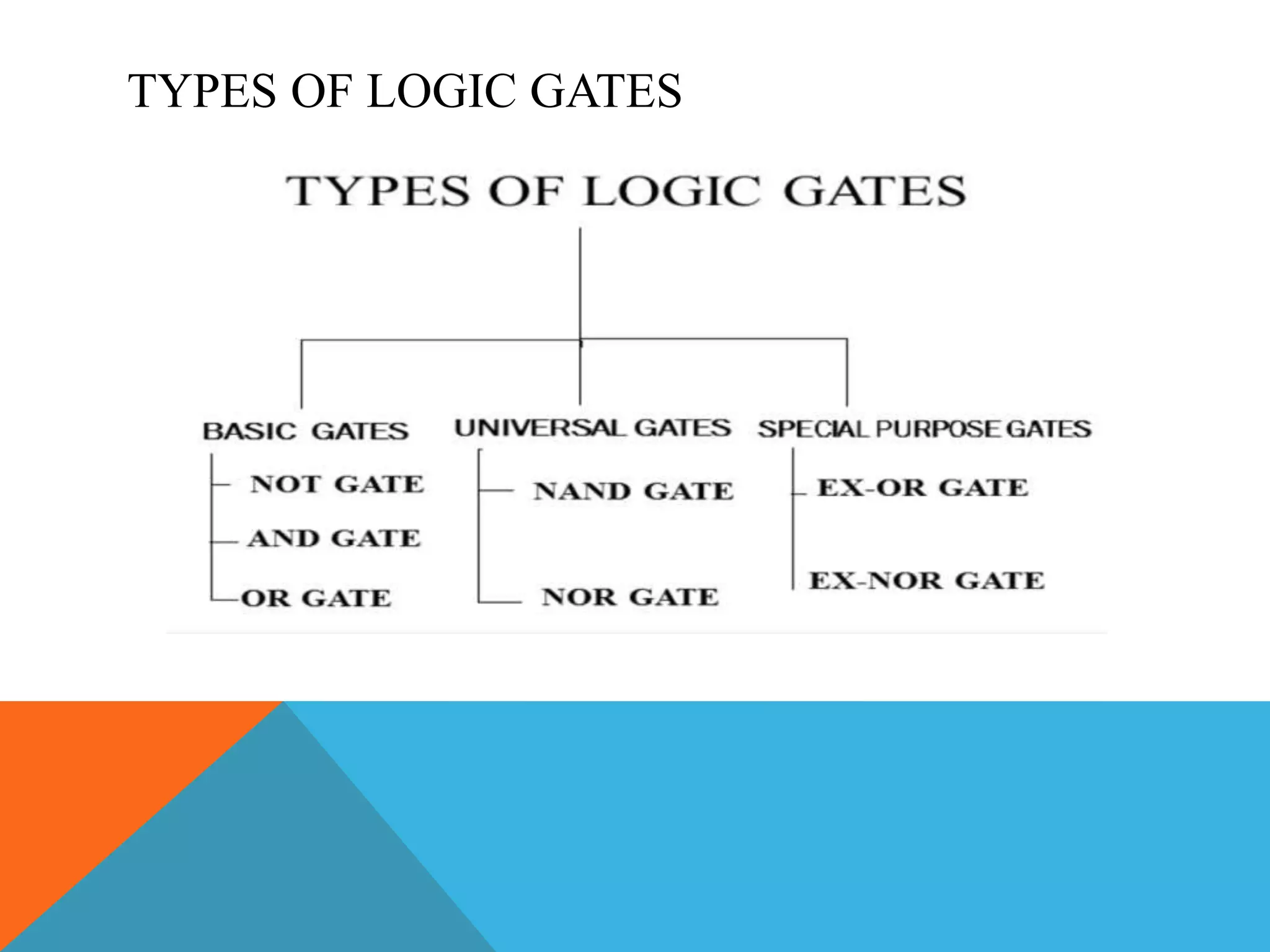
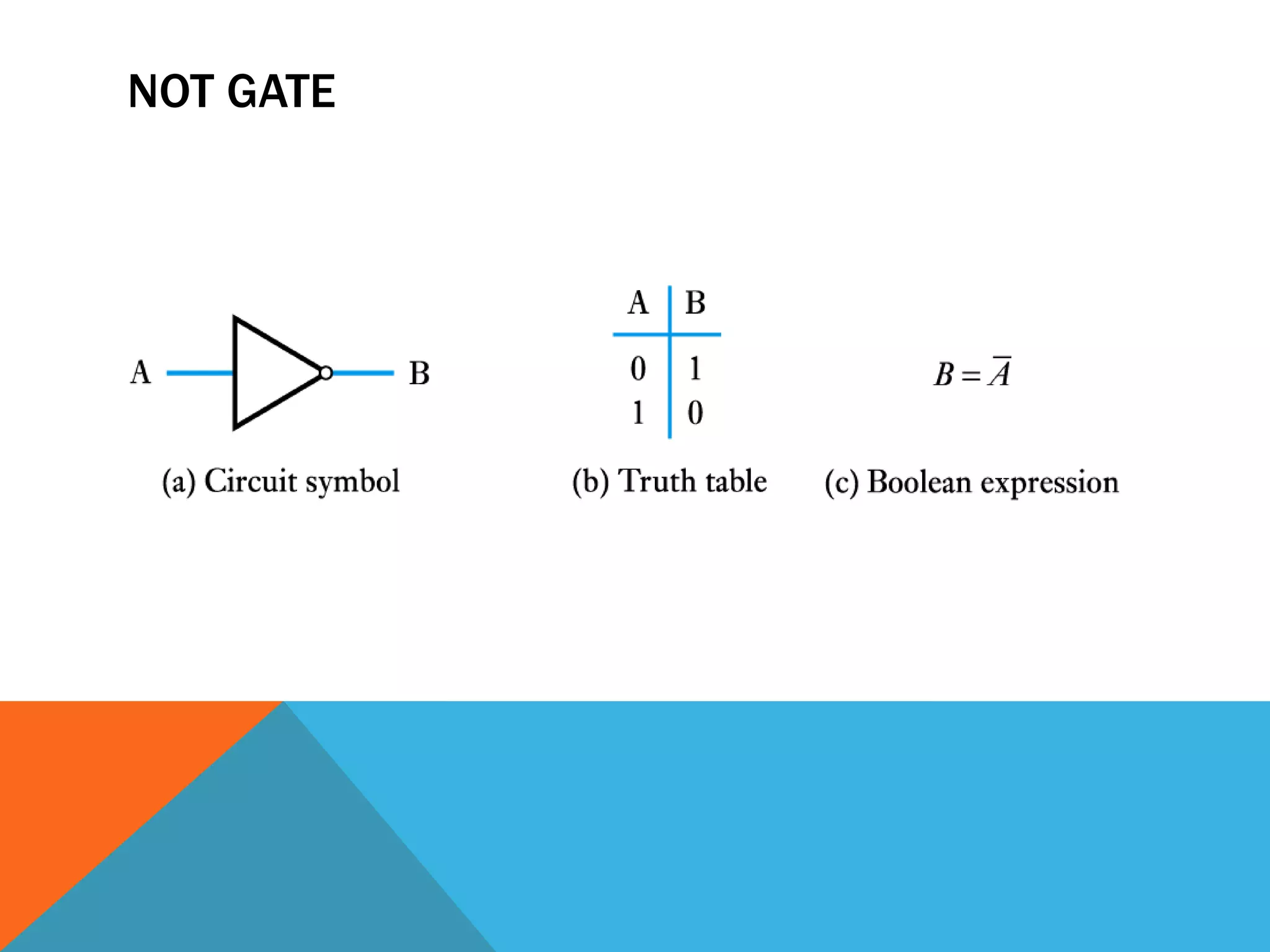
