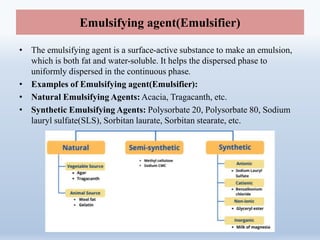
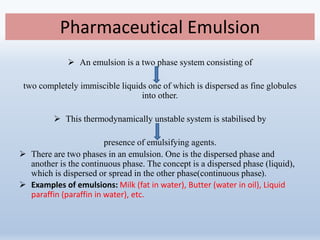
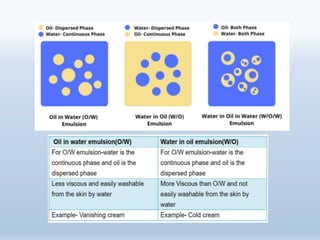
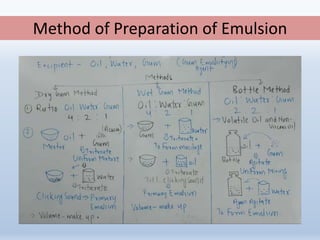
The document provides a comprehensive overview of liquid dosage forms in pharmaceuticals, including classifications such as monophasic and biphasic forms, with detailed sections on syrups, suspensions, and emulsions. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of liquid forms, the pharmaceutical additives used, and methods for enhancing solubility and stability. Additionally, the document outlines the applications of these dosage forms in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, and paint industries.