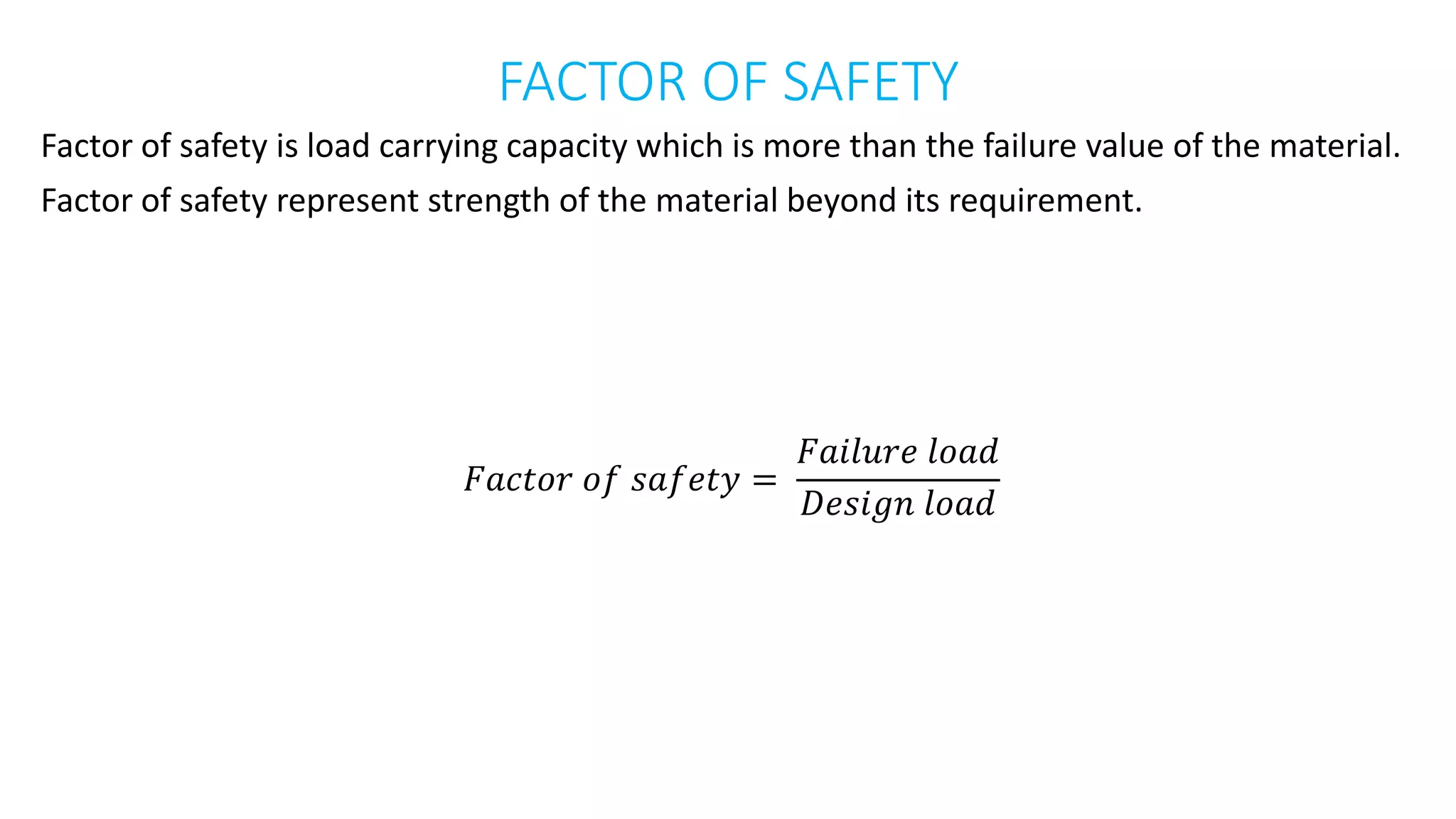
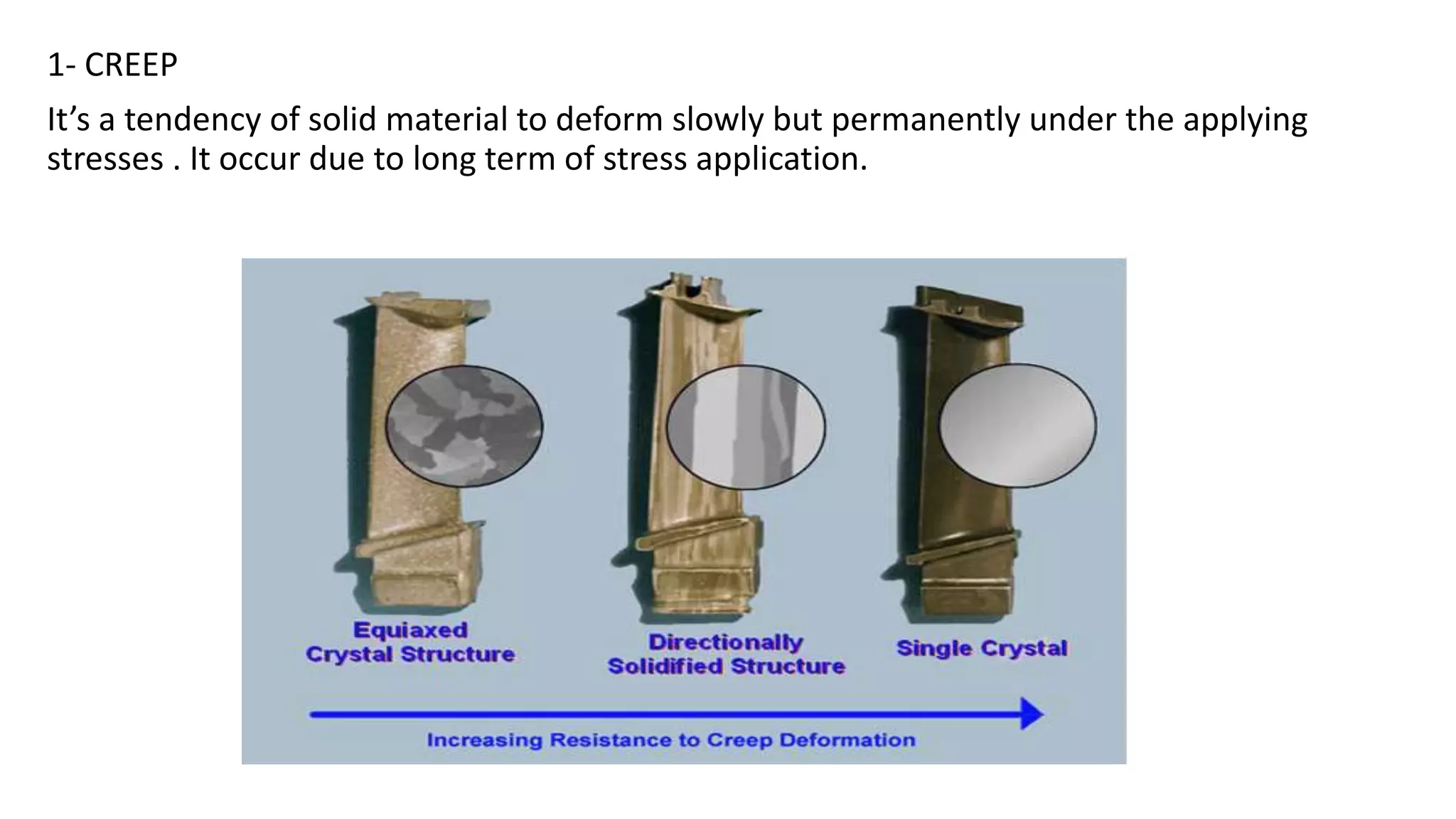
This document discusses key concepts in machine design and material stress including:
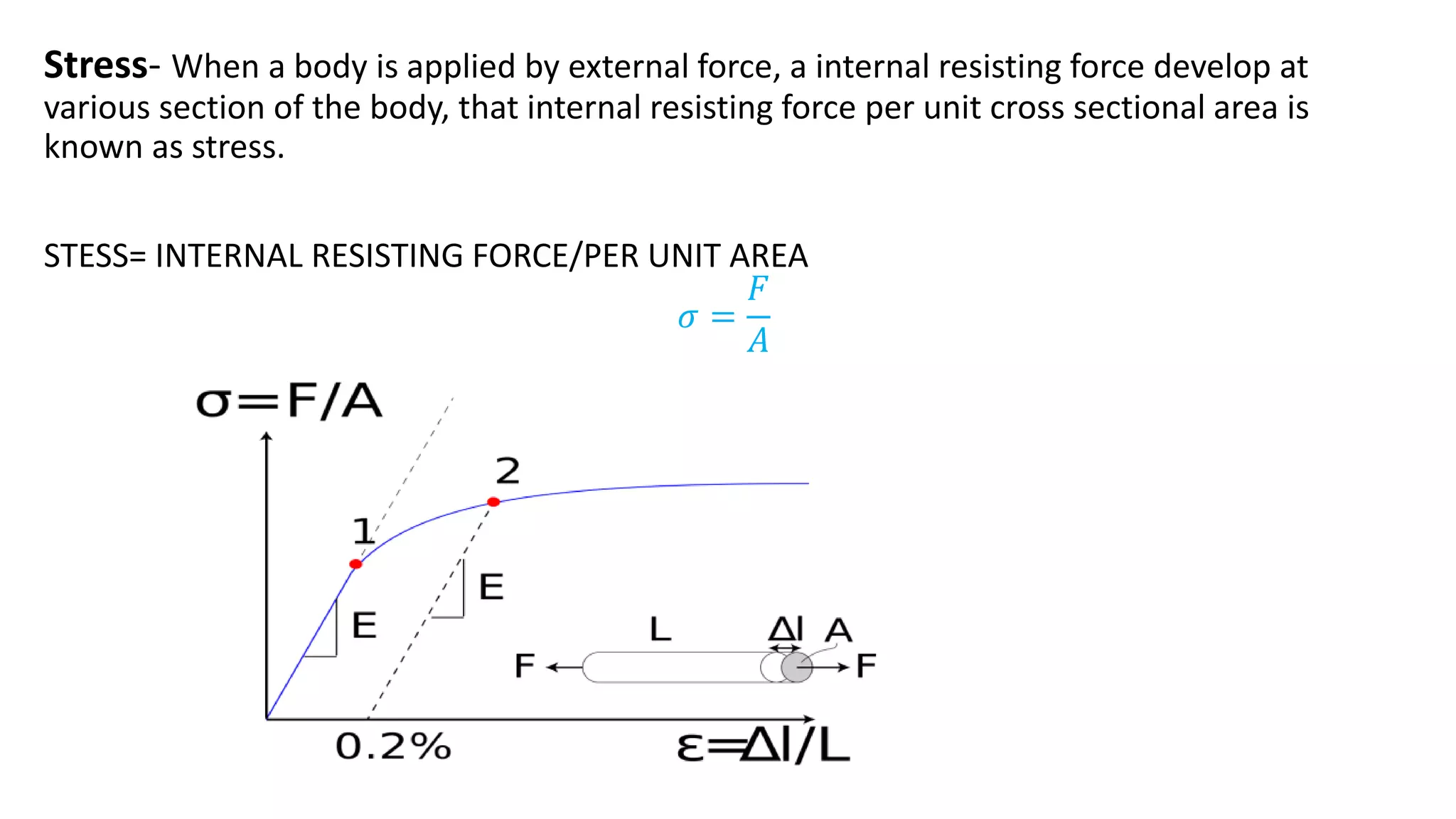
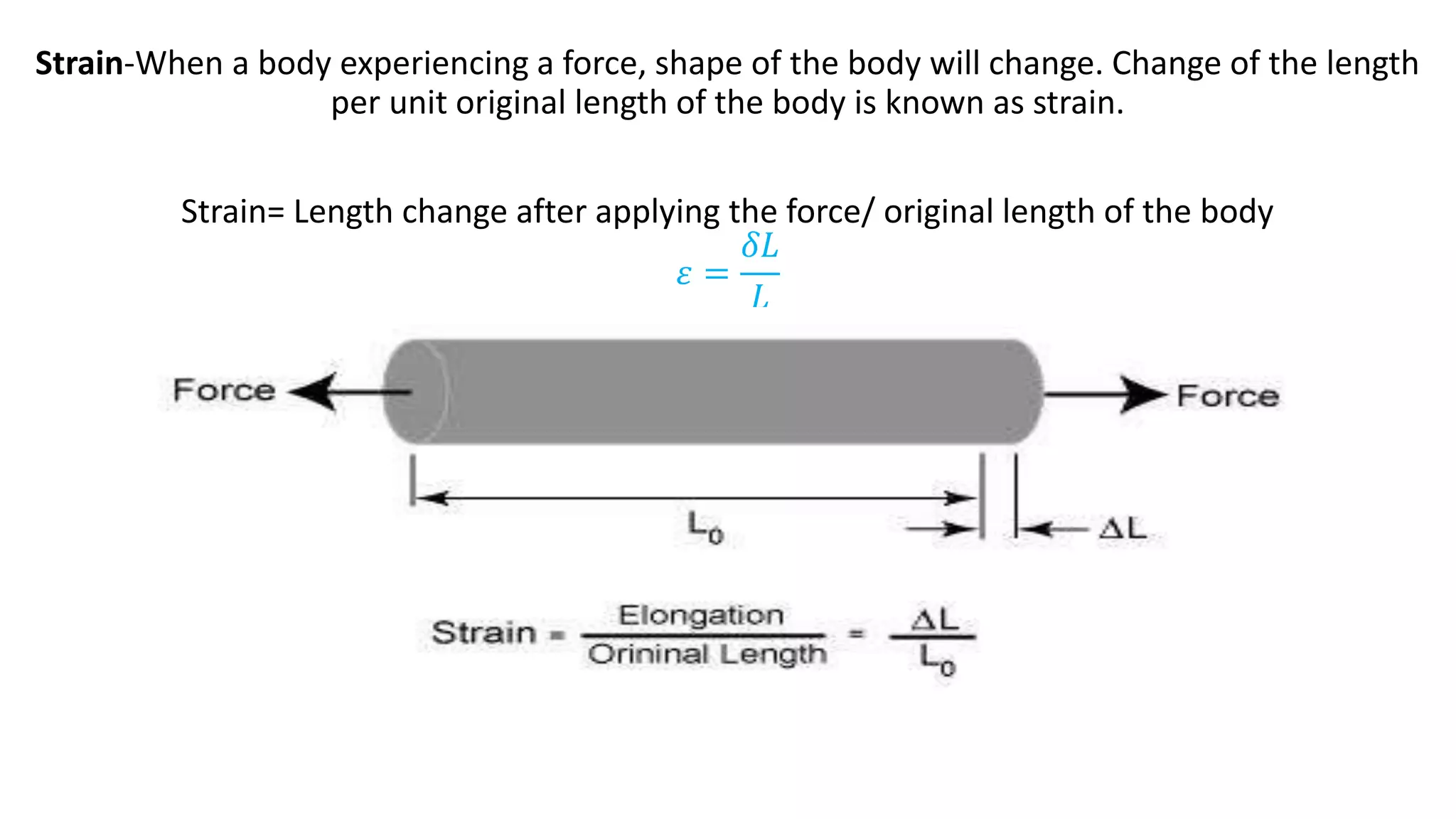
