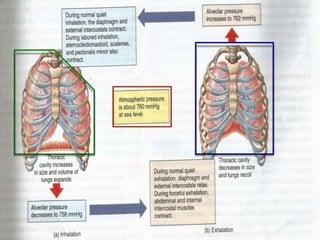
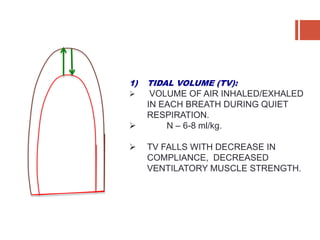
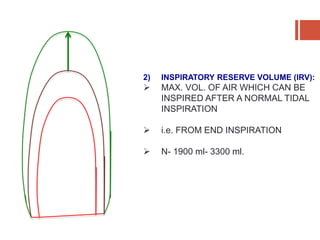
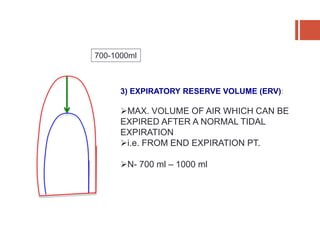
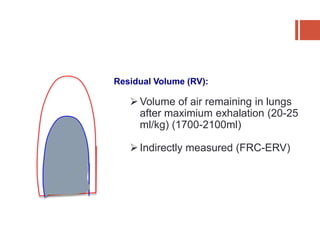
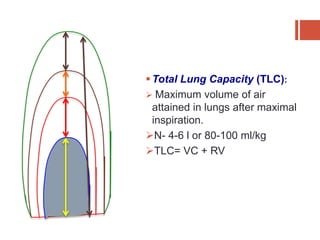
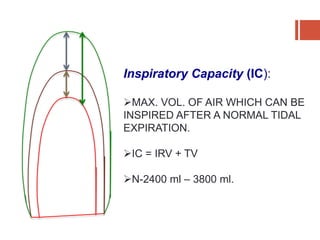
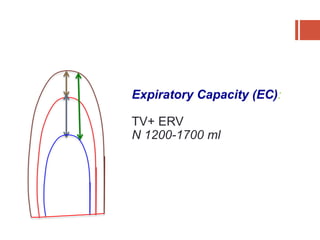
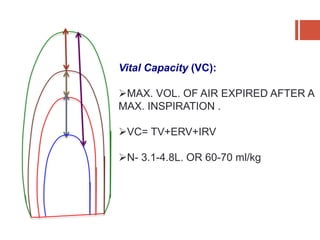
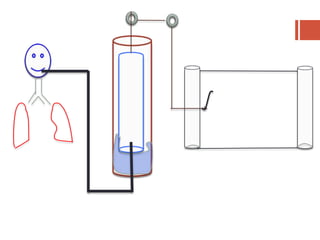
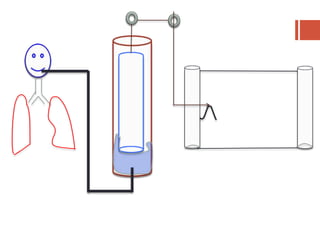
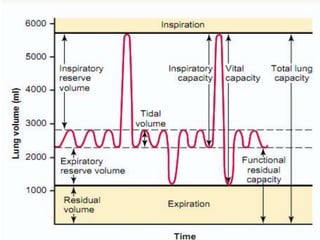
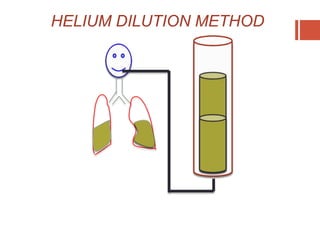
This document discusses lung volumes and capacities as measured through spirometry and bedside pulmonary function tests. It defines key lung volumes like tidal volume and residual volume. Lung capacities such as functional residual capacity and total lung capacity are combinations of volumes. Common bedside tests are described including the Sabrasez breath holding test, single breath count, modified match test, cough test, and Debono whistle test. Forced expiratory time is also discussed. Spirometry directly measures volumes while capacities are indirectly inferred.