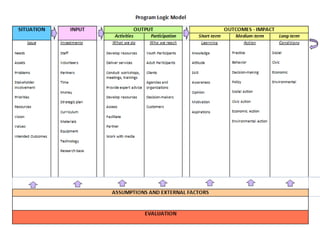
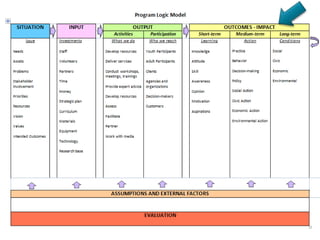
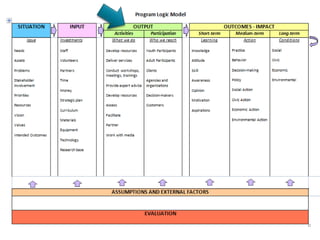
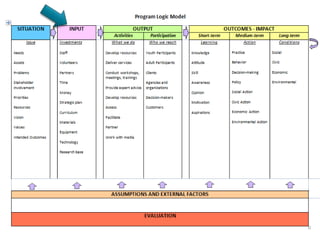
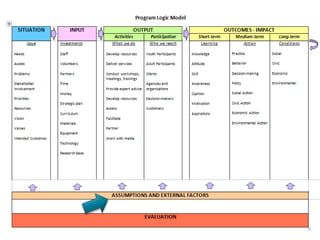
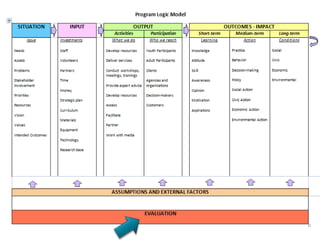
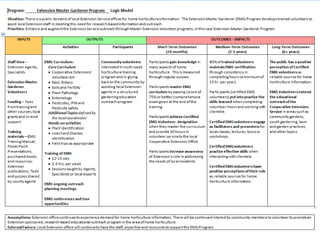
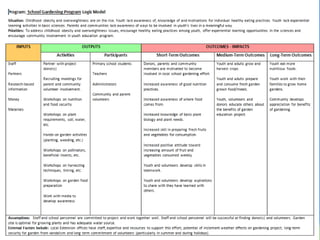
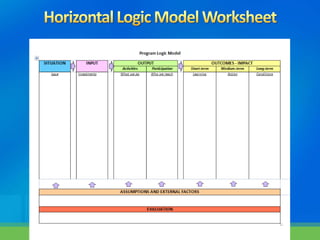
Rebecca White, Ph.D., discusses the creation of a program logic model for evaluating organization development and education programs. The document outlines the importance of identifying inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes, as well as assessing stakeholder needs and external factors. It emphasizes the need for a structured evaluation plan that connects actions to expected impacts on participants and the community.