This document discusses stress-strain curves and various material testing methods. It contains the following key points:
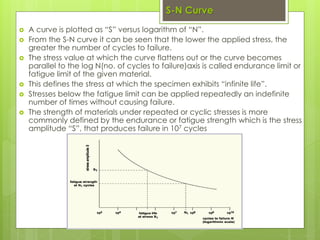
1. Creep testing involves applying a constant load to a material sample at high temperature and measuring deformation over time to evaluate materials performance. Fatigue testing subjects samples to repeated stresses to determine fatigue strength.
2. Stress-strain curves relate the stress and strain experienced by materials. They contain useful data like proportional limit, elastic limit, yield point, ultimate strength, and ductile vs. brittle fracture behavior.
3. True stress-strain diagrams account for changes in cross-sectional area during testing, while engineering stress-strain curves do not. Both are commonly used in design as long as strains remain