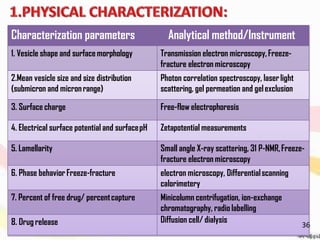
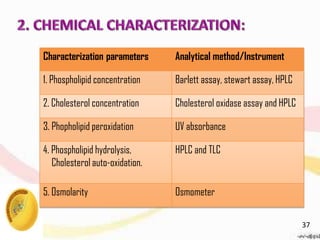
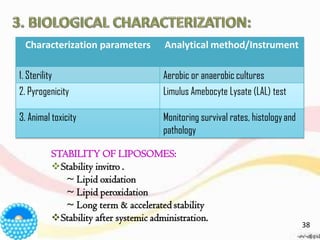
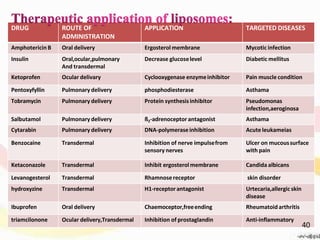
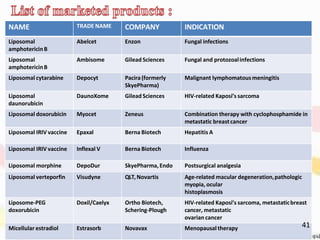
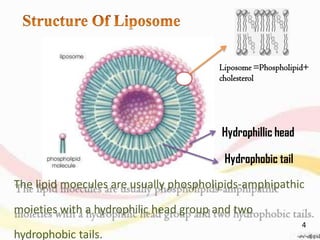
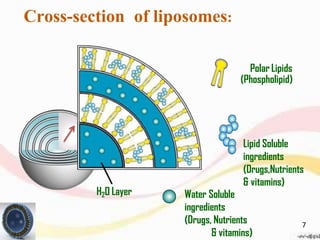
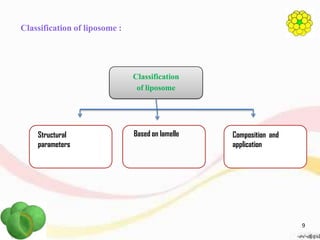
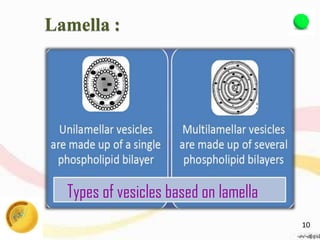
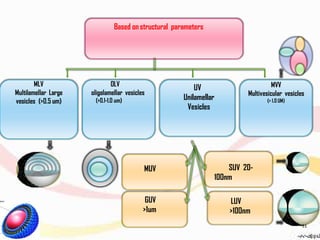
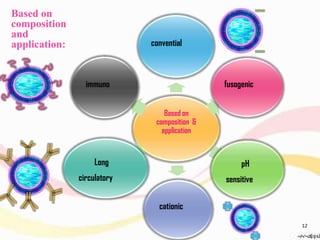
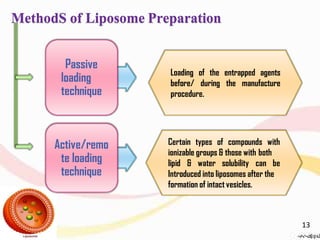
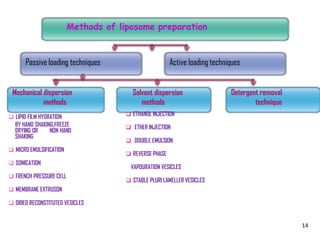
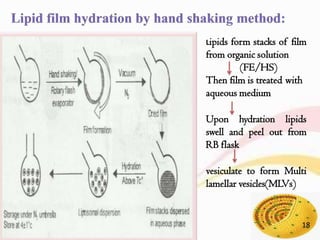
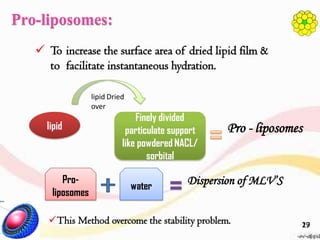
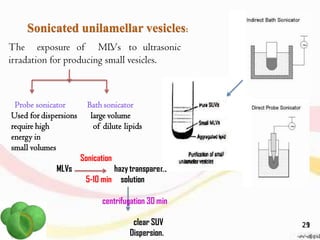
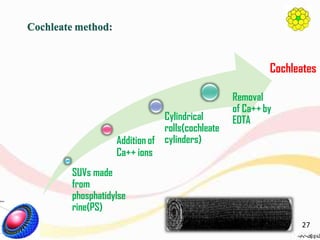
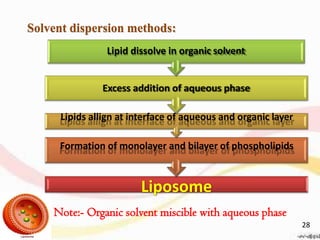
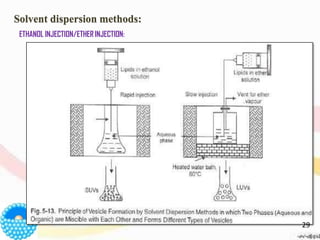
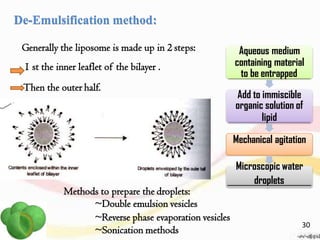
This document provides an overview of liposomes, including their structure, advantages, disadvantages, components, preparation methods, characterization, and applications. Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate aqueous volume. They were first produced in 1961 and range in size from 20 nm to several micrometers. Liposomes provide benefits like selective targeting to tissues, increased efficacy, reduced toxicity, and improved pharmacokinetics. Common preparation techniques include lipid film hydration, microemulsification, sonication, and detergent removal. Liposomes are characterized based on their physical properties and are used to deliver drugs for diseases like cancer, fungal infections, and more.













![pH gradient is created by preparingliposomes
with low internal pH.
Addtn of base to extraliposomal medium.
[Basic compds ( lipophilic (non ionic) athigh
pH & hydrophilic(ionic) at lowpH)]
Lipophilic (UNPROTONATED) drug diffuse through
thebilayer
At low pH side, the moleculesare
predominantly protonated .
Exchange of external medium by gelextrusion
chromatorapghy with neutralsolution.
Weak bases like doxorubicine,
adriamycin and vincristine are
encapsulated.
Solute bearing no
charge at neutral pH
Liposomes with low
internal pH
Neutral solute passes
easily through bilayer
membrane by diffusion
Charge aquired by solute
inside liposomes makes
them unable to exit
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/liposomes-converted-200409090918/85/Liposomes-converted-34-320.jpg)