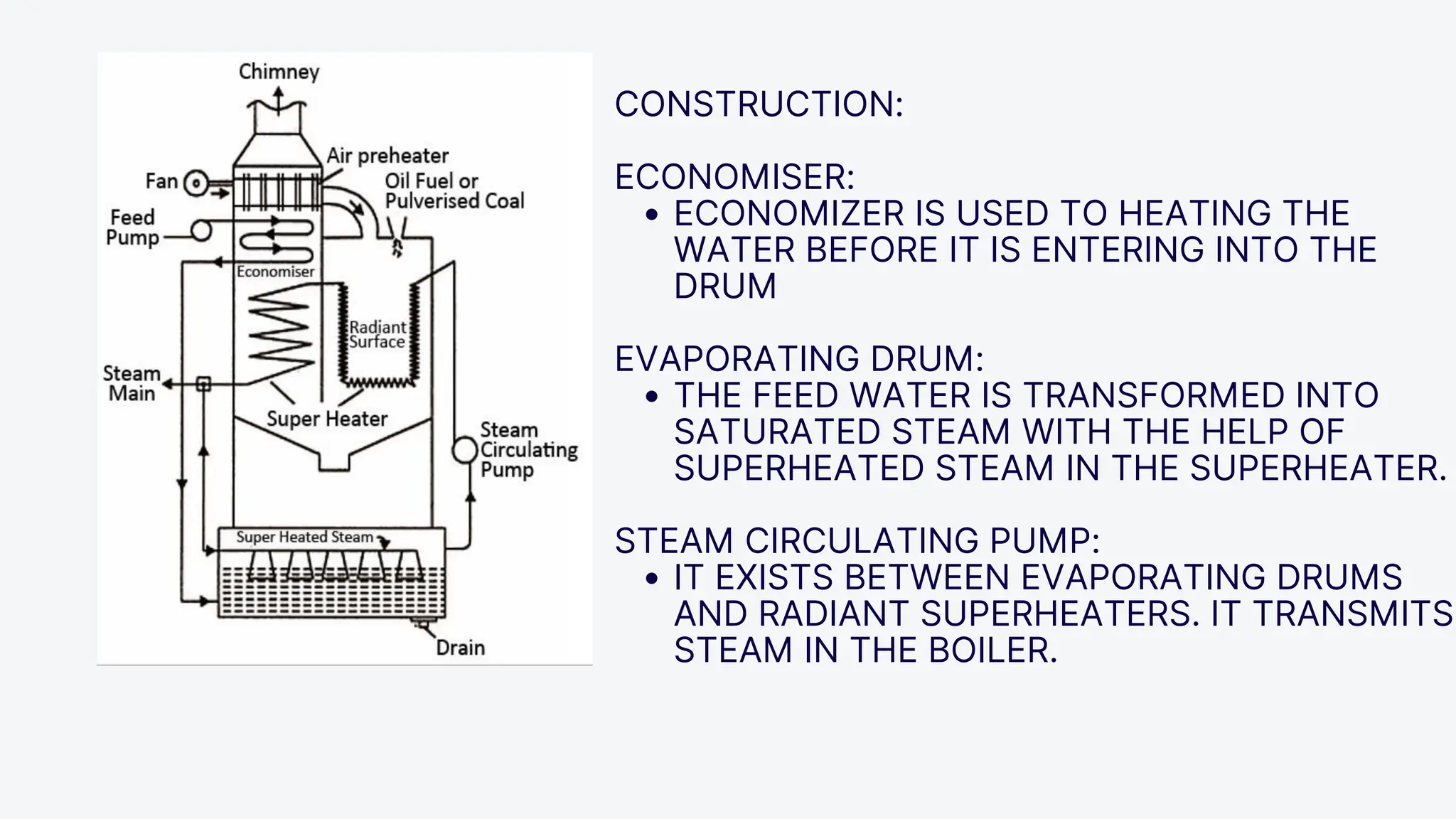
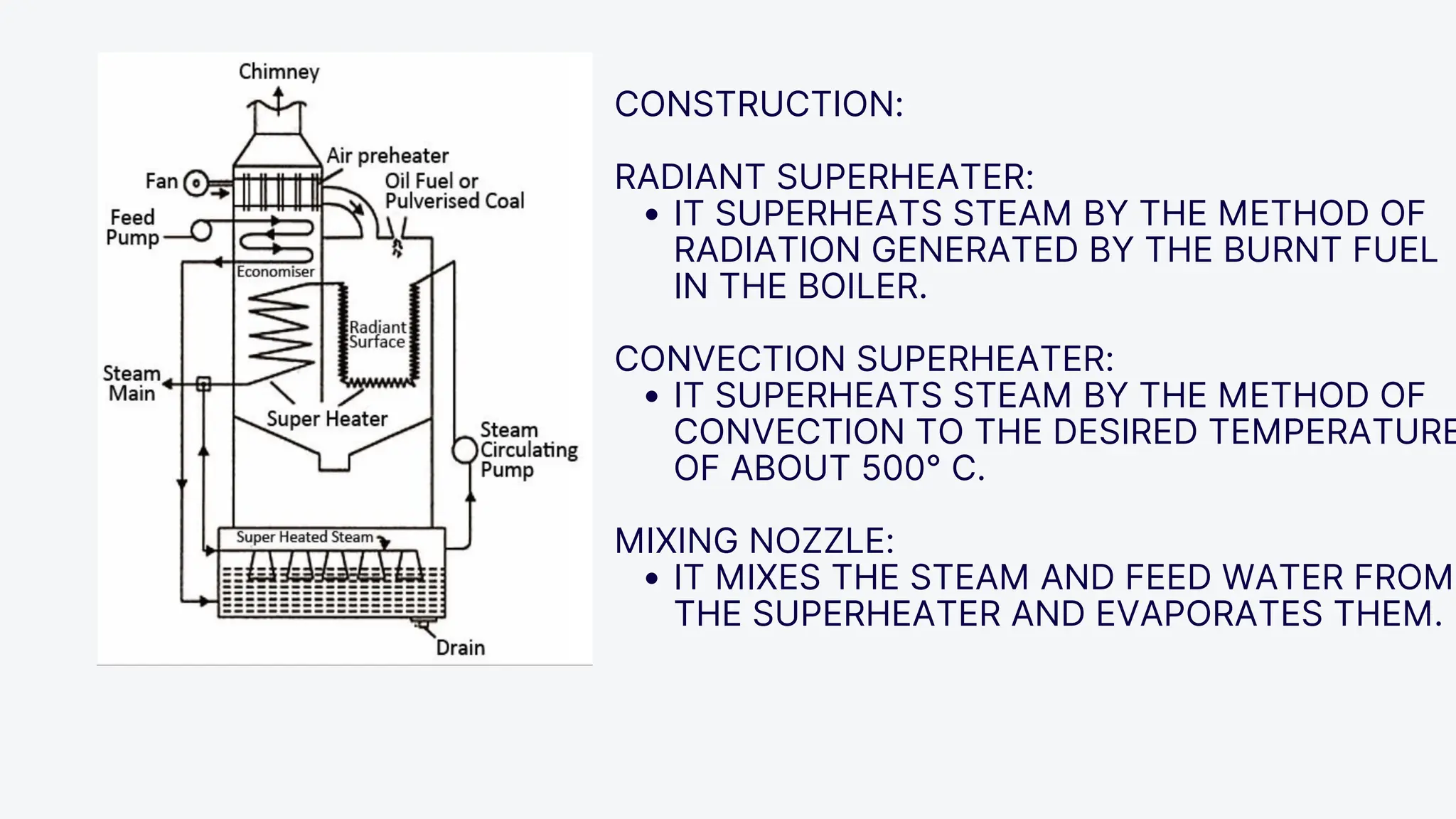
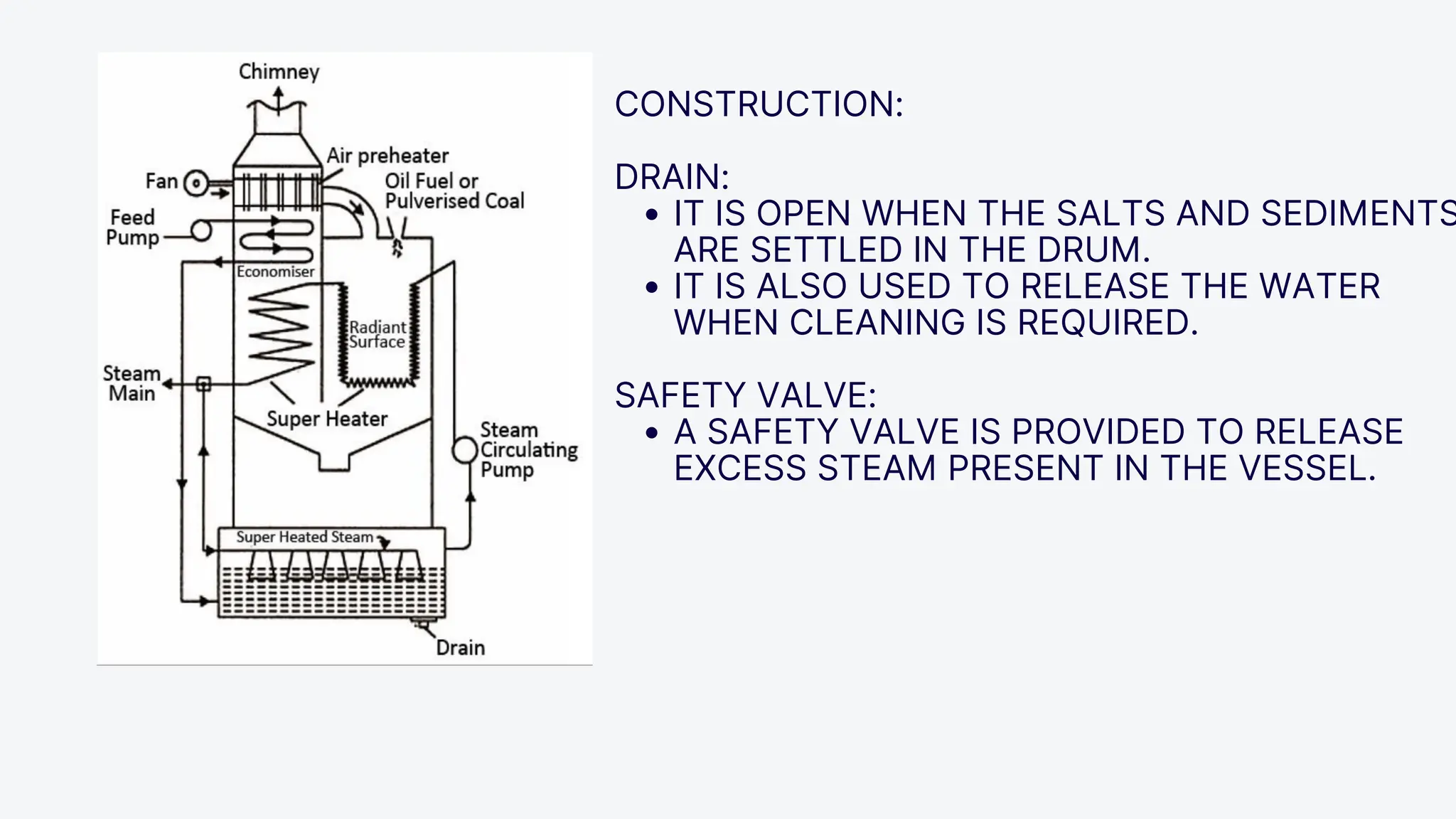