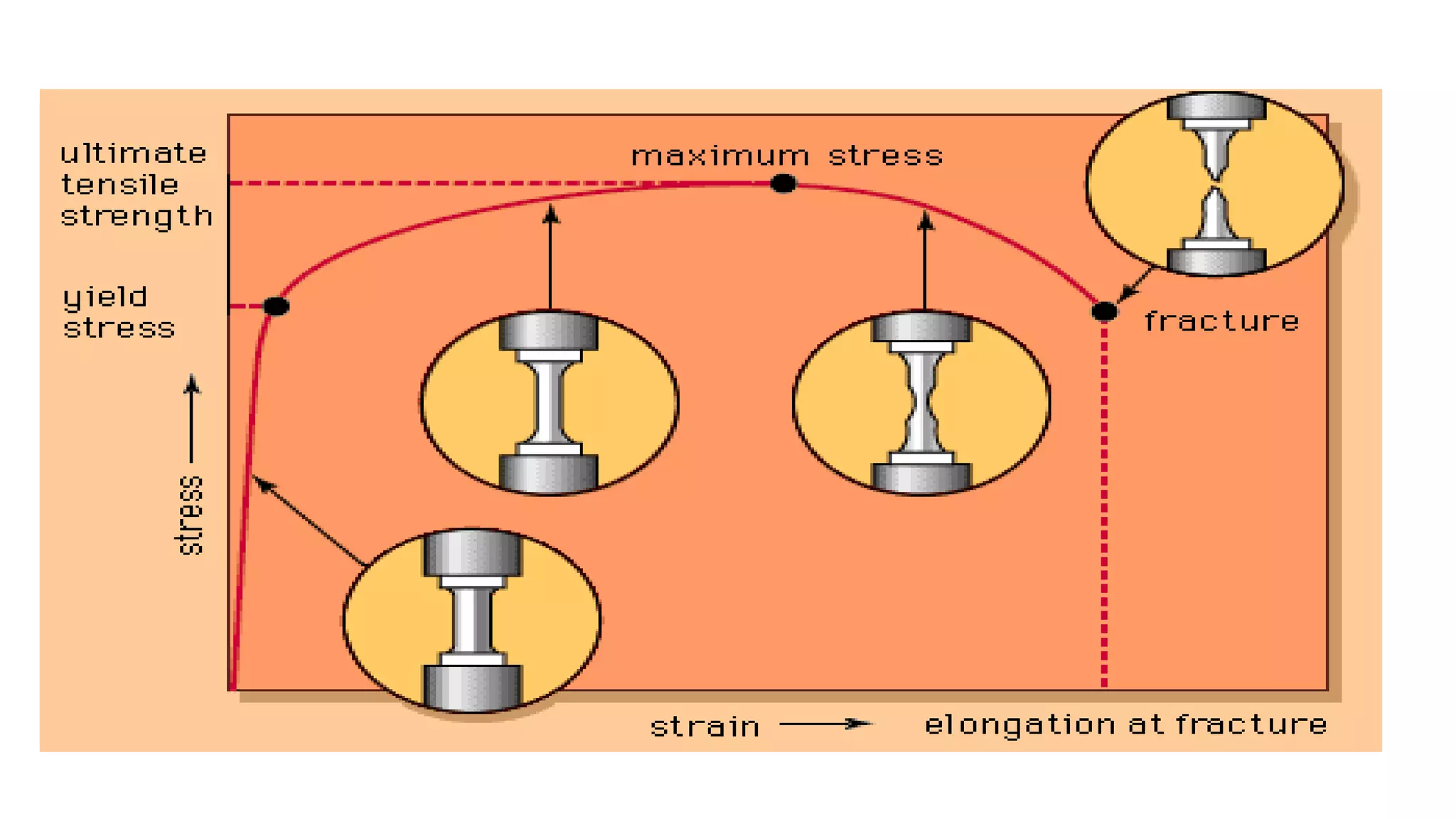
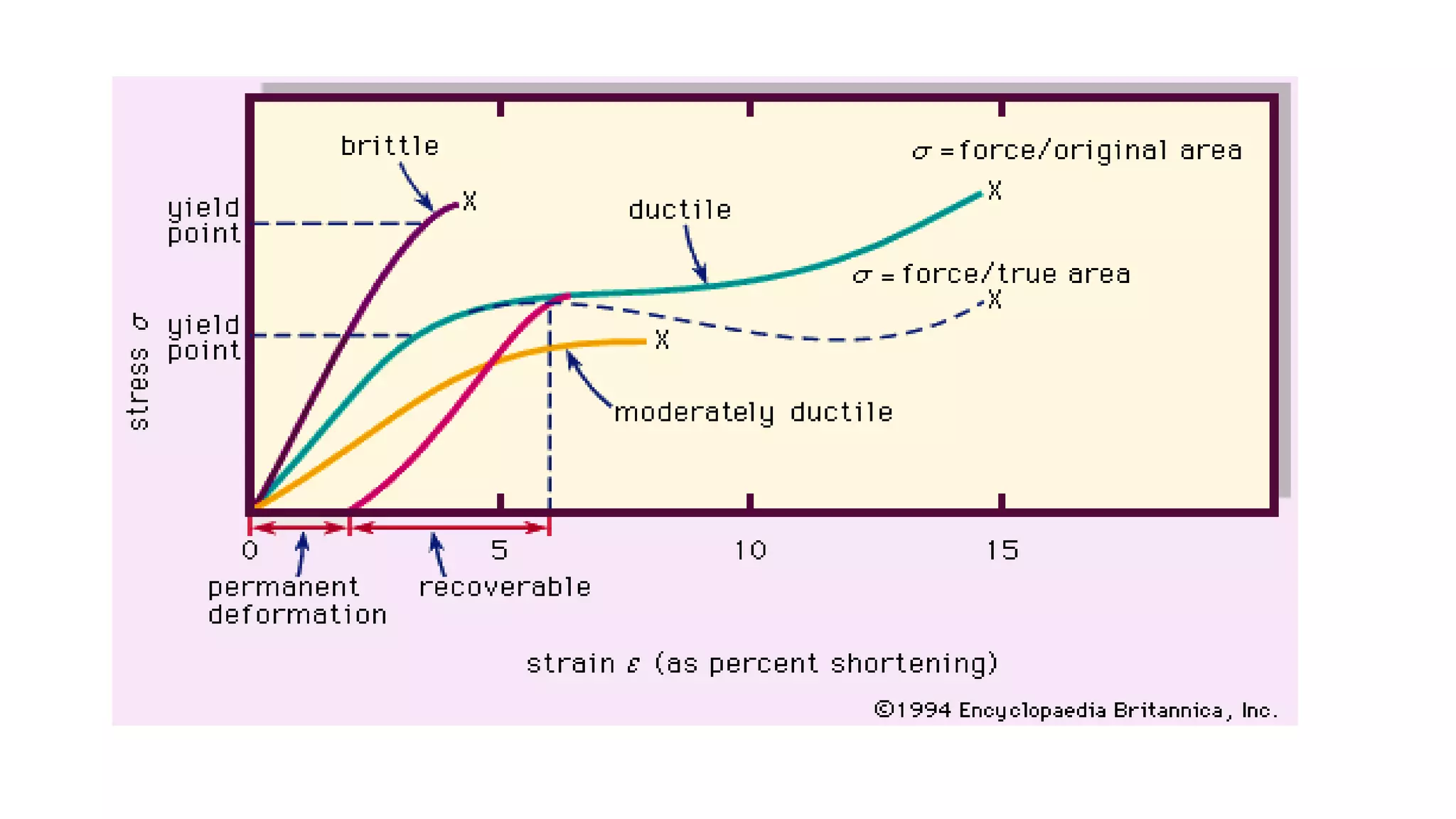
- Stress is defined as the internal resisting force per unit area when an external force is applied. Strain is the change in length per original length when a body experiences a force.