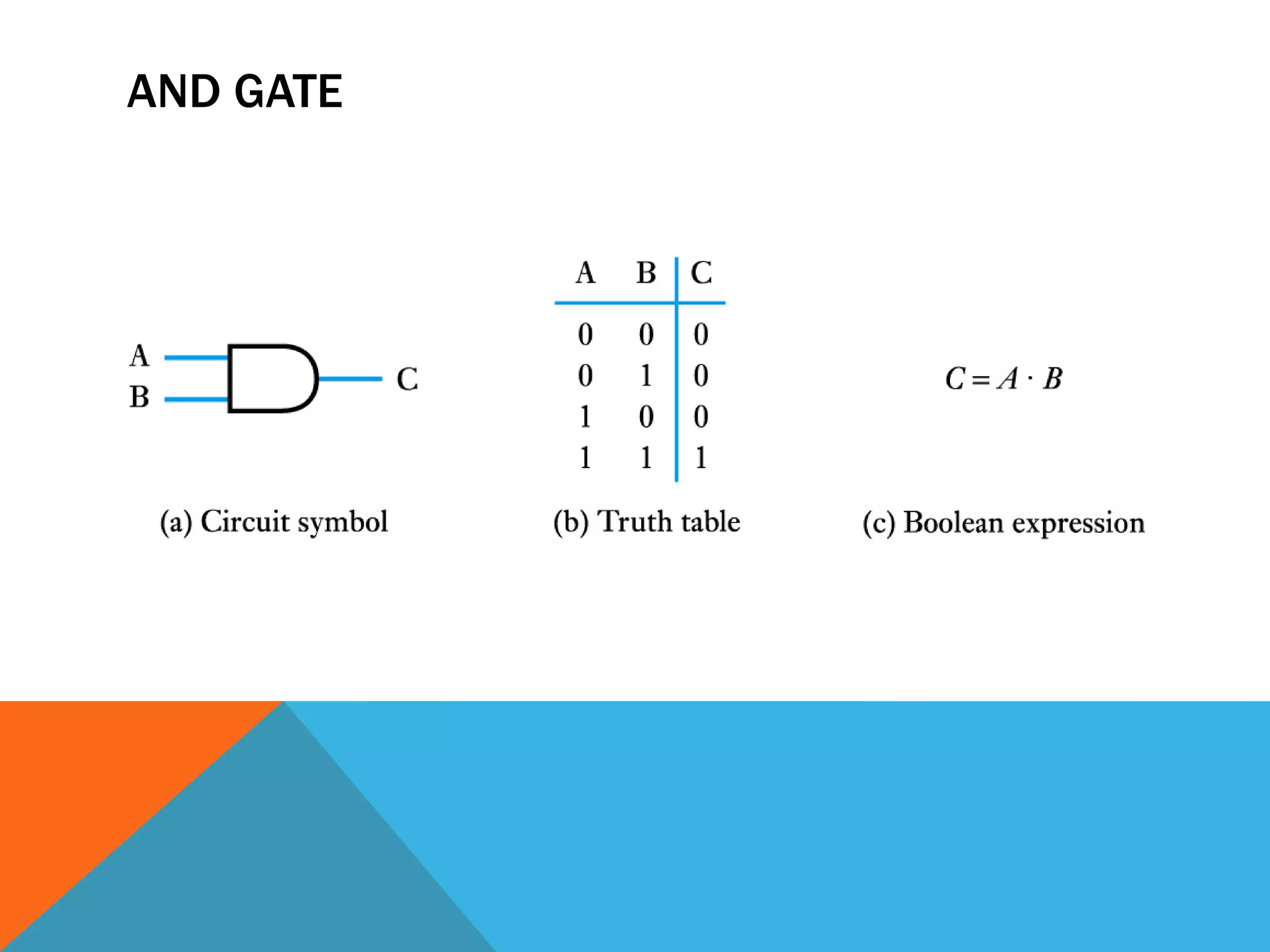
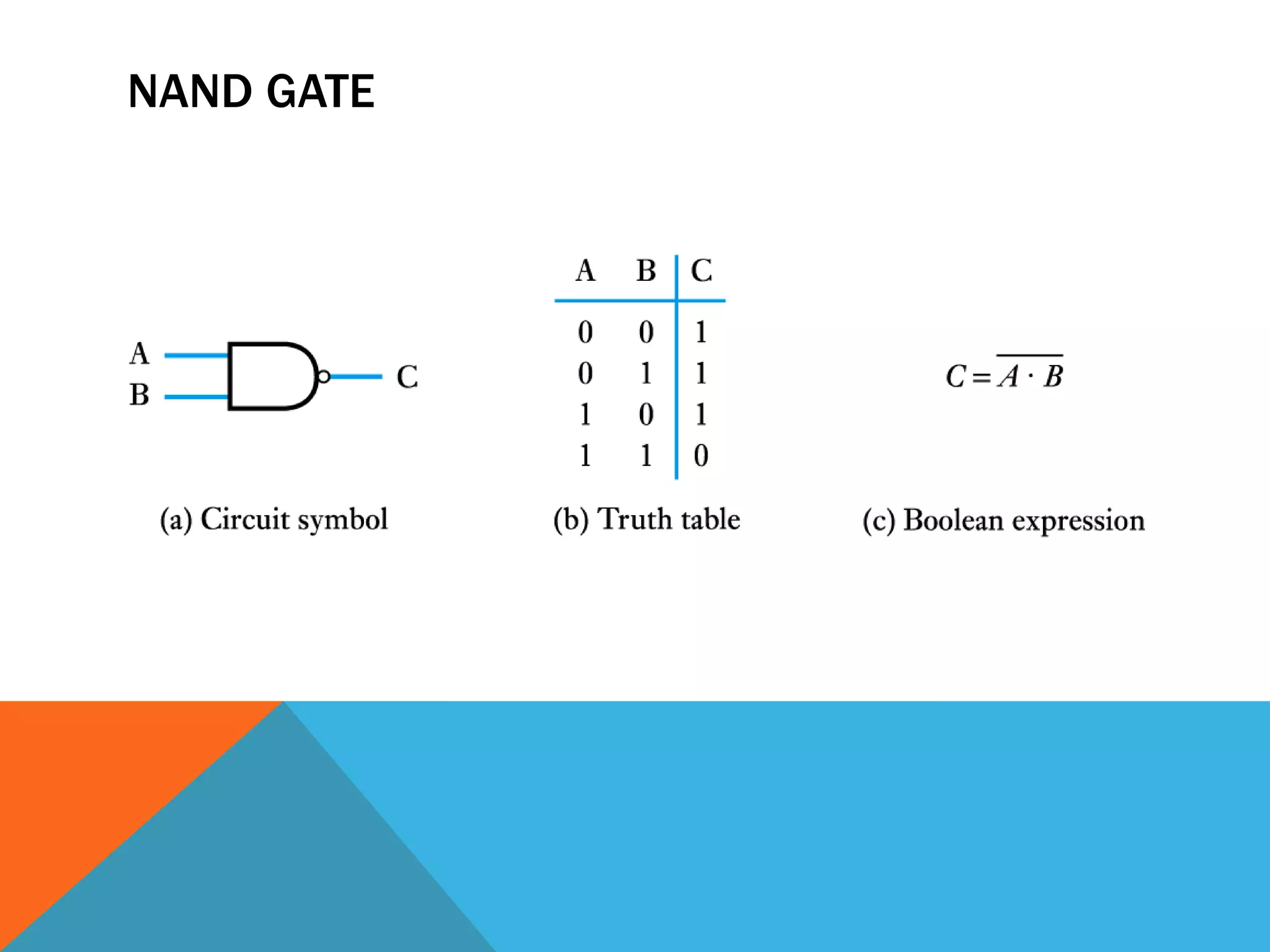
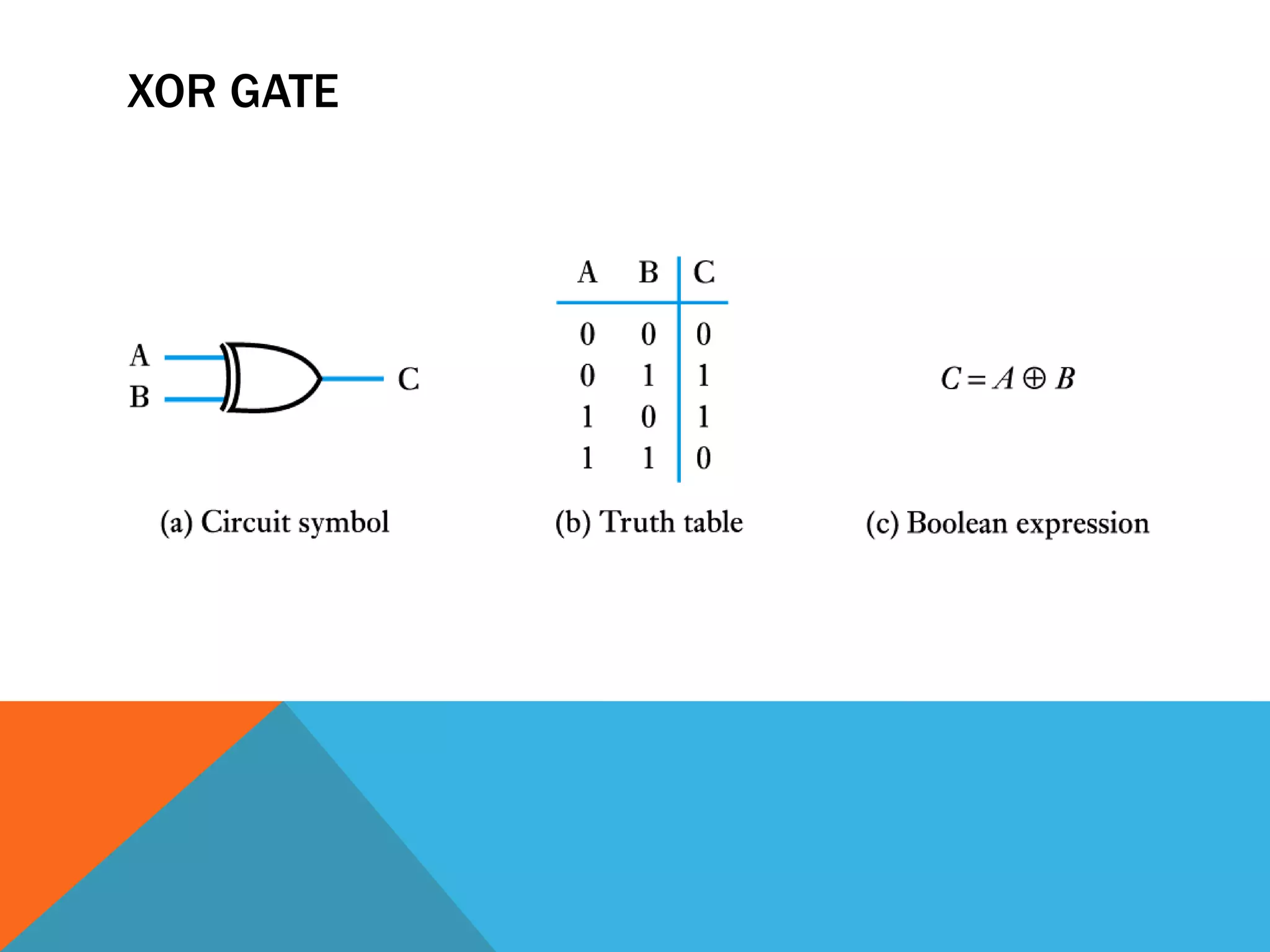
