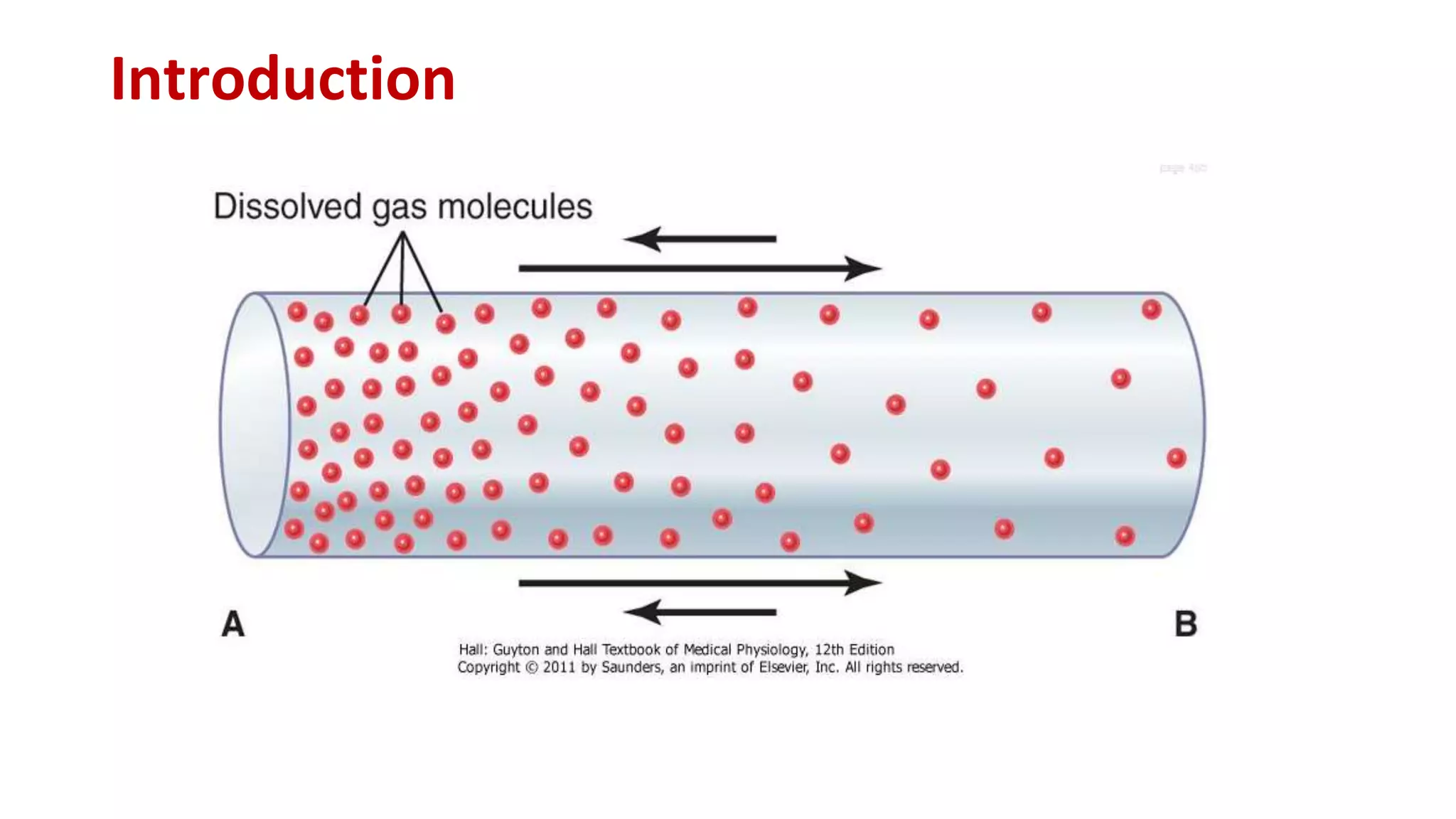
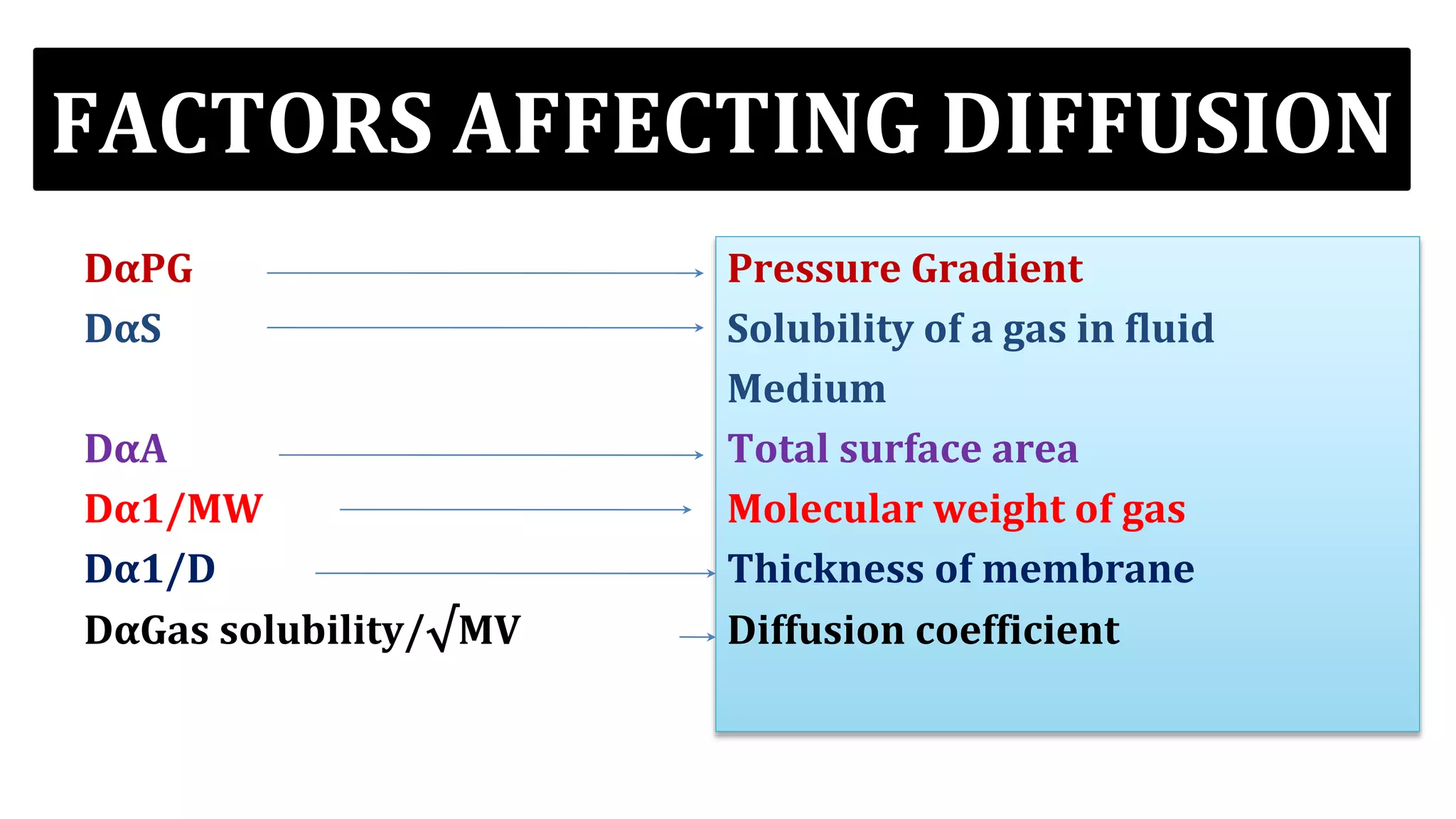
This document discusses gas exchange in the lungs, specifically the diffusion of gases. It covers three main factors that gas exchange depends on: the alveolar-capillary membrane, the partial pressure gradient, and pulmonary capillary blood flow. Several factors can affect the diffusion of gases across the alveolar-capillary membrane including differences in partial pressures, surface area, thickness, and solubility of the gas. The partial pressure gradient provides the driving force for diffusion. Various laws like Henry's Law and Fick's Law govern the diffusion process. Capillary blood flow and its measurement also influence gas exchange rates in the lungs.