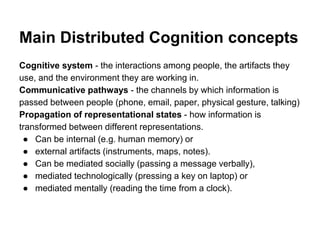
Distributed cognition is an approach that views cognition as extending beyond individuals to include interactions between people and tools or objects in their environment. It recognizes that cognitive processes involve interactions between internal and external representations. Analyzing a distributed cognitive system involves examining how information is propagated through communicative pathways between internal human representations and external artifacts. The DiCoT framework provides dimensions for analyzing physical layout, information flow, and artifacts to understand how a distributed system supports its goals.
![[M3]
modern theories
distributed cognition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m3lectureslides-141030025403-conversion-gate02/75/IFI7159-M3-1-2048.jpg)