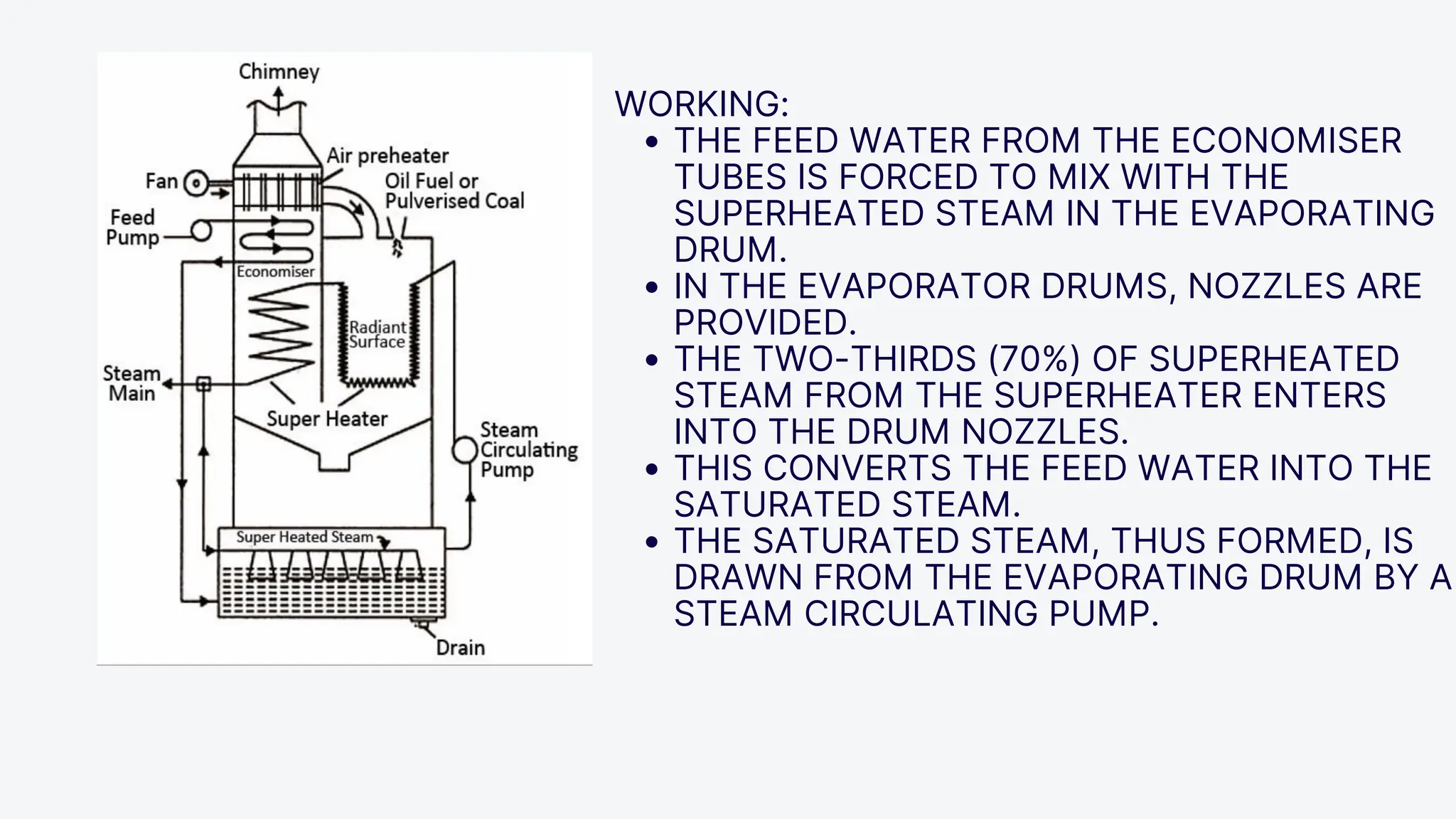
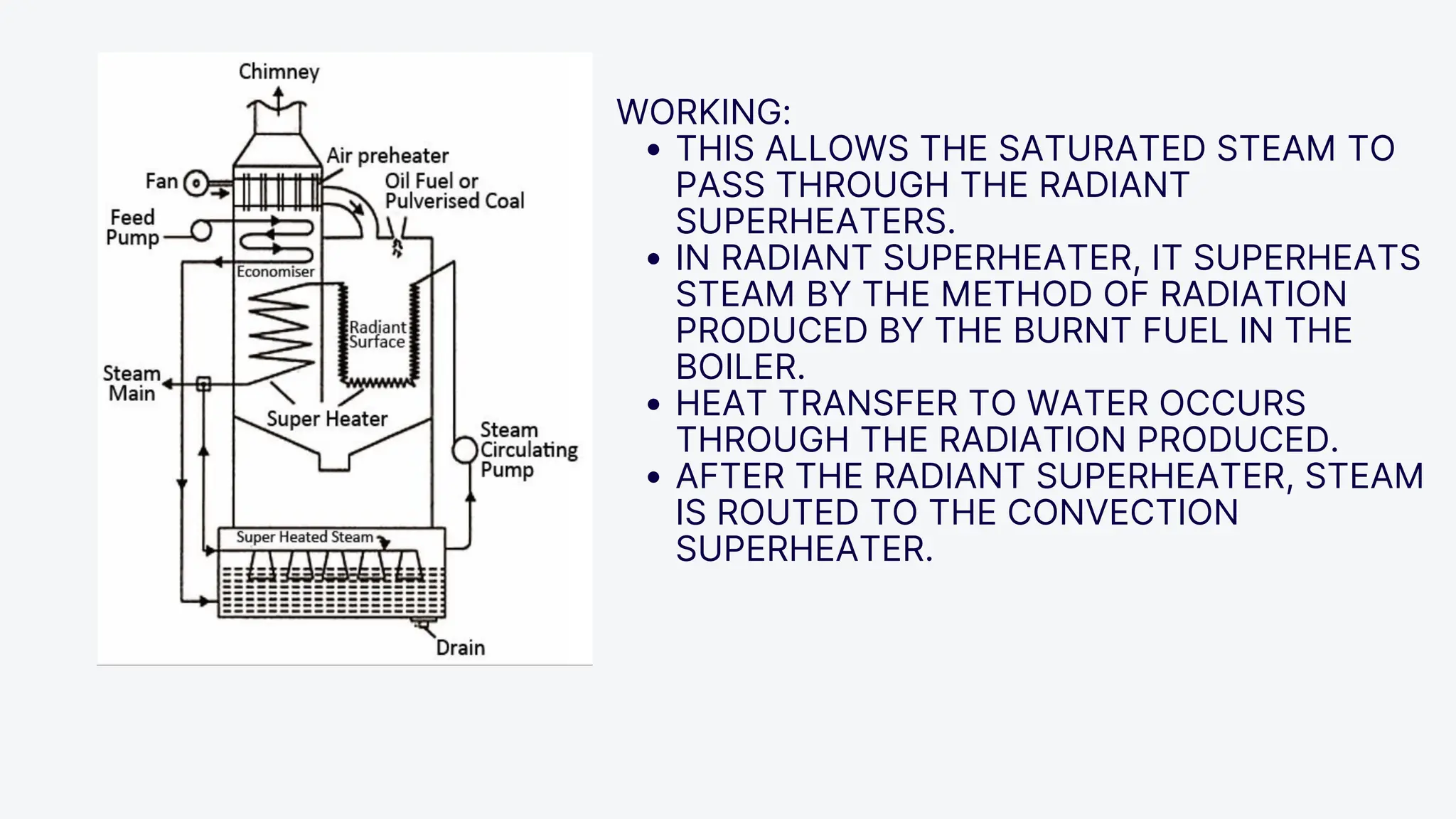
