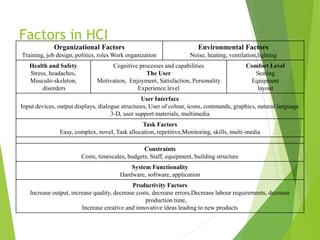
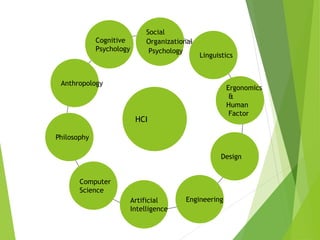
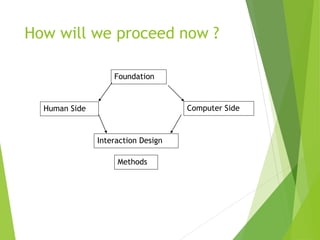
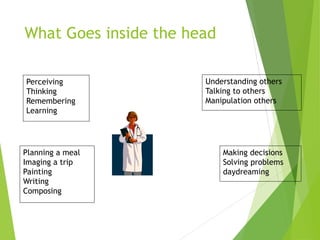
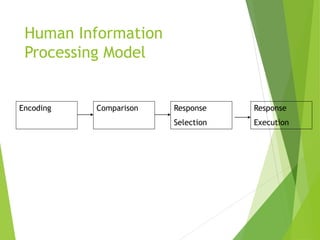
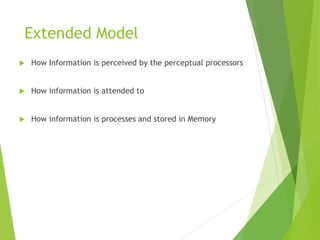
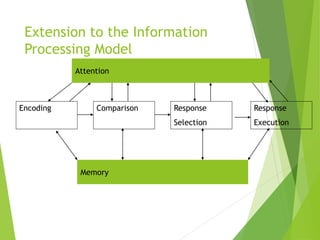
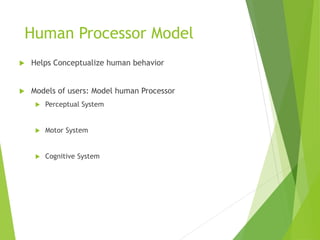
This document discusses frameworks for understanding human cognition and its relationship to human-computer interaction. It describes cognitive psychology and defines cognition as processes like understanding, remembering, reasoning and problem solving. It also discusses several models of human information processing, including how information is encoded, compared to memory, and a response is selected and executed. The document outlines some limitations of only using cognitive frameworks and introduces distributed and external cognition frameworks that consider how cognition is distributed across individuals, tools and environments.