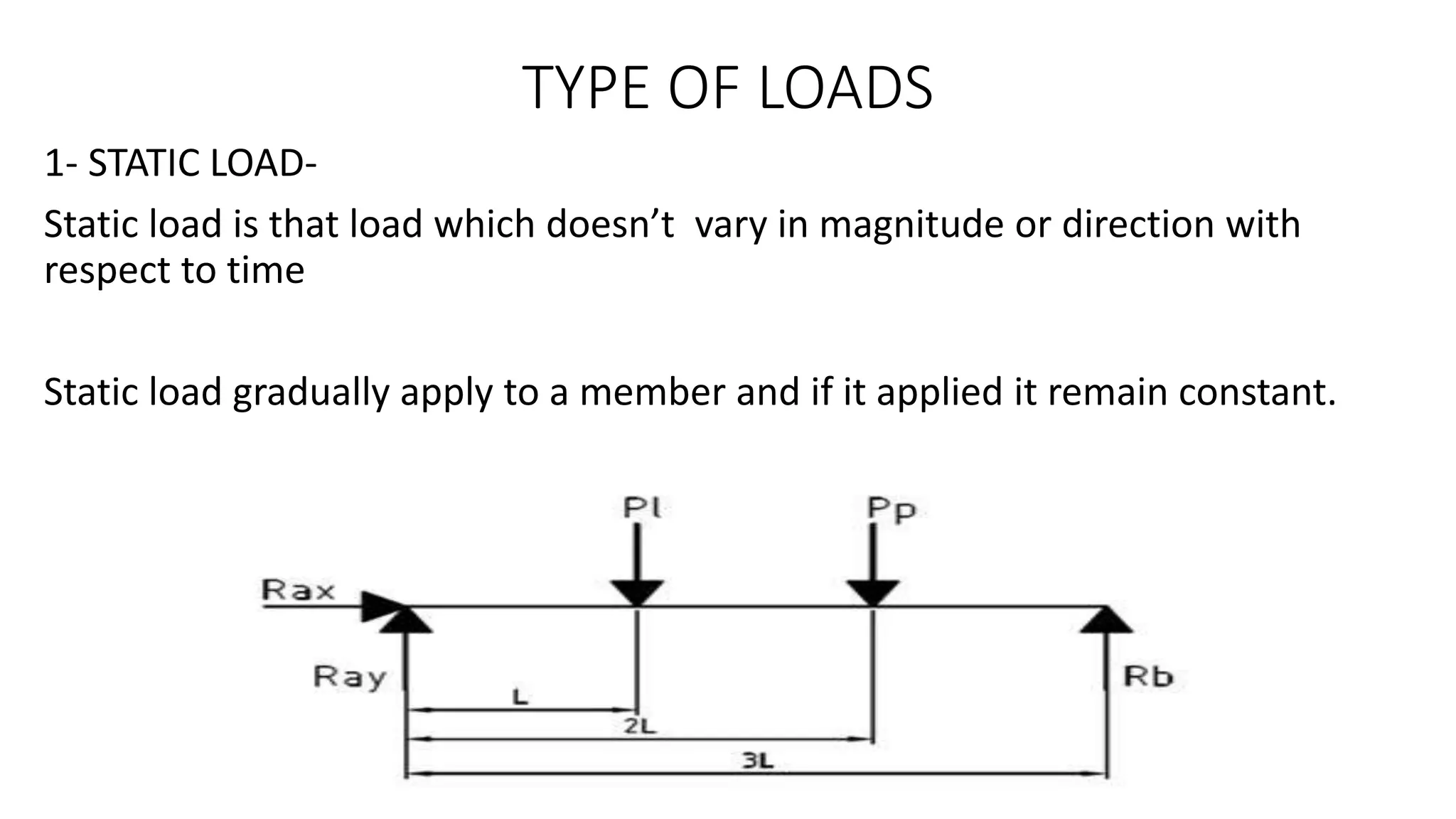
- There are two types of loads: static loads which do not vary over time, and dynamic loads where magnitude and direction vary over time, including cyclic and impact loads.
