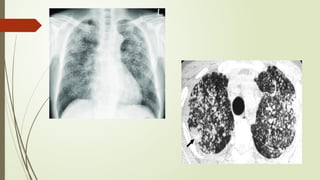
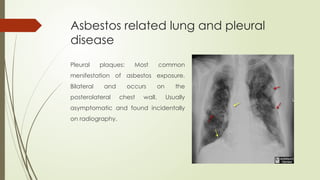
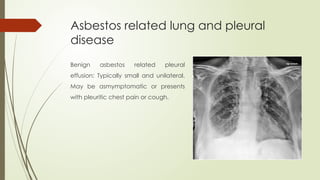
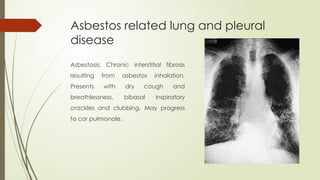
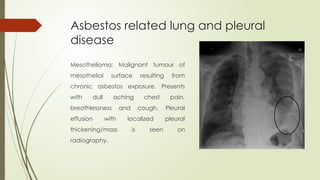
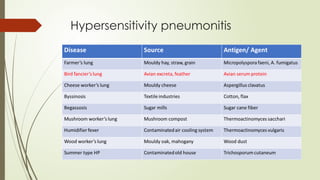
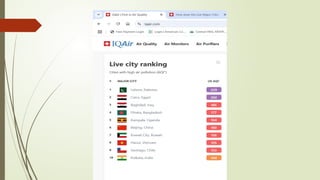
There are different health hazards related to occupation as well as environment. Occupational hazards are very much important to know in working place for maintaining self health and knowledge when to quit a job that are causing serious health issues. Environmental health is common issue for all of the public places and it is essential for a sustainable healthy society.