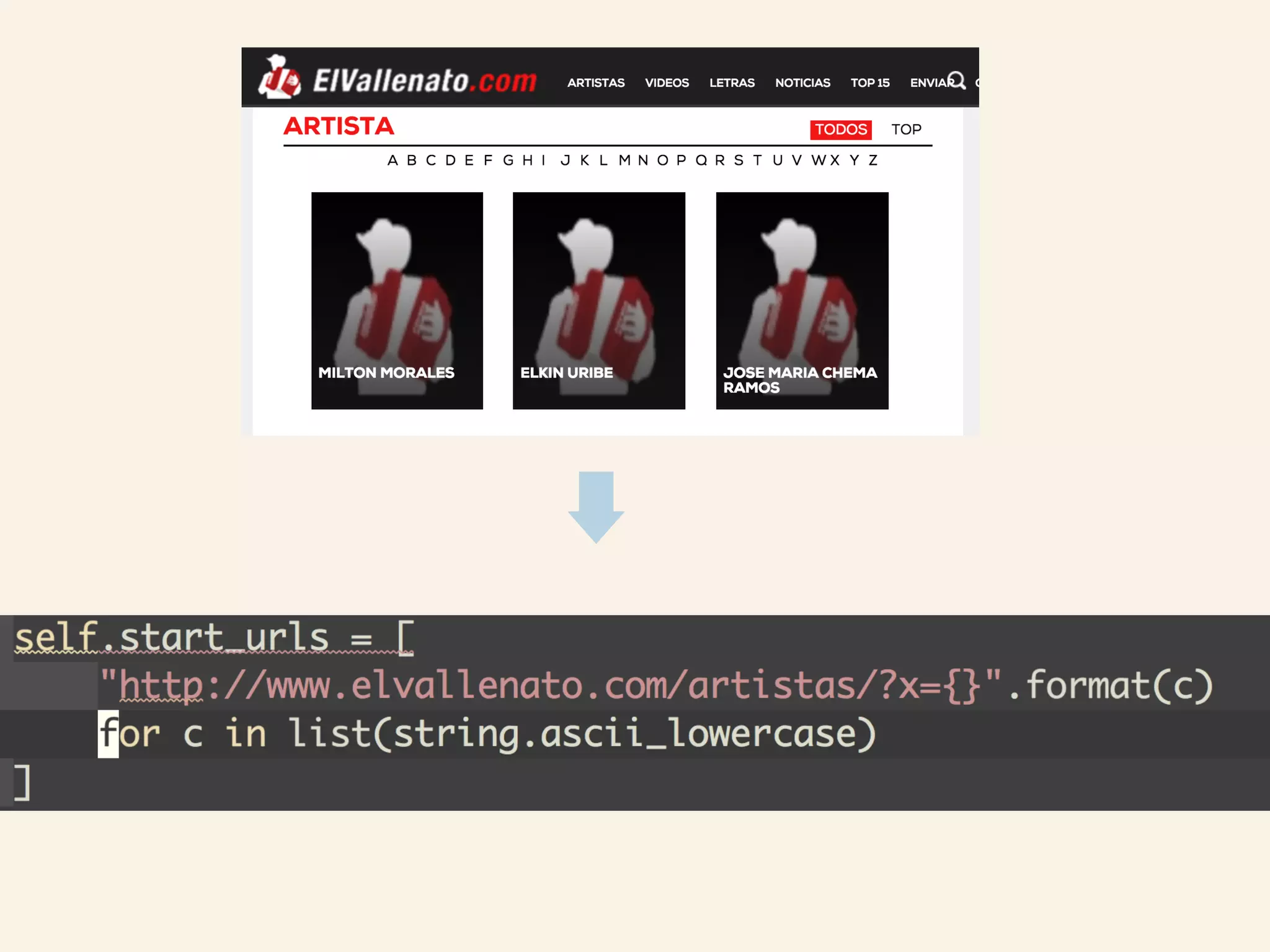
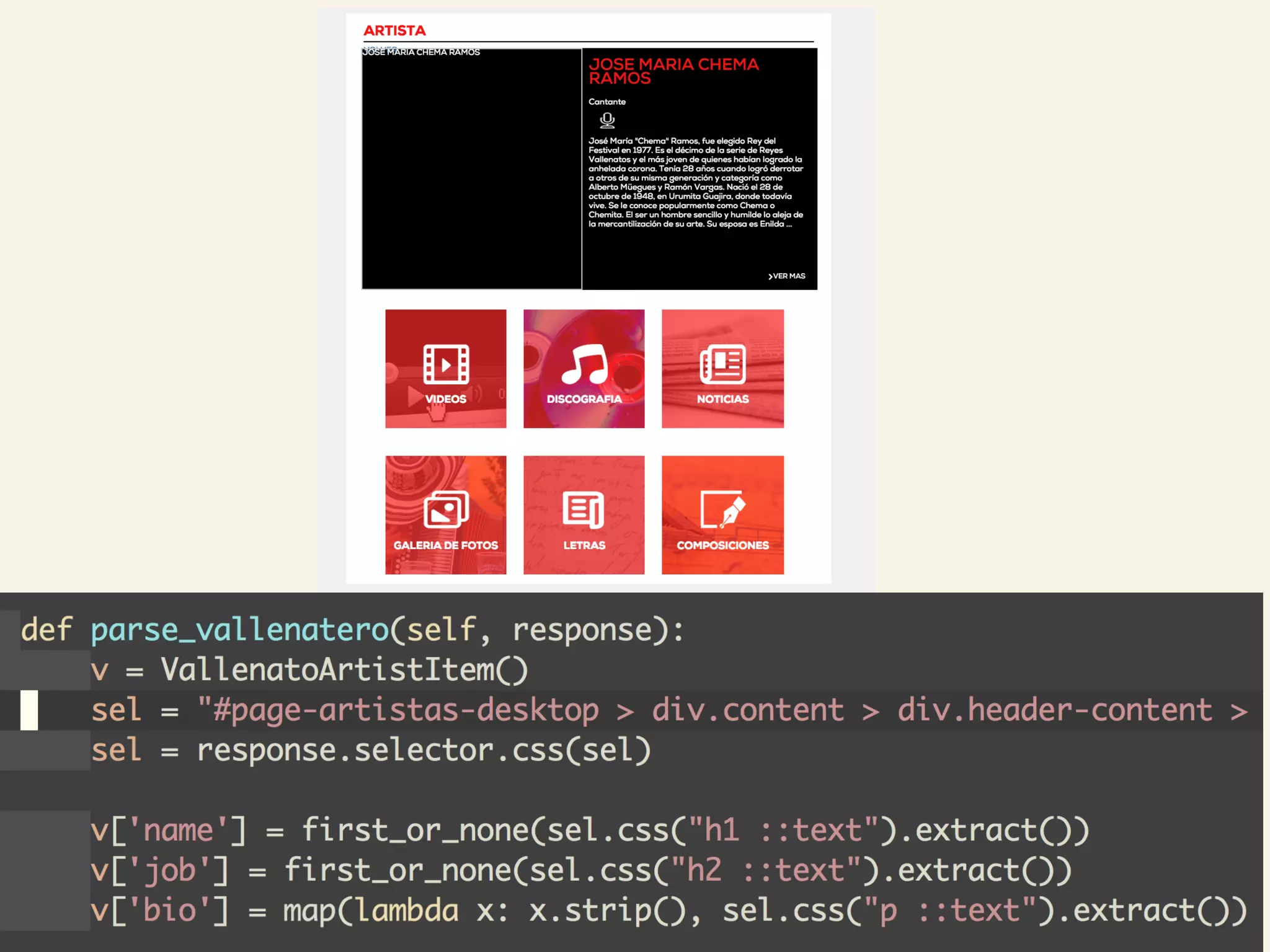
This document discusses how TrustYou processes large amounts of hotel review data to provide summaries to travelers. It crawls over 30 million reviews daily across 25 languages. Natural language processing and machine learning techniques are used to analyze the text and provide recommendations. Workflows are managed through Luigi and tasks include crawling, text processing, modeling word embeddings, and powering a sample application. Hadoop and Python are used extensively to handle the large scale processing.


































