1. Lung abscess is a bacterial infection in the lung tissue that causes pus to collect in dead tissue. It is challenging to treat and can be life-threatening.
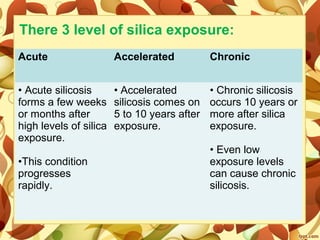
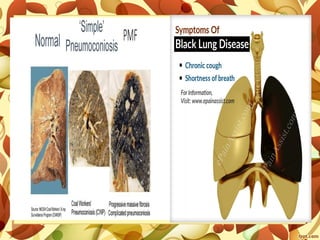
2. Occupational lung diseases result from inhaling dust or chemicals at work. Pneumoconiosis like silicosis and asbestosis are caused by inhaling mineral dust and cause scarring of lung tissue.
3. Other occupational lung diseases include hypersensitivity reactions like asthma from allergens at work, and byssinosis from cotton dust exposure without proper ventilation. Prevention focuses on protective equipment and measures to reduce exposure.