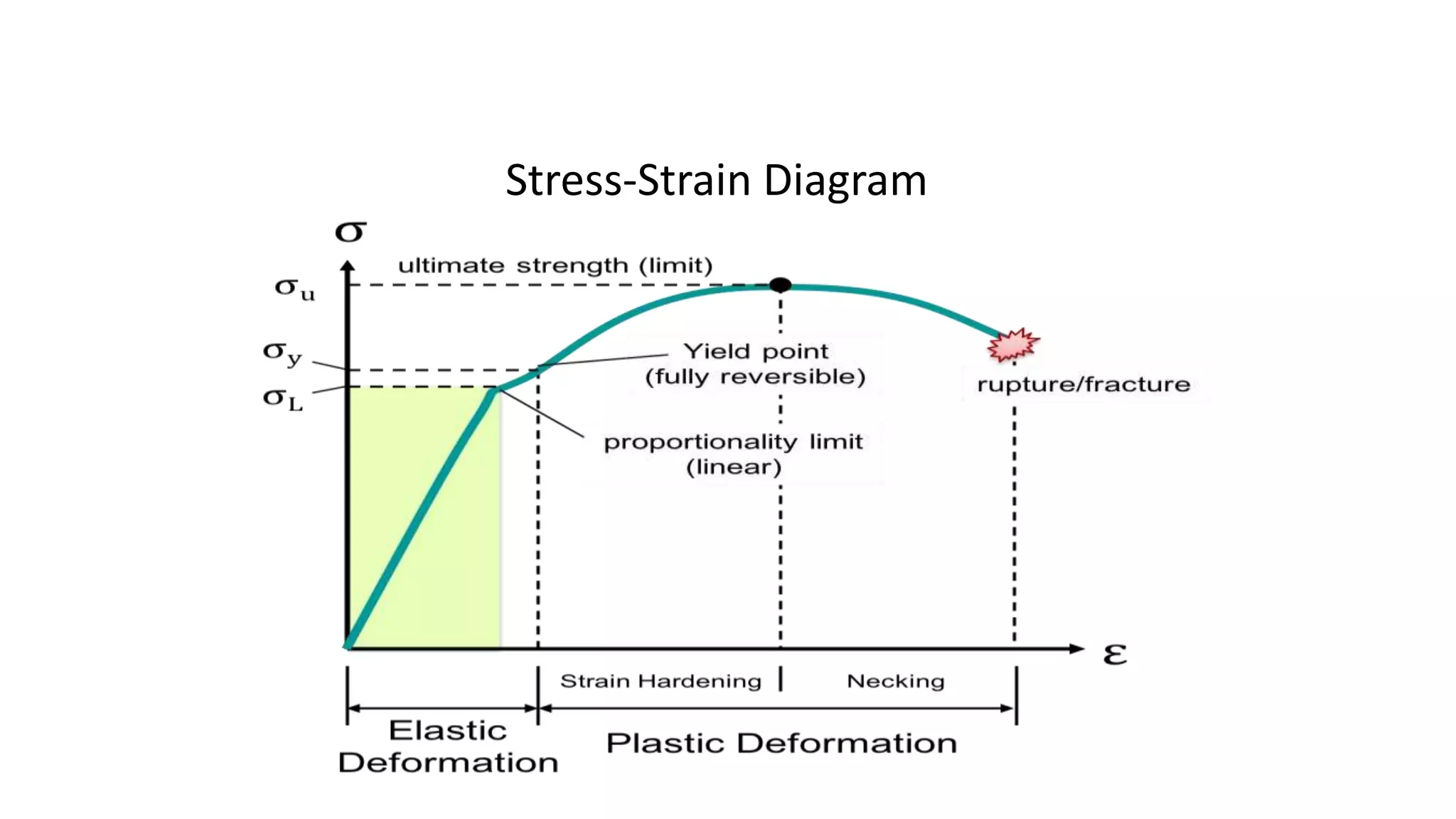
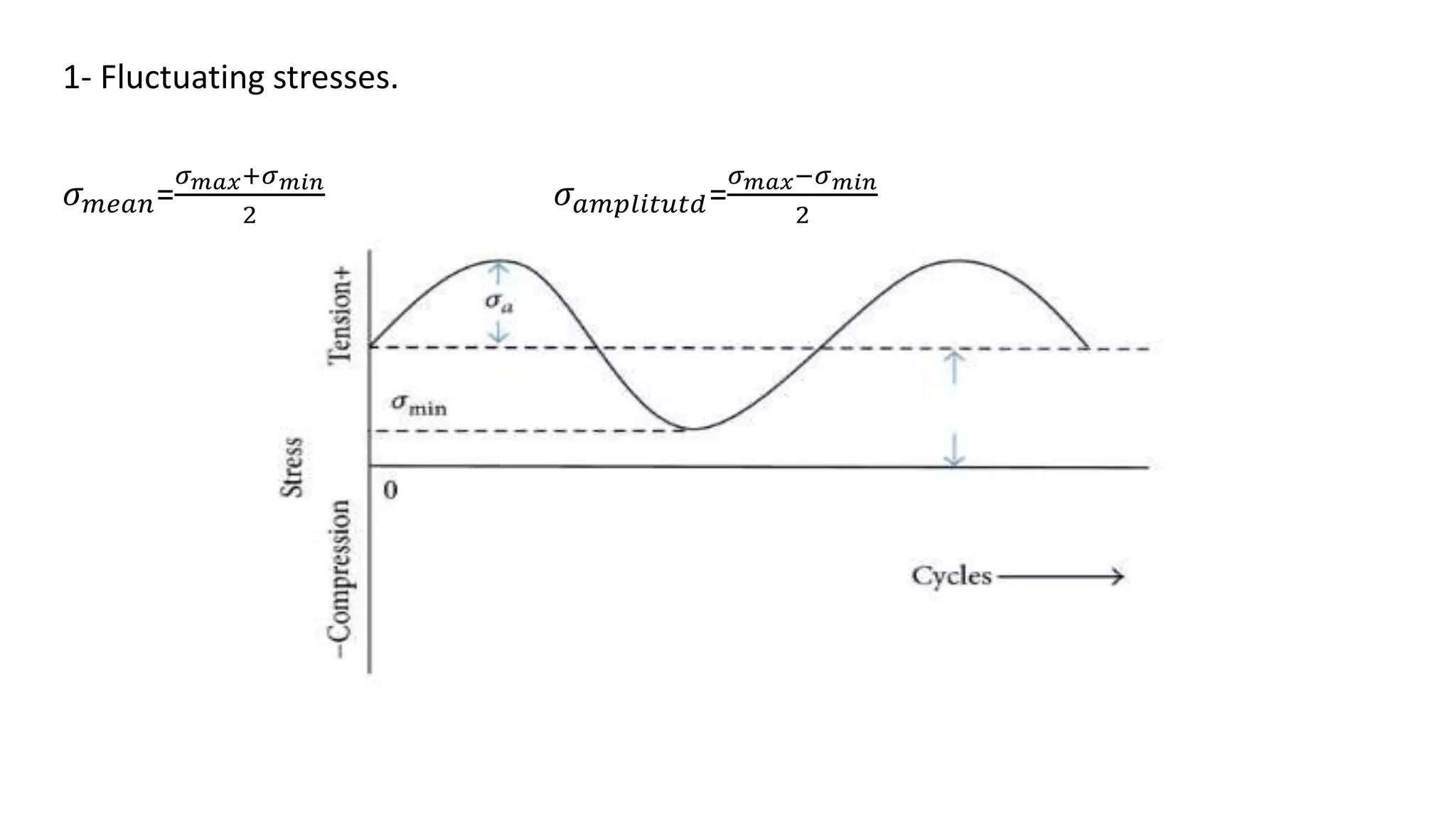
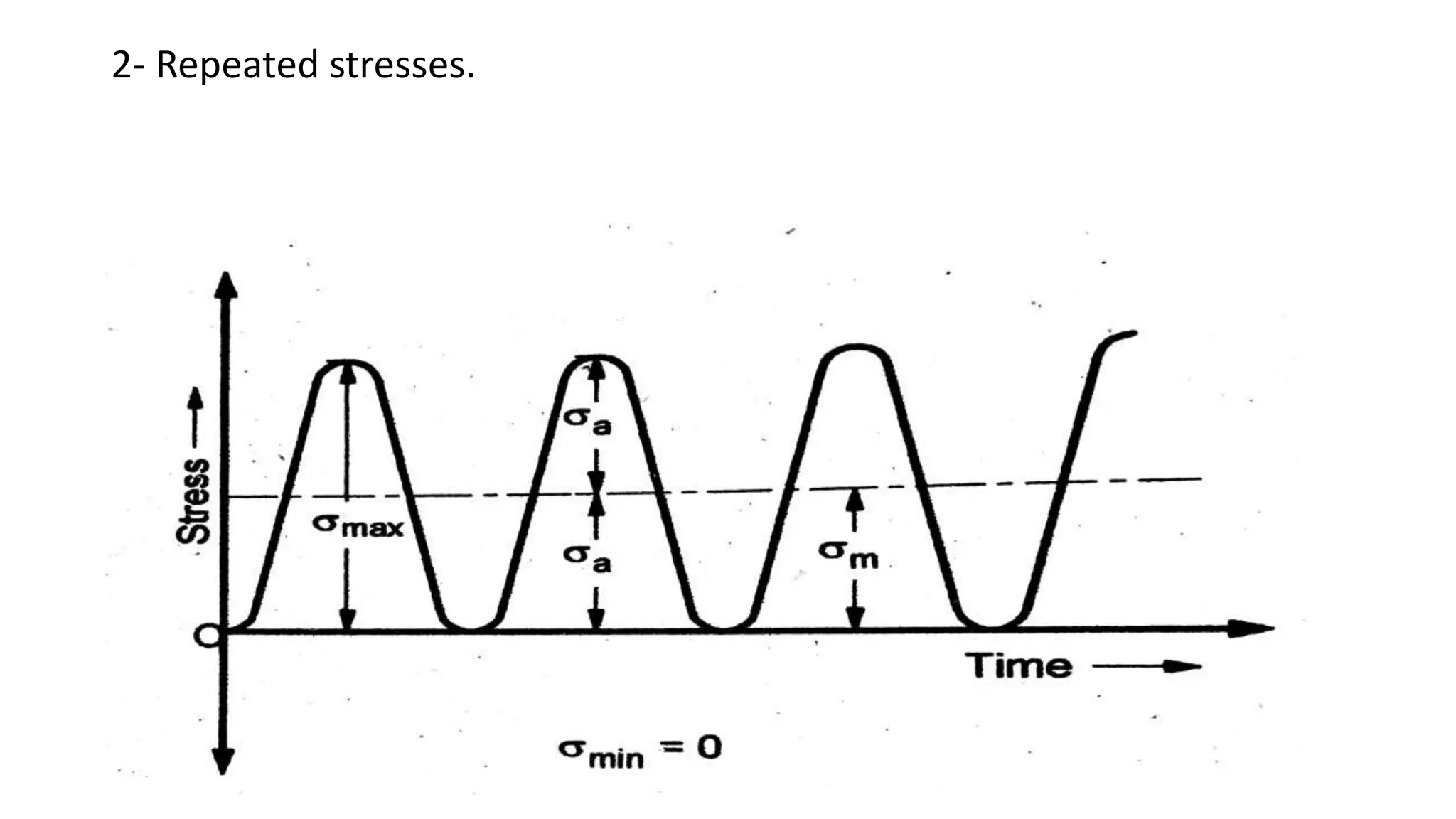
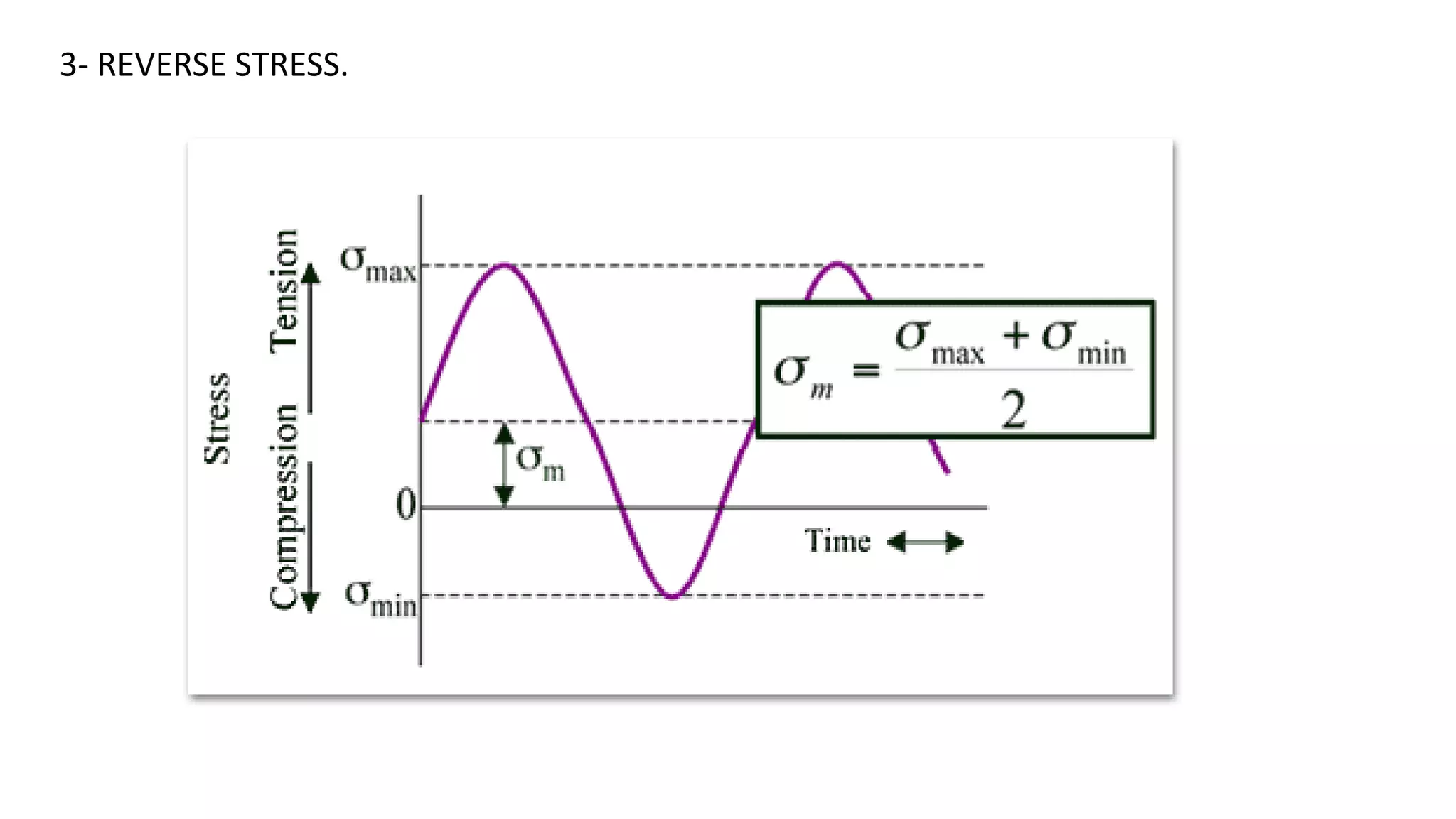
