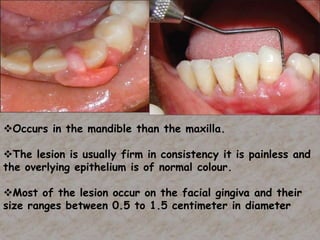
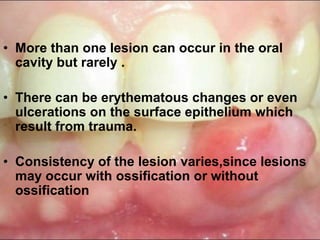
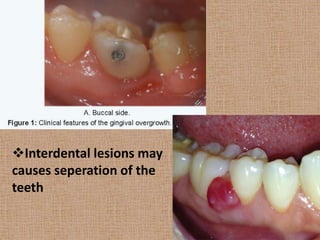
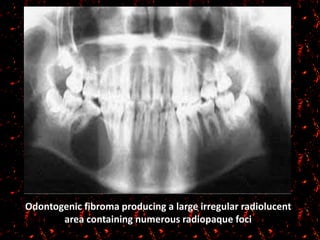
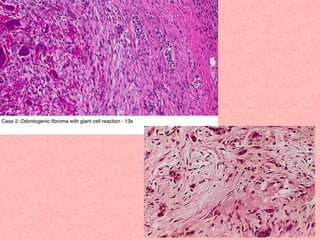
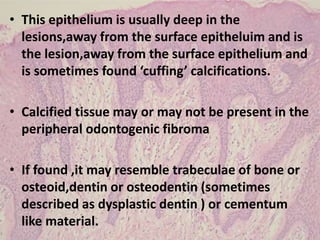
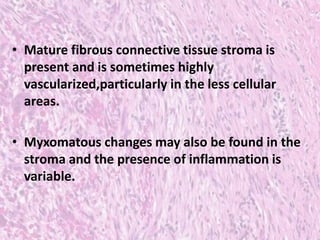
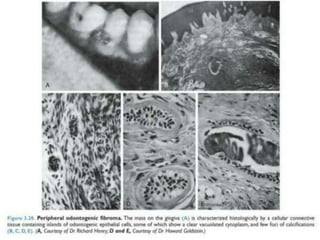
Peripheral odontogenic fibroma is a rare benign tumor originating from odontogenic connective tissue, classified as an extraosseous lesion most commonly found in the jaw. It typically presents as a painless, well-circumscribed growth within the gingiva, with variations in size and consistency, characterized by specific histopathological features. Surgical excision is the recommended treatment, and recurrence is infrequent.