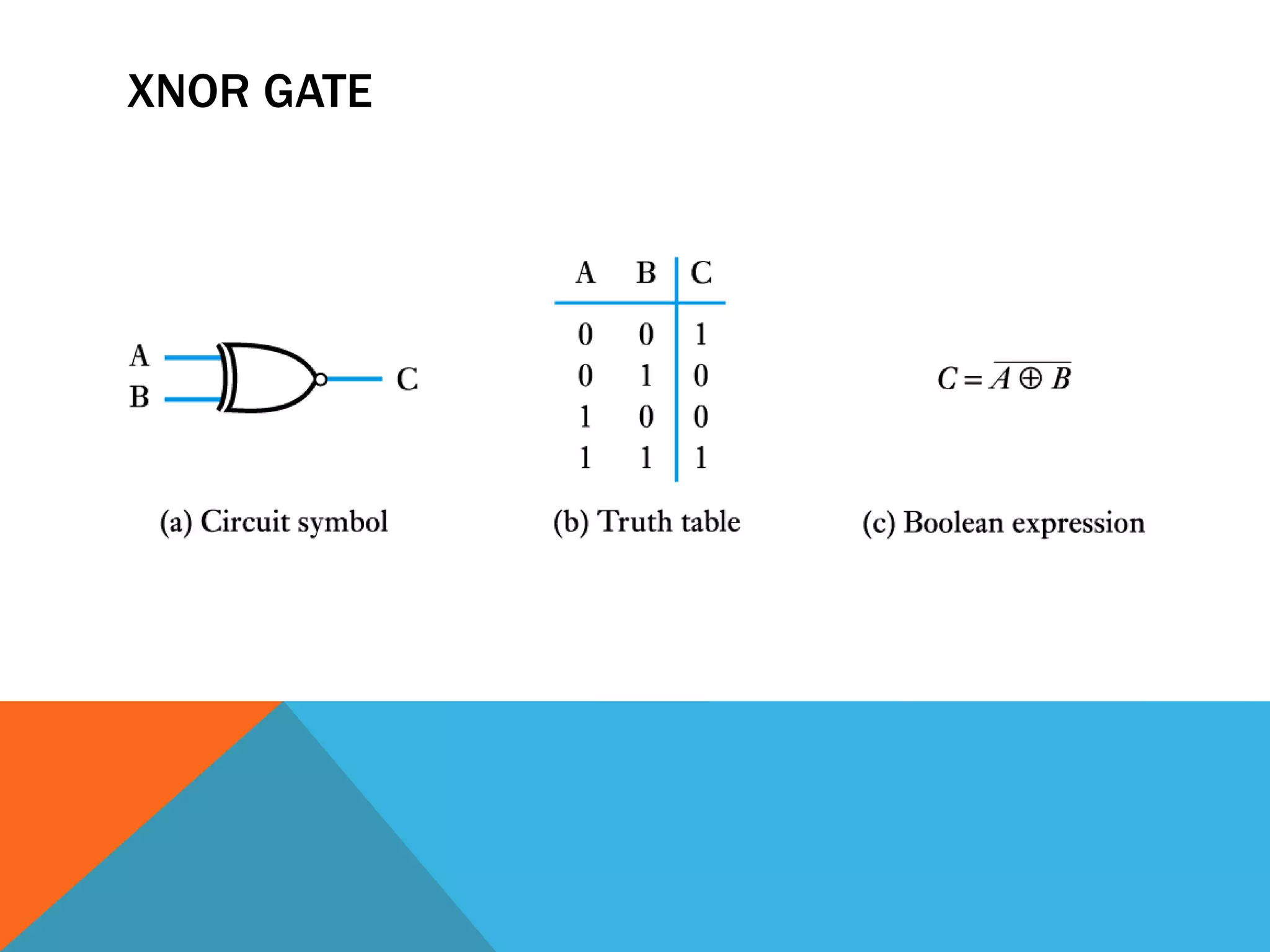
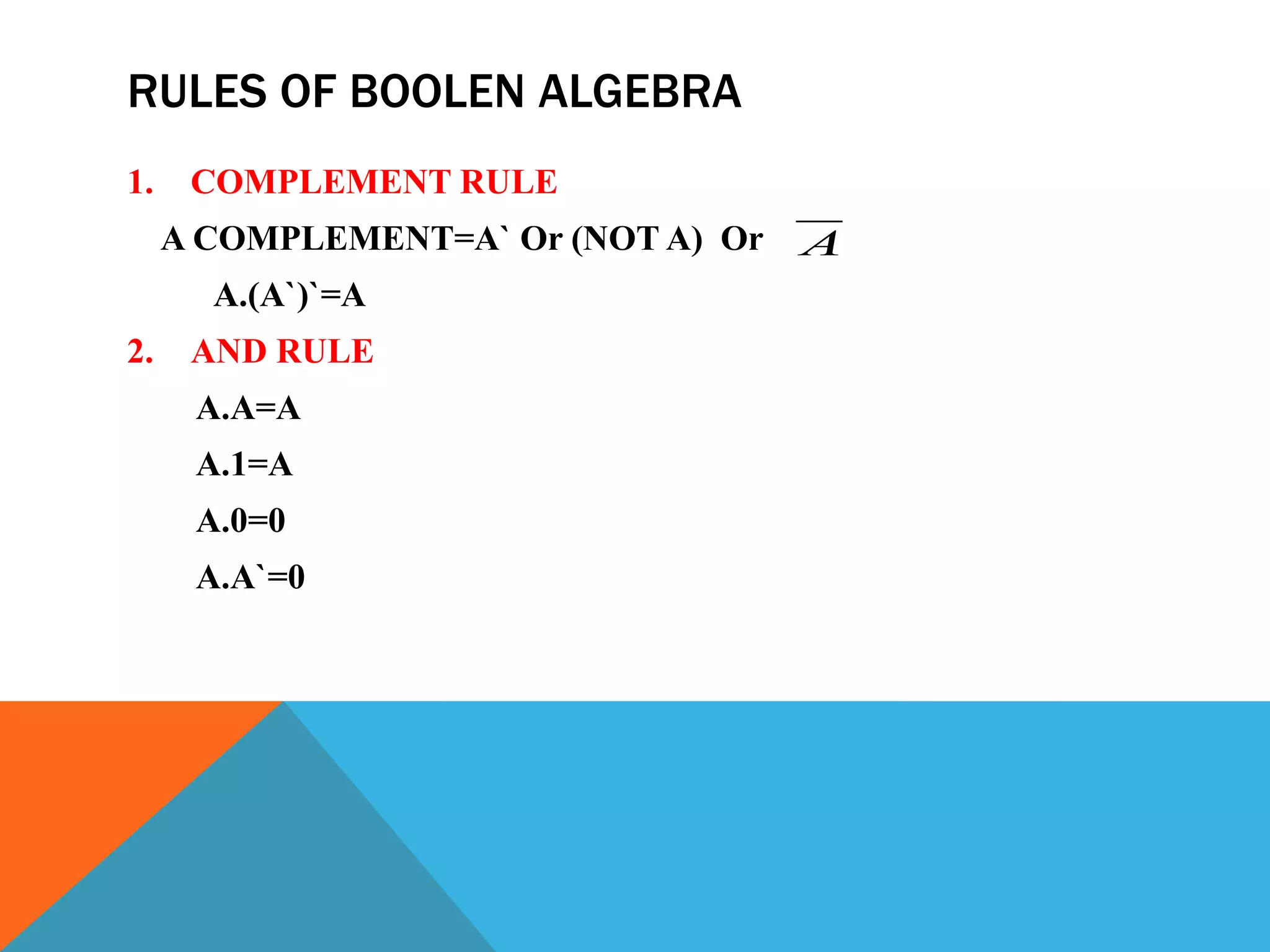