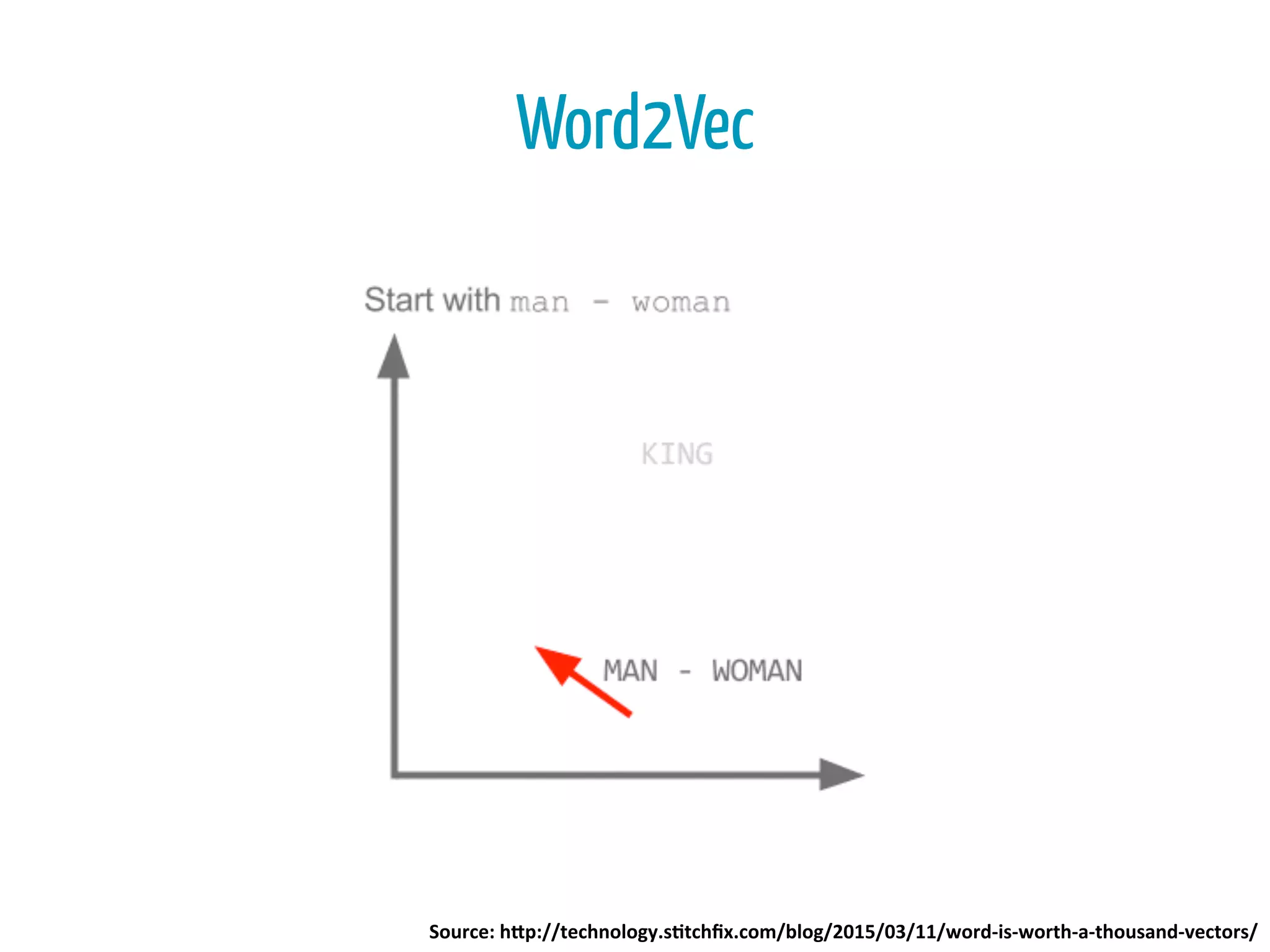
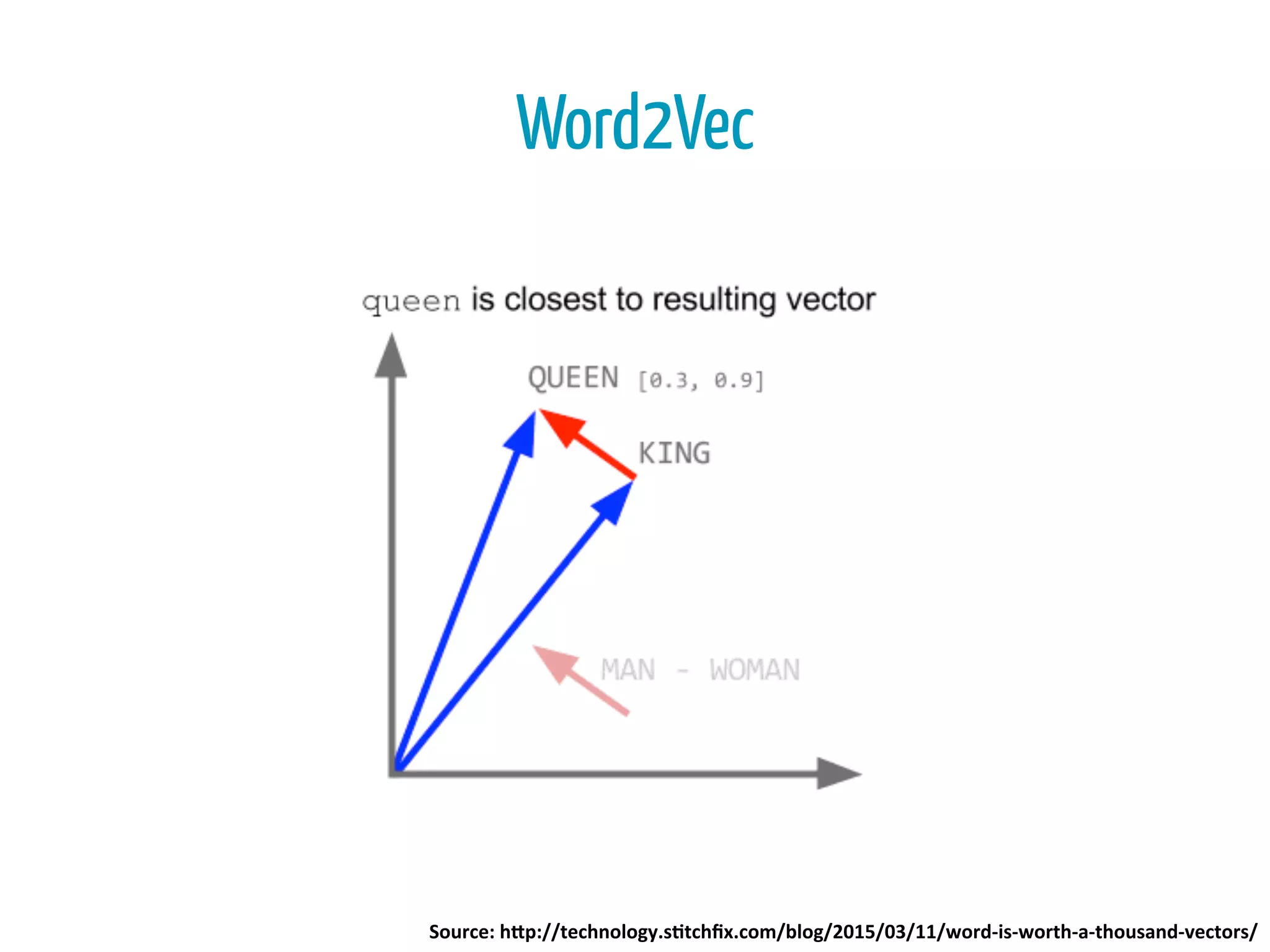
![• “great rooms”
• “great hotel”
• “rooms are terrible”
• “hotel is terrible”
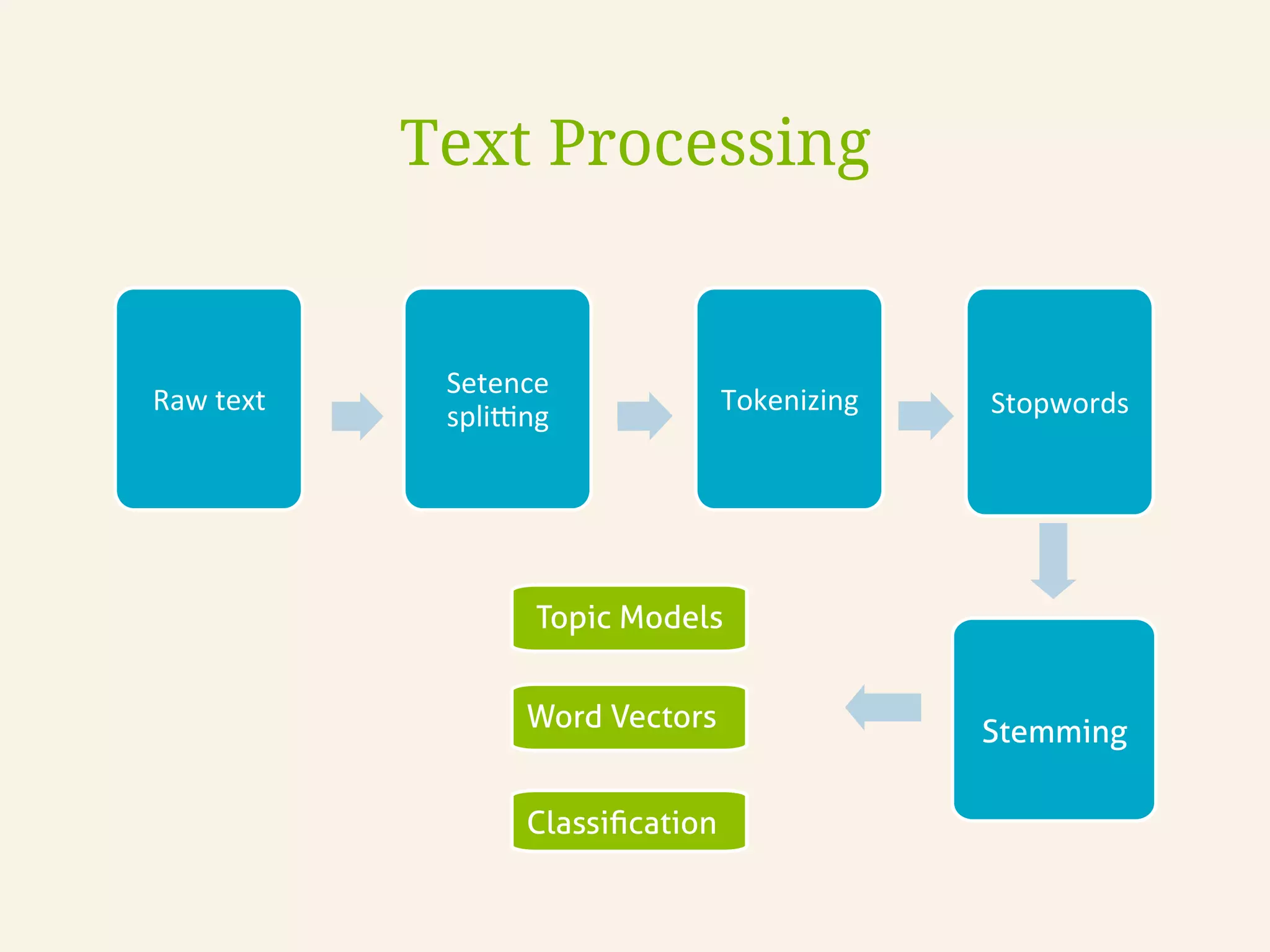
Text Processing
JJ NN
JJ NN
NN VB JJ
NN VB JJ
>> nltk.pos_tag(nltk.word_tokenize("hotel is
terrible"))
[('hotel', 'NN'), ('is', 'VBZ'), ('terrible', 'JJ')]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-45-2048.jpg)




















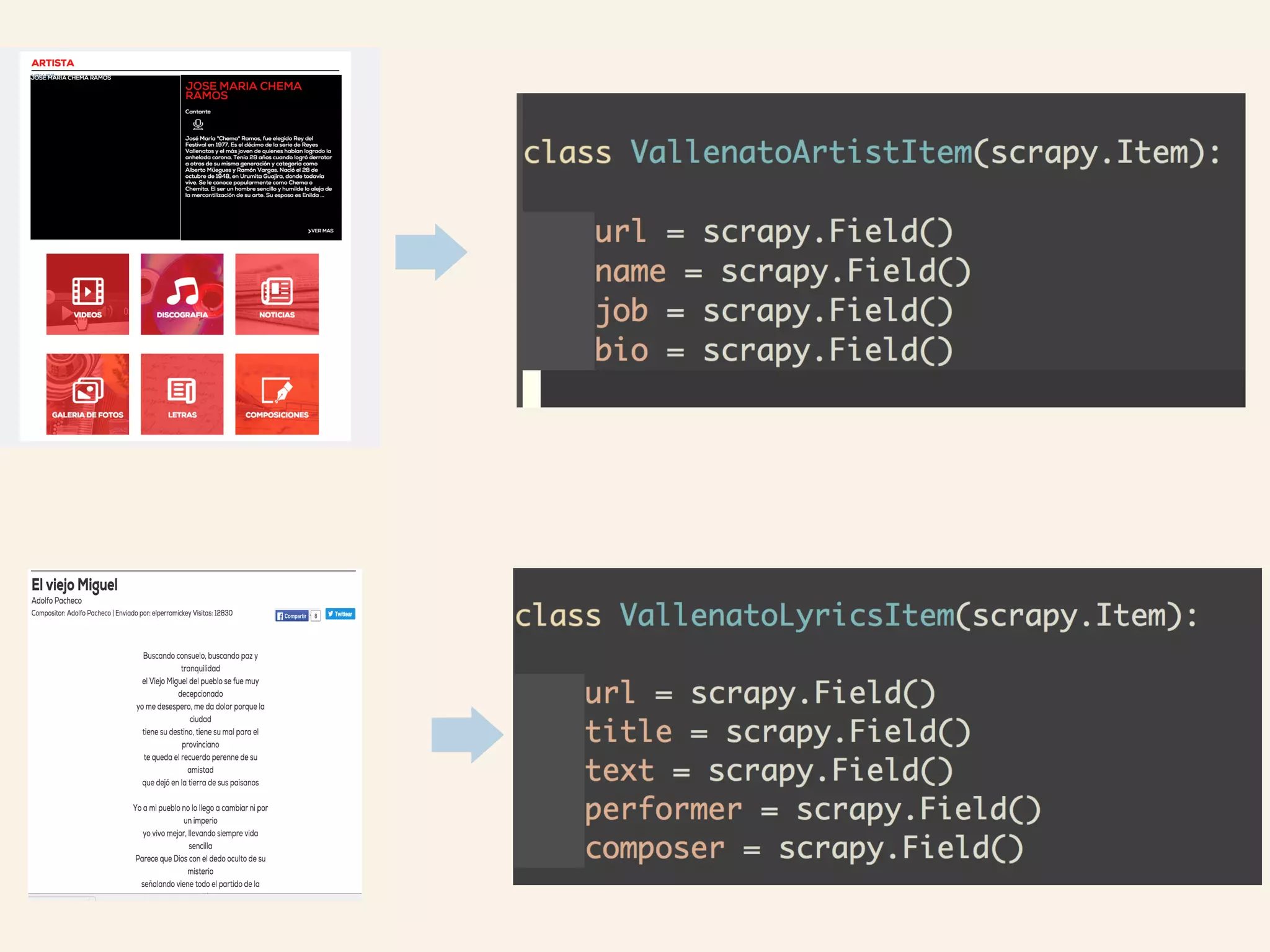
![Minimal Bolerplate Code
class WordCount(luigi.Task):
date = luigi.DateParameter()
def requires(self):
return InputText(date)