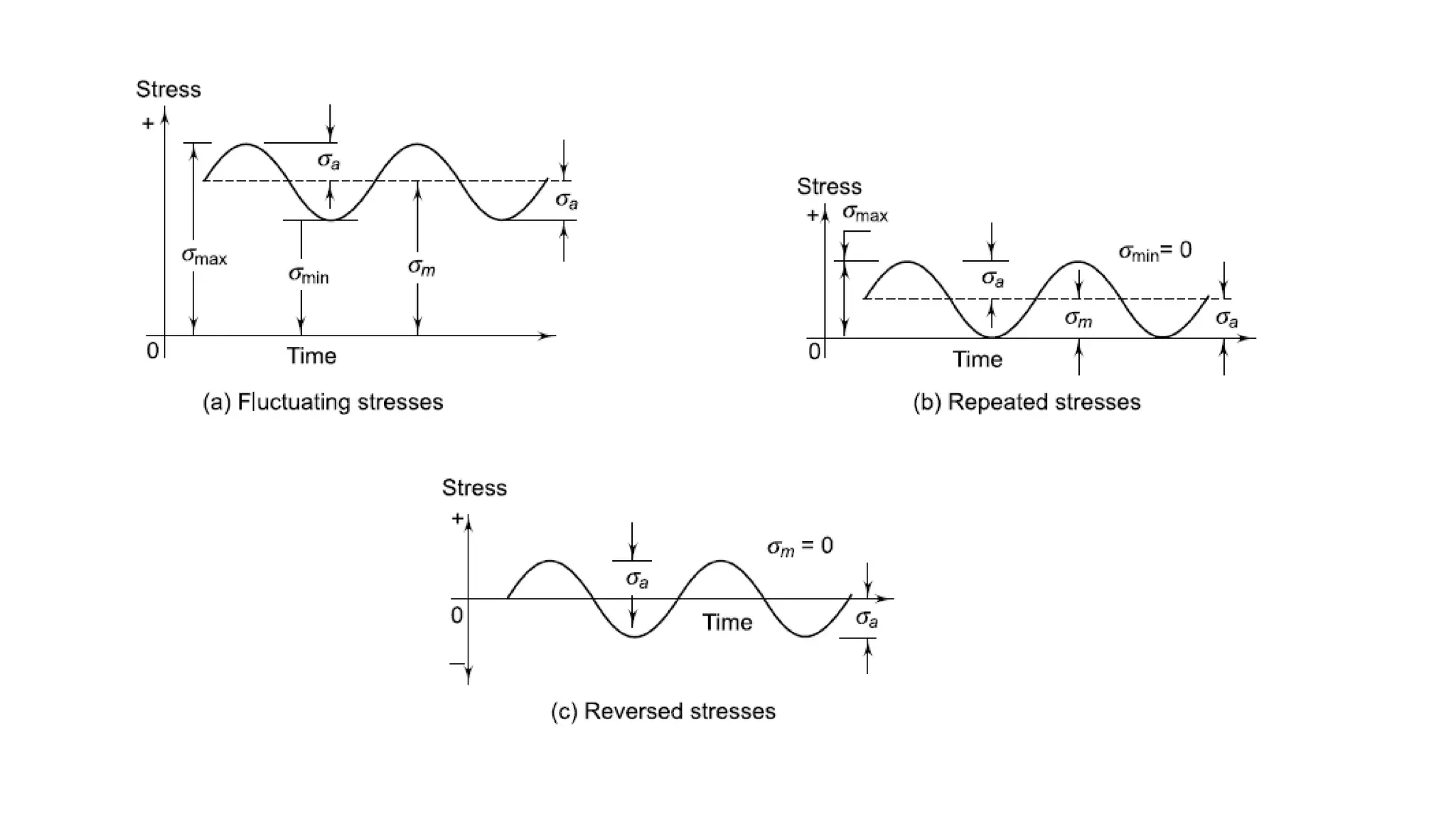
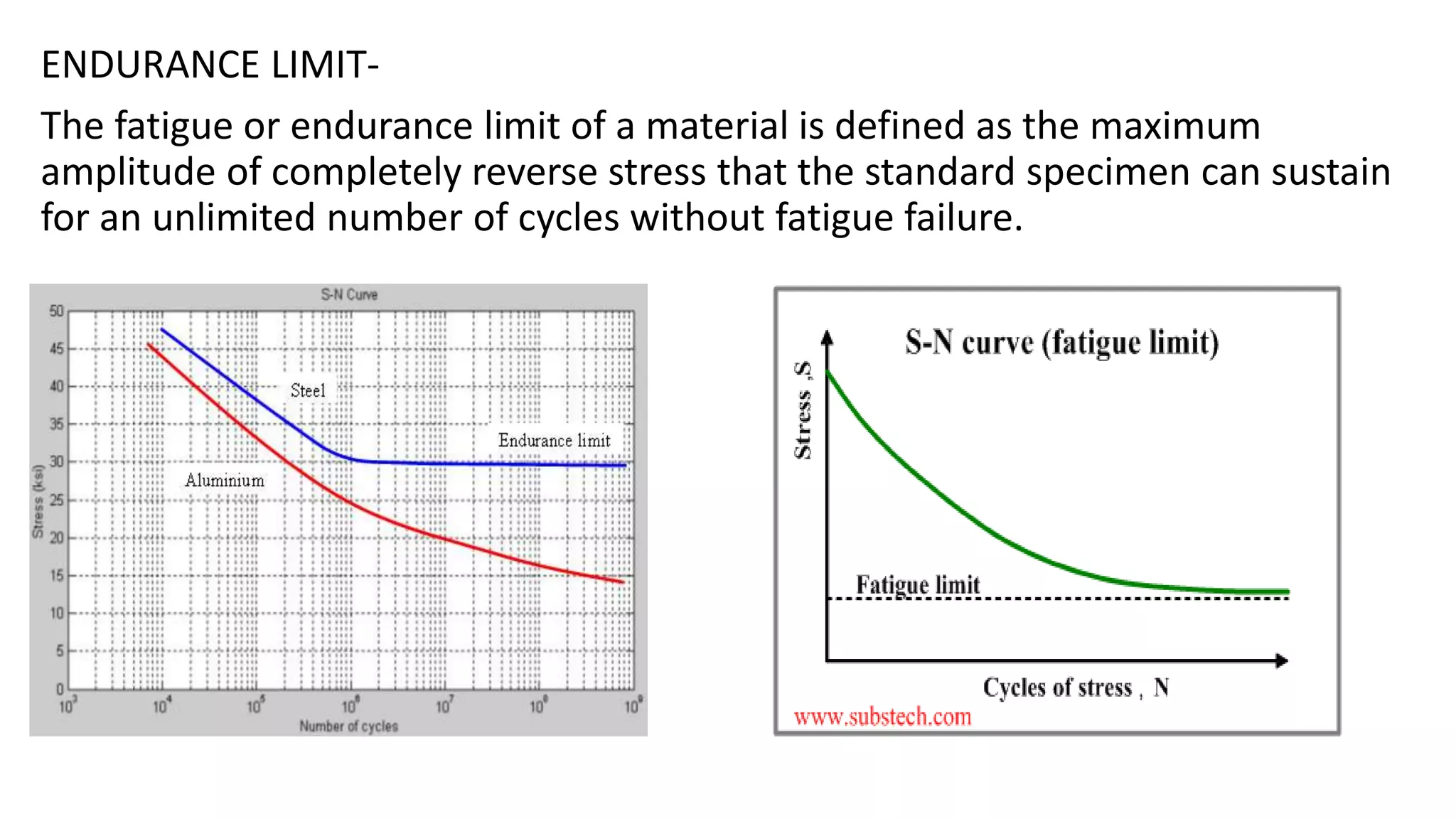
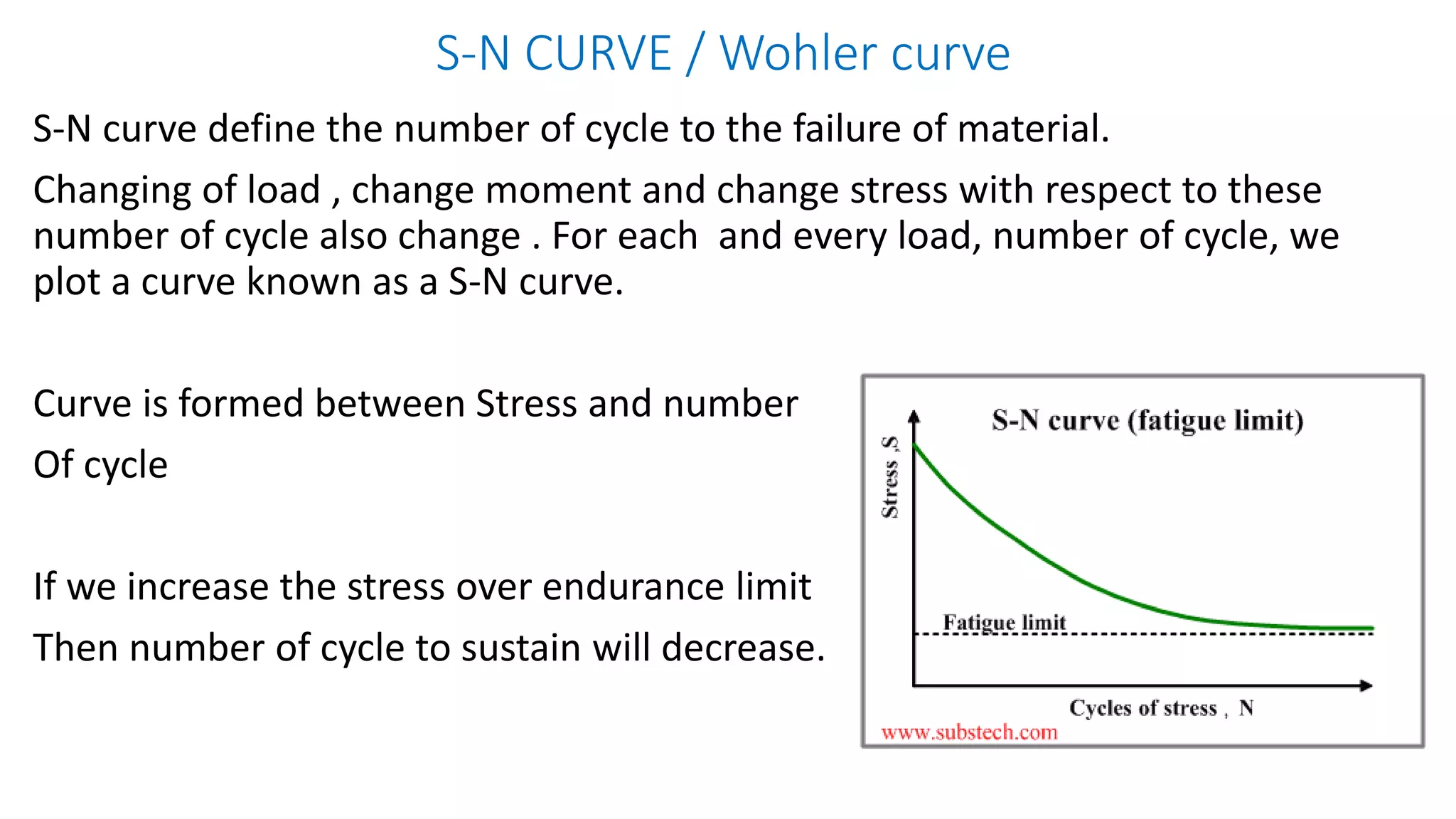
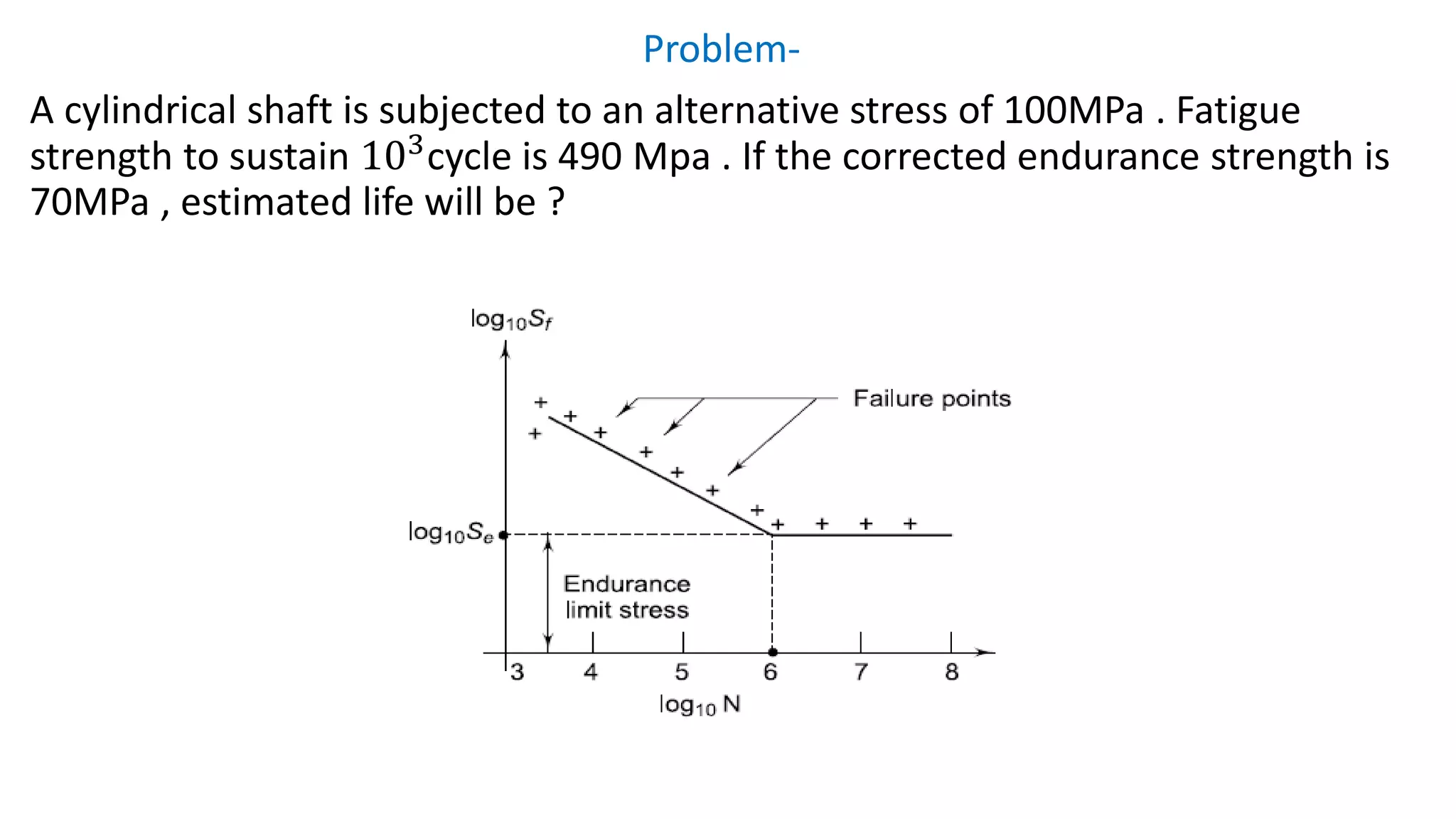
