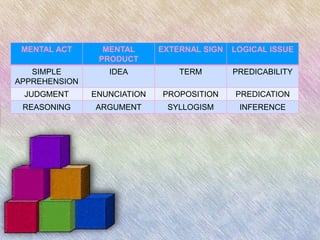
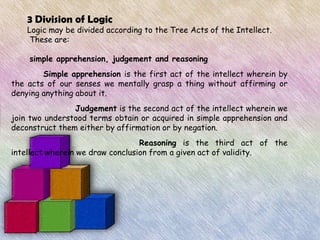
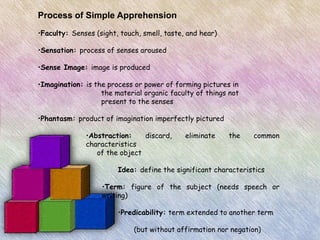
This document discusses different definitions and perspectives on philosophy. It defines philosophy etymologically as the love of wisdom and knowledge. It also examines philosophy as the study of fundamental problems regarding existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. The document further breaks down philosophy into practical fields like logic, ethics, and axiology, and speculative fields like epistemology, metaphysics, and political philosophy. It provides examples of how concepts are apprehended through the mental acts of simple apprehension, judgment, and reasoning.