def output(self):
return luigi.LocalTarget(’/tmp/%s' % self.date_interval)
def run(self):
count = {}
for f in self.input():
for line in f.open('r'):
for word in line.strip().split():
count[word] = count.get(word, 0) + 1
f = self.output().open('w')
for word, count in six.iteritems(count):
f.write("%st%dn" % (word, count))
f.close()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-70-2048.jpg)
![class WordCount(luigi.Task):
date = luigi.DateParameter()
def requires(self):
return InputText(date)
def output(self):
return luigi.LocalTarget(’/tmp/%s' % self.date_interval)
def run(self):
count = {}
for f in self.input():
for line in f.open('r'):
for word in line.strip().split():
count[word] = count.get(word, 0) + 1
f = self.output().open('w')
for word, count in six.iteritems(count):
f.write("%st%dn" % (word, count))
f.close()
Task Parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-71-2048.jpg)
![class WordCount(luigi.Task):
date = luigi.DateParameter()
def requires(self):
return InputText(date)
def output(self):
return luigi.LocalTarget(’/tmp/%s' % self.date_interval)
def run(self):
count = {}
for f in self.input():
for line in f.open('r'):
for word in line.strip().split():
count[word] = count.get(word, 0) + 1
f = self.output().open('w')
for word, count in six.iteritems(count):