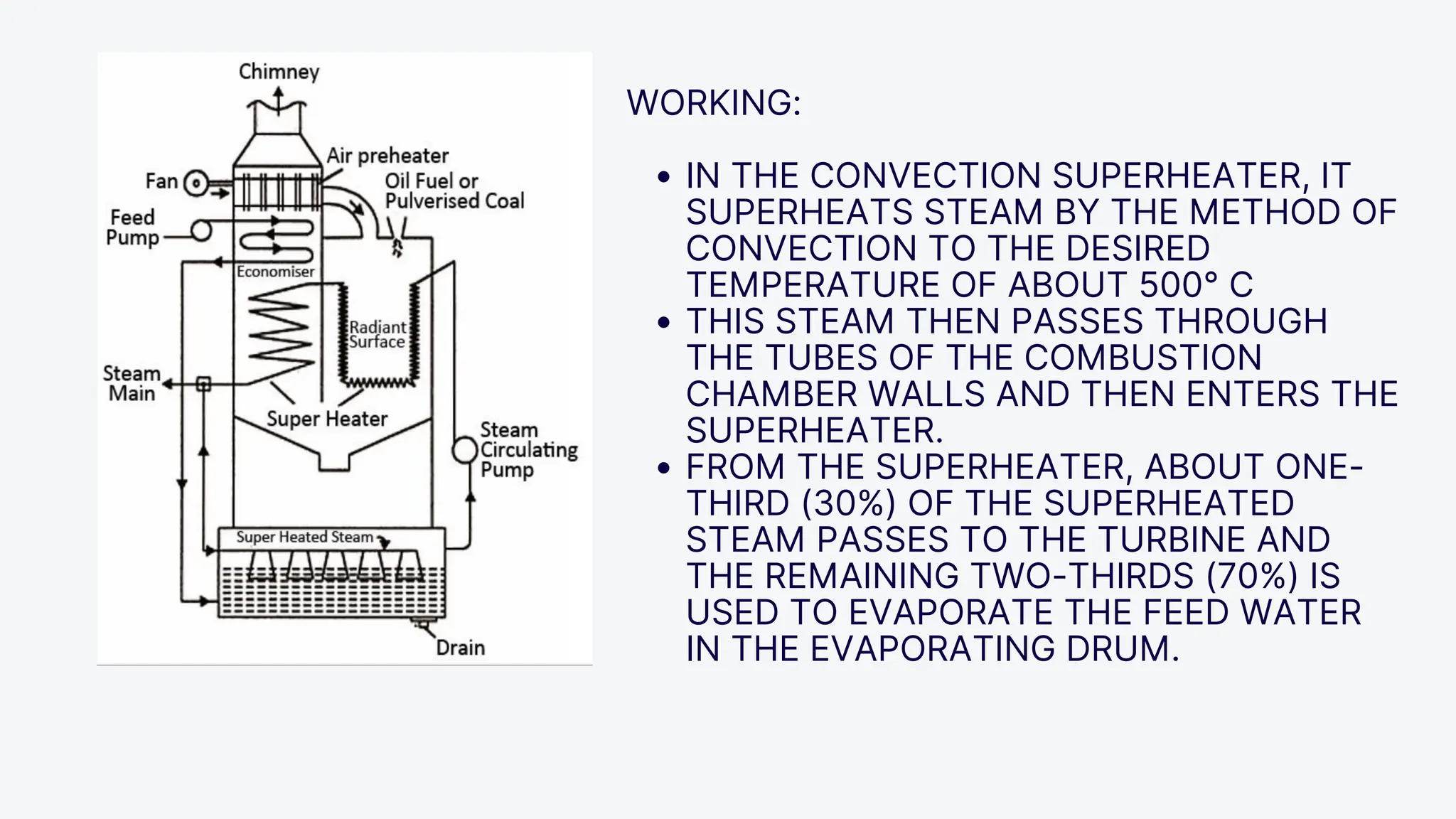
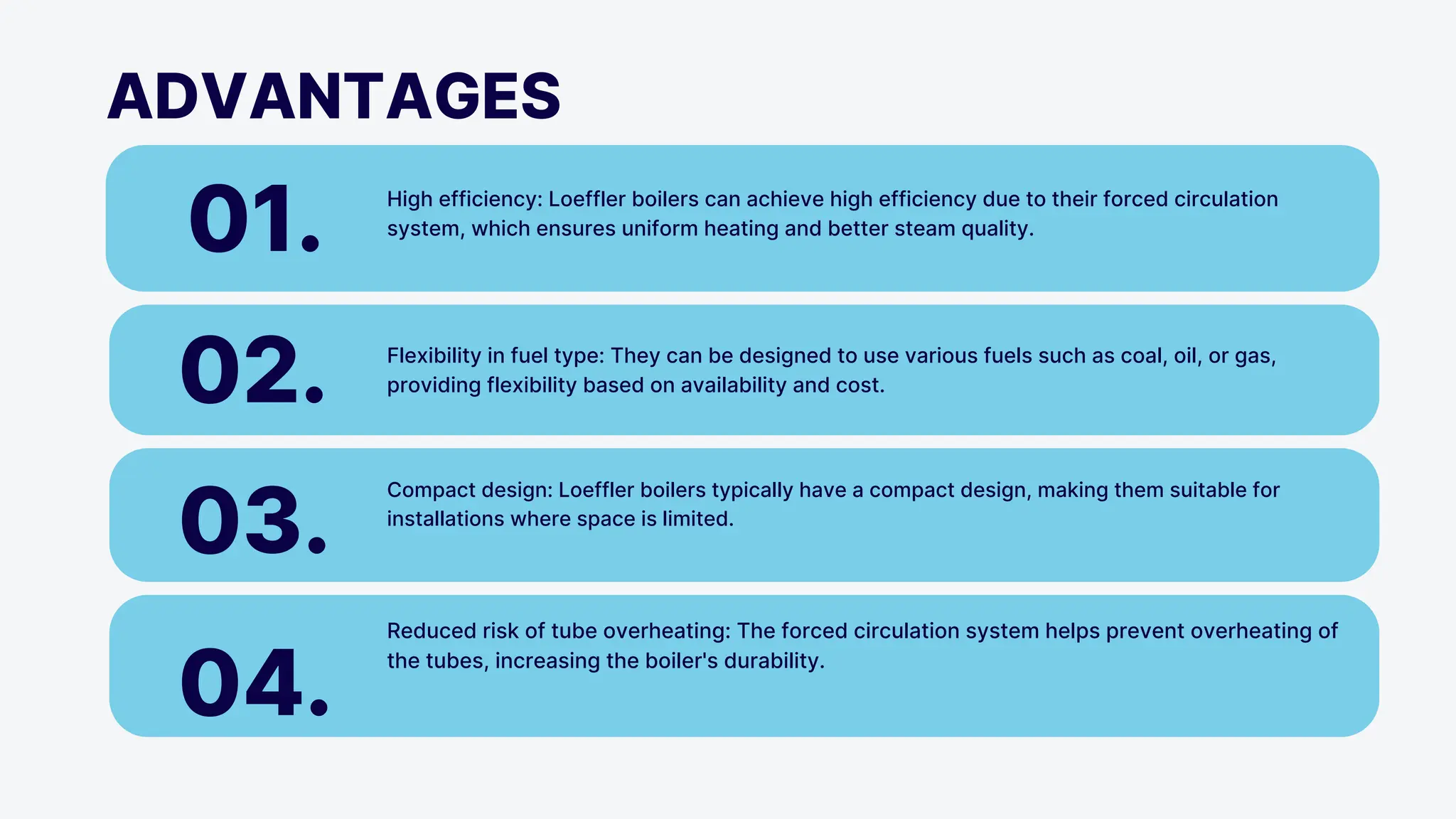
The Loeffler boiler is an advanced version of the Lamont boiler, addressing issues such as salt and sediment deposition that hinder heat transfer and cause overheating. It operates on forced circulation and utilizes superheated steam, with 75% used for evaporating water and 25% for turbine operation. The boiler design features high efficiency, flexibility in fuel types, and compactness, while facing challenges such as complexity, higher initial costs, and strict water quality requirements.