- Fatigue failure can occur when components fail under cyclic stress levels below the ultimate tensile strength due to repeated loading. The endurance limit is the maximum stress amplitude a material can withstand without failing.
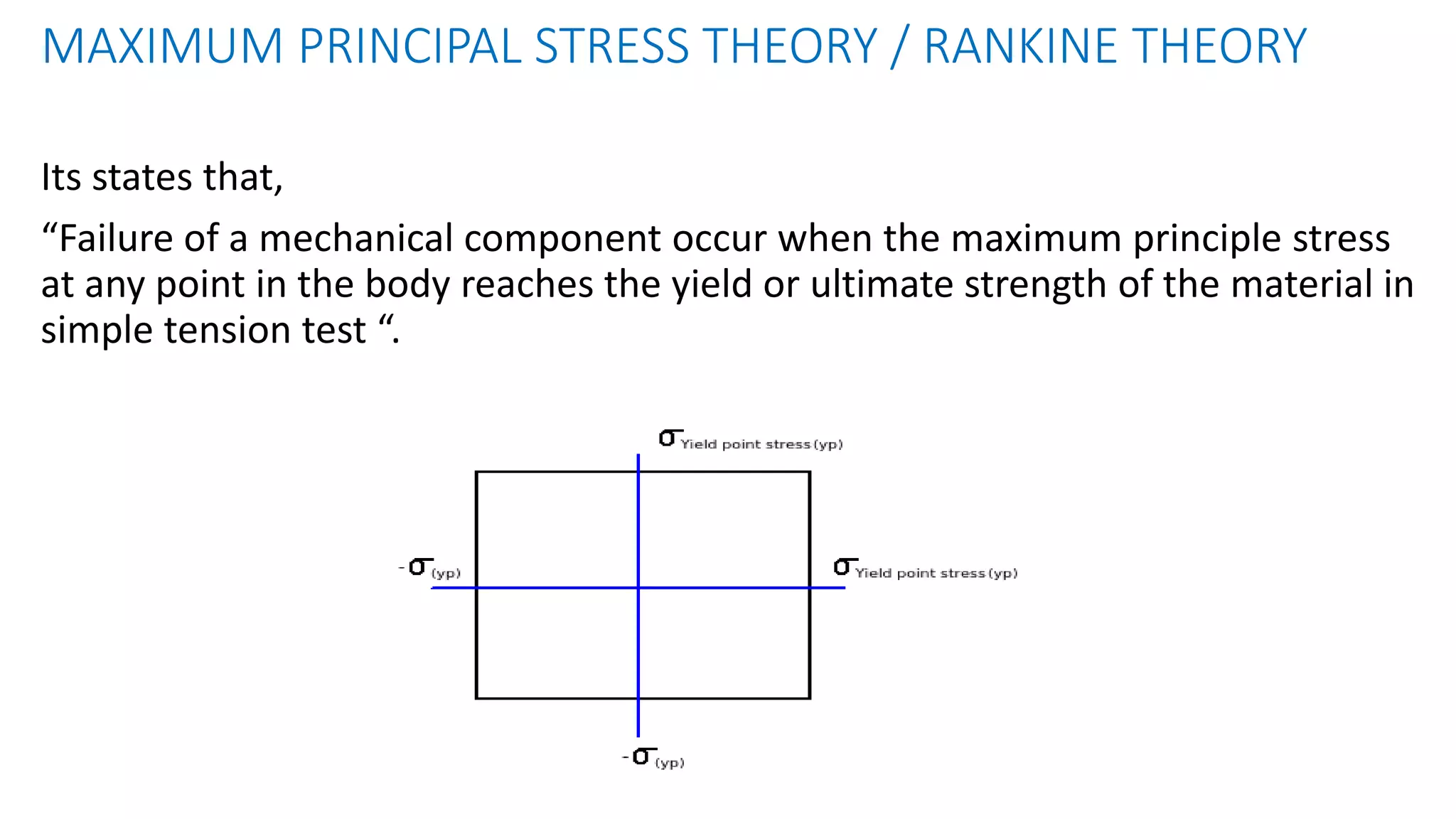
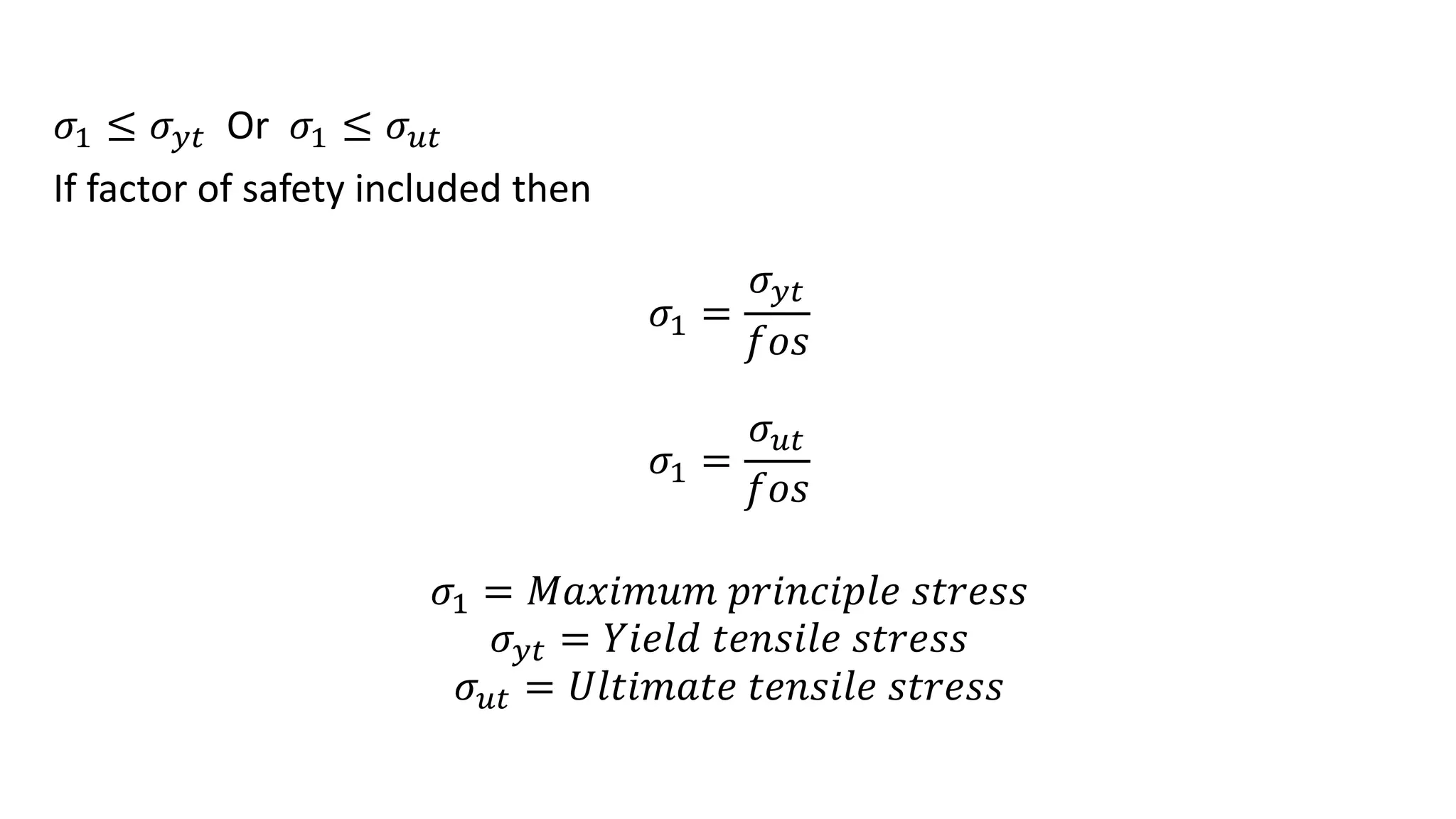