f.write("%st%dn" % (word, count))
f.close()
Programmatically Defined Dependencies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-72-2048.jpg)
![class WordCount(luigi.Task):
date = luigi.DateParameter()
def requires(self):
return InputText(date)
def output(self):
return luigi.LocalTarget(’/tmp/%s' % self.date_interval)
def run(self):
count = {}
for f in self.input():
for line in f.open('r'):
for word in line.strip().split():
count[word] = count.get(word, 0) + 1
f = self.output().open('w')
for word, count in six.iteritems(count):
f.write("%st%dn" % (word, count))
f.close()
Each Task produces an ouput](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-73-2048.jpg)
![class WordCount(luigi.Task):
date = luigi.DateParameter()
def requires(self):
return InputText(date)
def output(self):
return luigi.LocalTarget(’/tmp/%s' % self.date_interval)
def run(self):
count = {}
for f in self.input():
for line in f.open('r'):
for word in line.strip().split():
count[word] = count.get(word, 0) + 1
f = self.output().open('w')
for word, count in six.iteritems(count):
f.write("%st%dn" % (word, count))
f.close()
Write Logic in Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatabogota-2016-160414234821/75/Ayudando-a-los-Viajeros-usando-500-millones-de-Resenas-Hoteleras-al-Mes-74-2048.jpg)