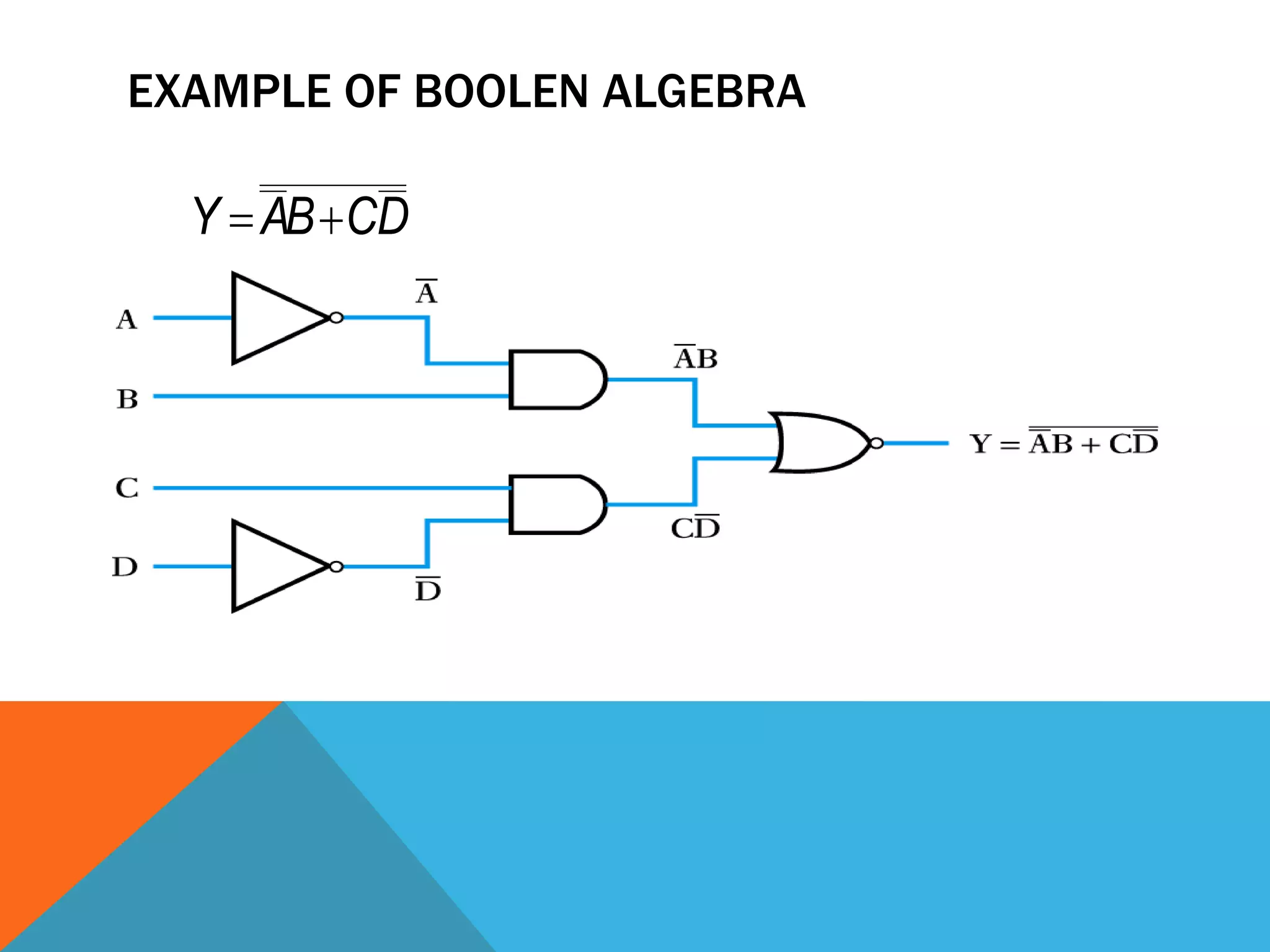
The document provides an introduction to logic gates and Boolean algebra. It discusses the different types of logic gates including NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR gates. Truth tables and logic circuit diagrams are presented as ways to represent the working of logic circuits. Boolean algebra rules are introduced as a way to simplify logic expressions without changing their functionality. Examples of Boolean algebra rules and their applications are also provided.