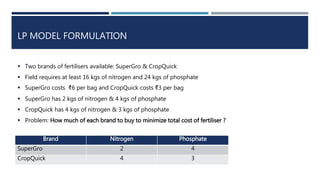
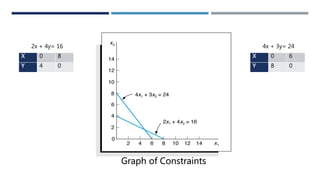
This document describes a linear programming problem (LPP) to minimize cost. The problem involves determining the optimal amounts of two fertilizer brands, SuperGro and CropQuick, to purchase to minimize total cost while meeting nitrogen and phosphate requirements. The LPP constructs decision variables for amounts of each brand, an objective function to minimize total cost, and constraints on nitrogen and phosphate levels. The optimal solution is to purchase 8 bags of CropQuick for a minimum total cost of 24.