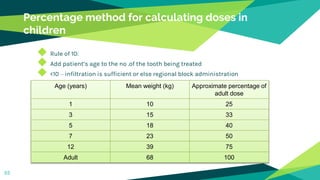
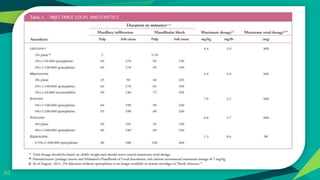
Local anaesthesia and exodontia in children is discussed. Key points include:
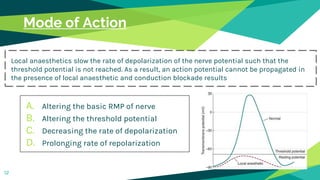
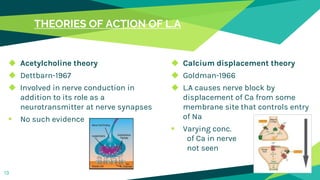
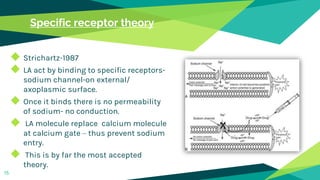
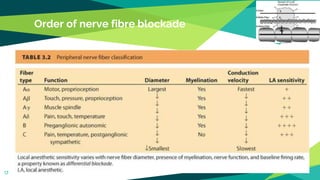
1. Local anaesthesia works by reversibly interrupting nerve conduction. The most accepted theory is that local anaesthetics bind to sodium channels on nerves, preventing sodium entry and conduction.
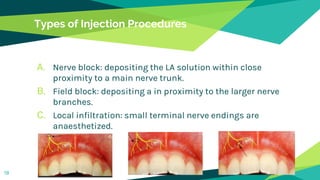
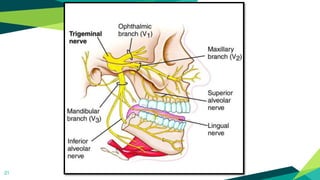
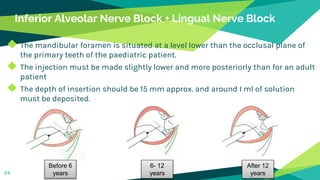
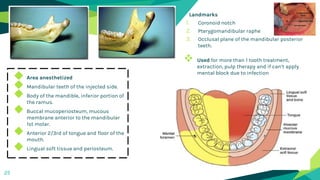
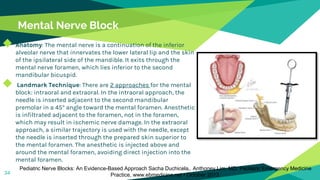
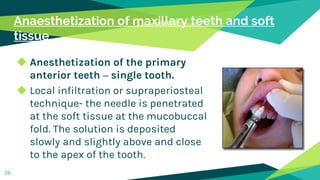
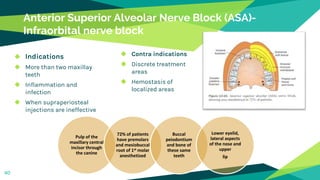
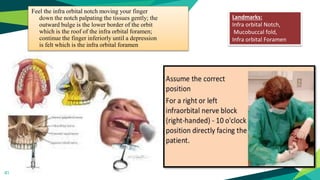
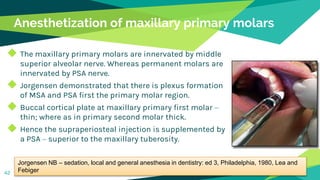
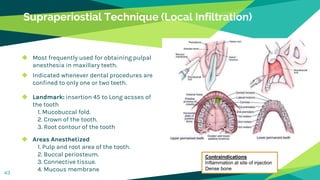
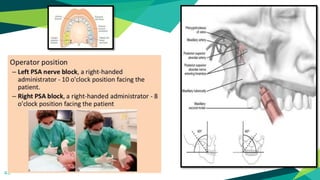
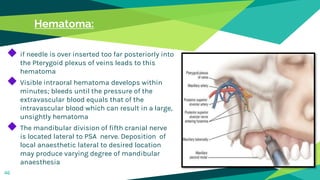
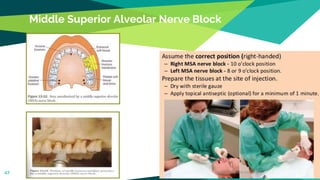
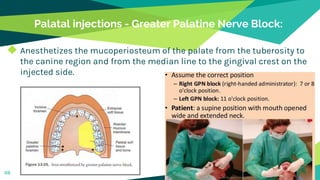
2. Techniques for anaesthetizing primary teeth include inferior alveolar nerve block, mental nerve block, infiltration and supraperiosteal injections.
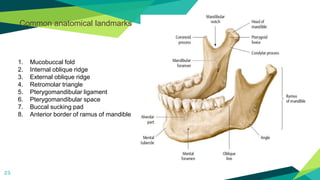
3. Landmarks and techniques may need modification for paediatric patients due to anatomical differences compared to adults.