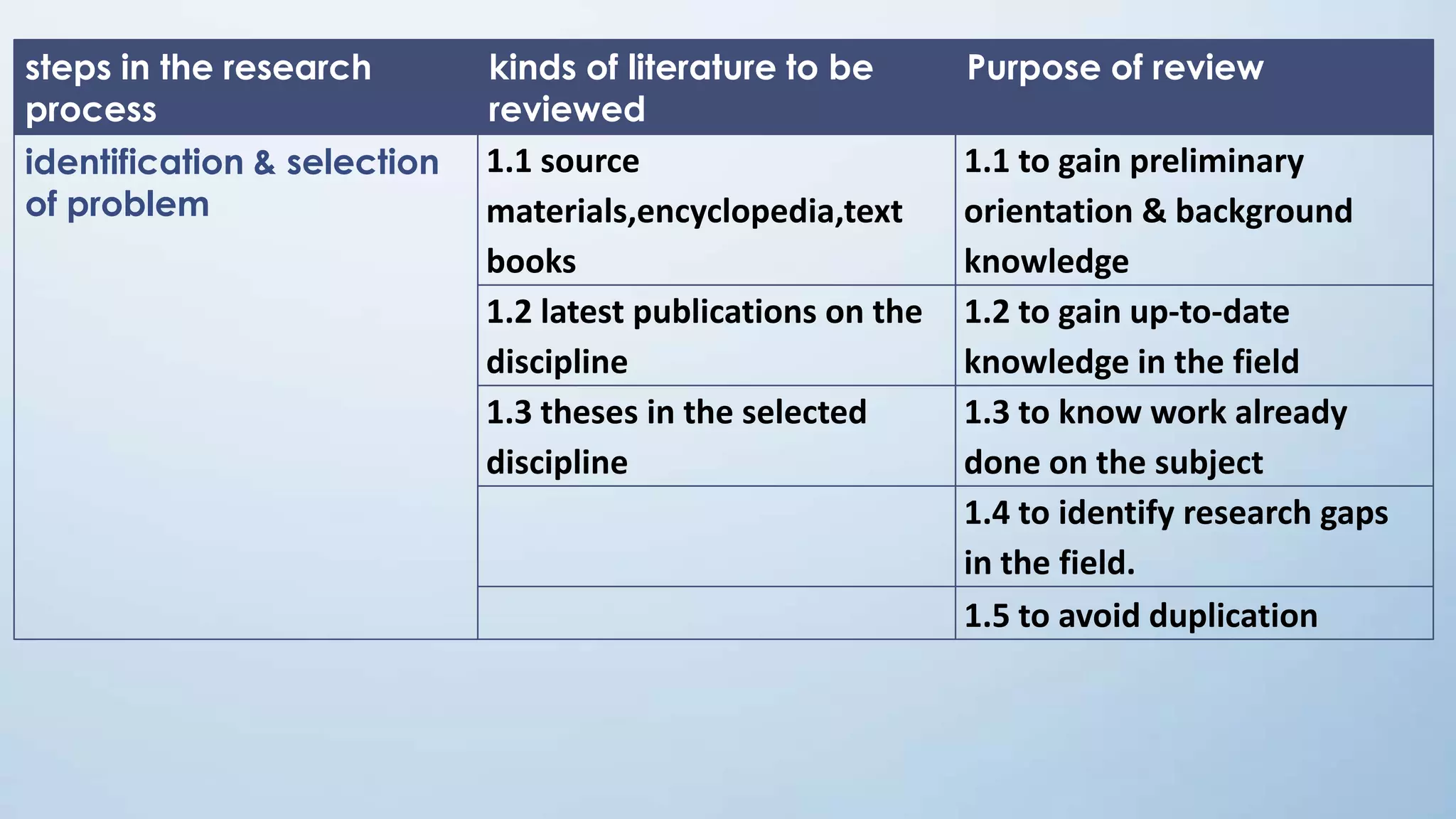
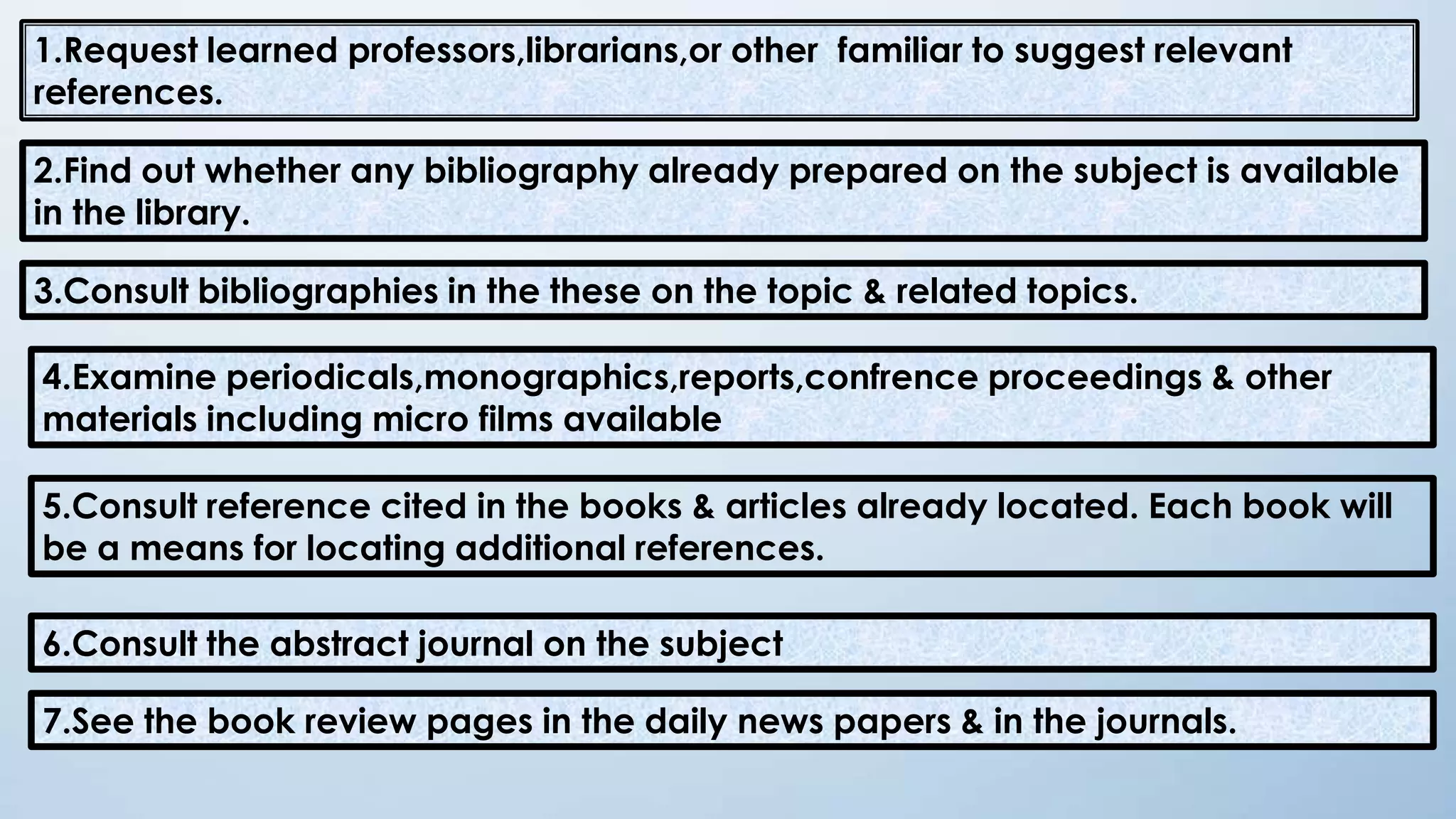
This document provides an overview of the literature review process. It defines a literature review, discusses the types and purposes of literature reviews. It outlines the key steps in conducting a literature review including defining the research problem, searching relevant literature, planning the review, taking notes, and summarizing findings. Sources of literature are primary sources like reports and theses, secondary sources like books and journals, and tertiary sources like indexes and abstracts. The document provides examples of formatting literature in bibliographies and taking structured notes on index cards to organize the review.