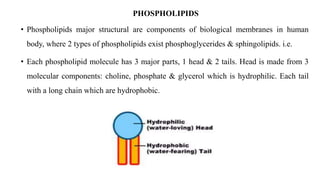
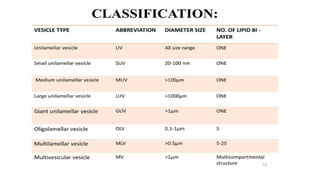
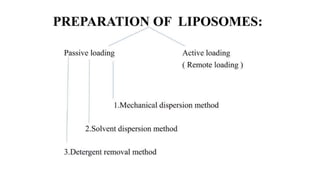
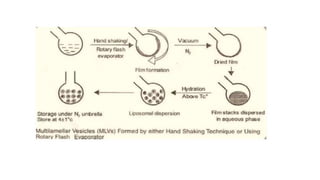
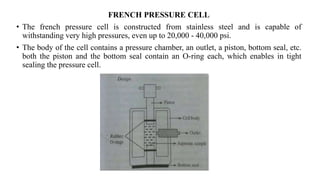
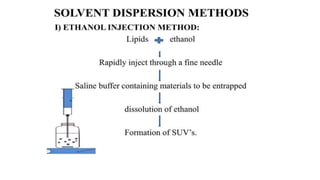
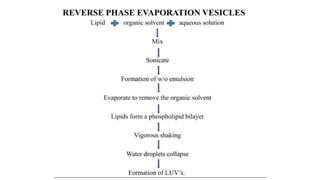
This document provides an overview of liposomes, including their composition, advantages, classification, preparation methods, characterization, and applications. Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate drugs. They range in size from 20nm to several micrometers. Key advantages include biodegradability, protection of encapsulated drugs, and improved drug pharmacokinetics. Common preparation methods include mechanical dispersion, solvent dispersion, and detergent removal. Liposomes are characterized based on size, surface charge, drug entrapment percentage, and lamellarity. They have applications as drug and gene delivery vehicles in cancer therapy, antimicrobial therapy, and more.