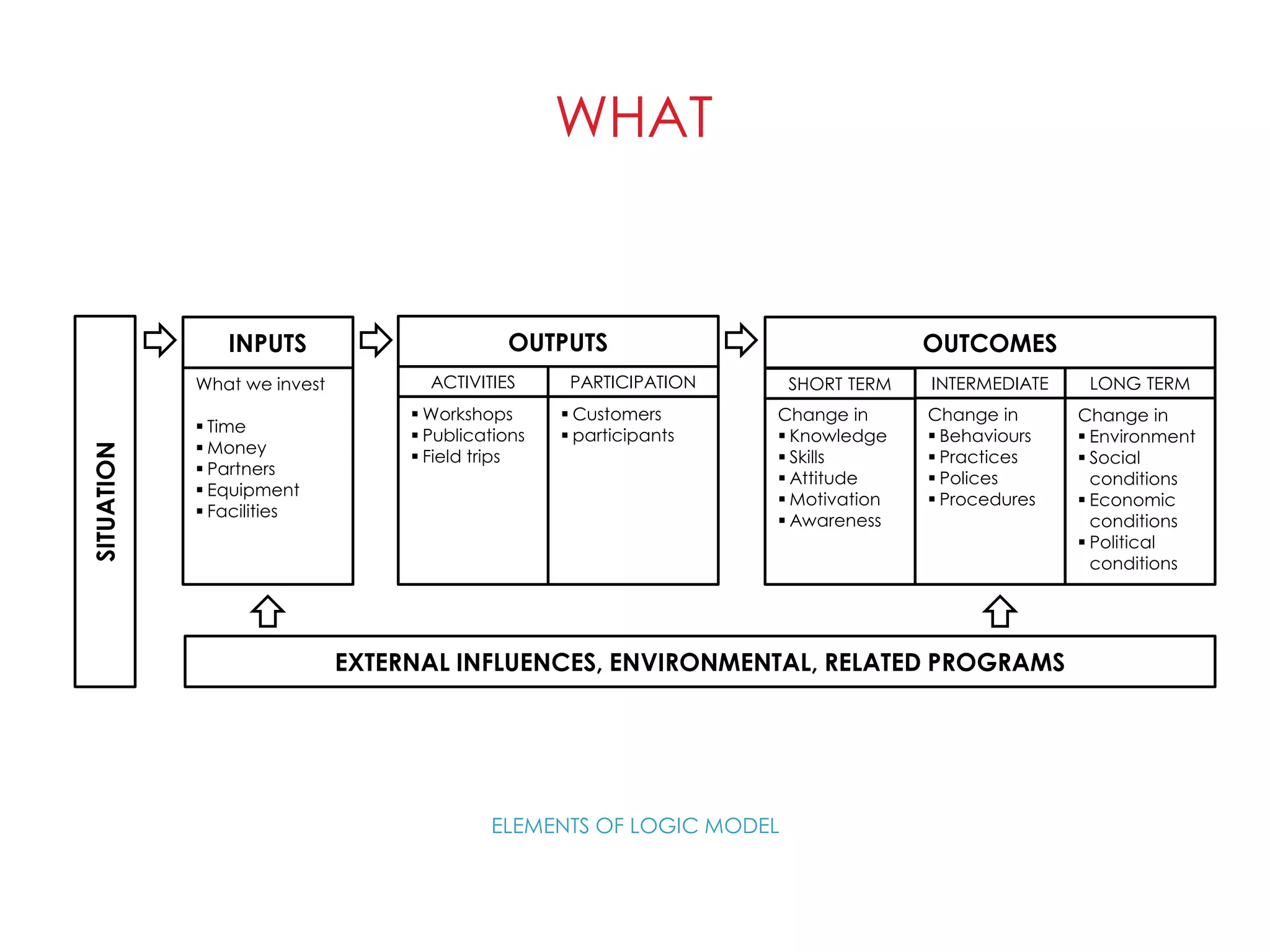
The document discusses logic models which depict programs and projects by showing what they will do and accomplish through a series of "if-then" relationships. Logic models focus accountability on important outcomes and provide a common language for stakeholders. They make assumptions explicit and promote communication. Building a logic model involves determining the current and desired situations, necessary behavior changes, required knowledge and skills, and needed activities and resources. Evaluation assesses implementation fidelity, participant reach and reactions, and intended and unintended outcome changes.