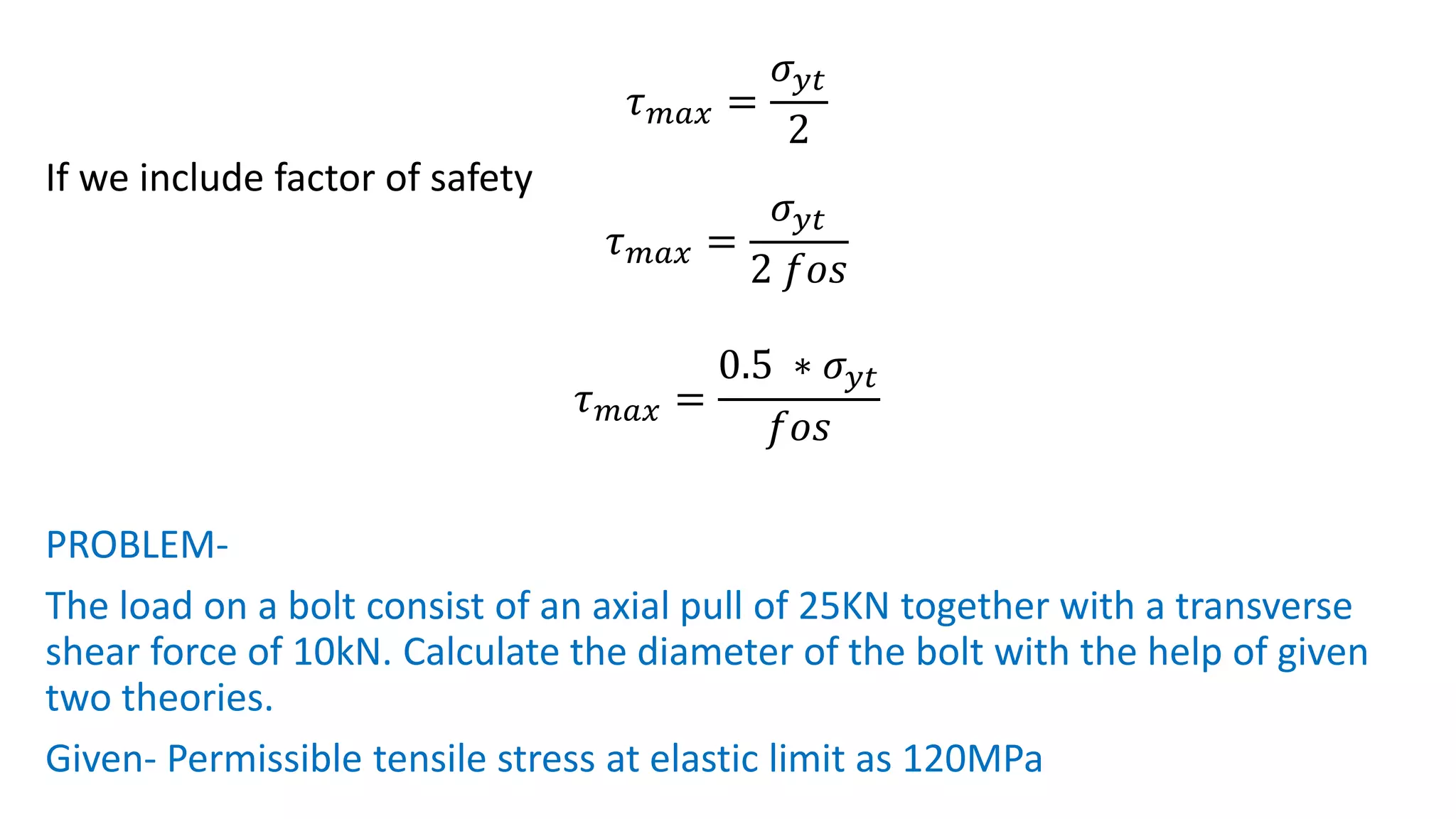
- Failure theories like maximum principal stress and maximum shear stress theories define when failure