This document provides an introduction and overview of Linux commands and Perl basics. It discusses key Linux commands for system information, user management, files/directories, permissions, processes, networking and more. It also covers Perl data types, variables, input/output, strings, arithmetic, comparisons, functions and file handling. The document aims to teach Linux commands and Perl programming basics.



![User Information and Management:-
o w #show who is logged in and what they are doing.
12:07:00 up 14 days, 21:29, 0 users, load average: 21.66, 24.14, 24.30
USER TTY LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
o who #who is logged into the system
o whoami #who are you logged in as
[2018-01-01 17:41.43] ~
[SAGAR.workgroup] ➤ whoami
SAGAR
o id #display the current user id and group id
[2018-01-01 17:41.49] ~
[SAGAR.workgroup] ➤ id
uid=1001(SAGAR) gid=513(UsersGrp) groups=1002(HomeUsers),1004(ORA_DBA),559(Performance Log Users),545(Users)
o last #who logged in last](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxperl-190316125336/75/Linux-And-perl-5-2048.jpg)




![Networking:
o ifconfig #Displays network interface and ip address
o ping #to check given address is alive or not
o dig domain_name #display DNS information for domain
o dig –x IP_Address #Reverse lookup of IP_Address
o host domain #display DNS IP address for domain
o hostname #display the hostname
[2018-01-01 19:06.49] ~
[SAGAR.workgroup] ➤ hostname
workgroup
o netstat #Display listening tcp and udp ports and corresponding programs
[2018-01-01 19:11.20] ~
[SAGAR.workgroup] ➤ netstat
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 10.10.156.9:4280 hk2sch130022025:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.10.156.9:4294 sb-in-f188:5228 ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.10.156.9:6010 static:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.10.156.9:9327 static:https ESTABLISHED
TCP 10.10.156.9:9635 13.75.42.223:https TIME_WAIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxperl-190316125336/75/Linux-And-perl-10-2048.jpg)









![Example for Arrays subroutines:
#perl 5.22.1
use strict;
use warnings;
my @arr;
print "Enter the number of element you want to enter n"; #Enter Size
my $n = <STDIN>;
print "n Enter the elements n"; # Enter Elements
for (my $i= 0; $i<$n; $i++){
my $ele = <STDIN>;
$arr[$i]=$ele;
}
print "Entered Elements are : --- n"; #print Elements
for (my $i= 0; $i<$n; $i++){
print $arr[$i];
}
print "Size of the array is : - ".scalar @arr."n"; # get Size
print "Your sorted array is : -n";
my @sorted_arr = sort(@arr); #sort Array
print @sorted_arr;
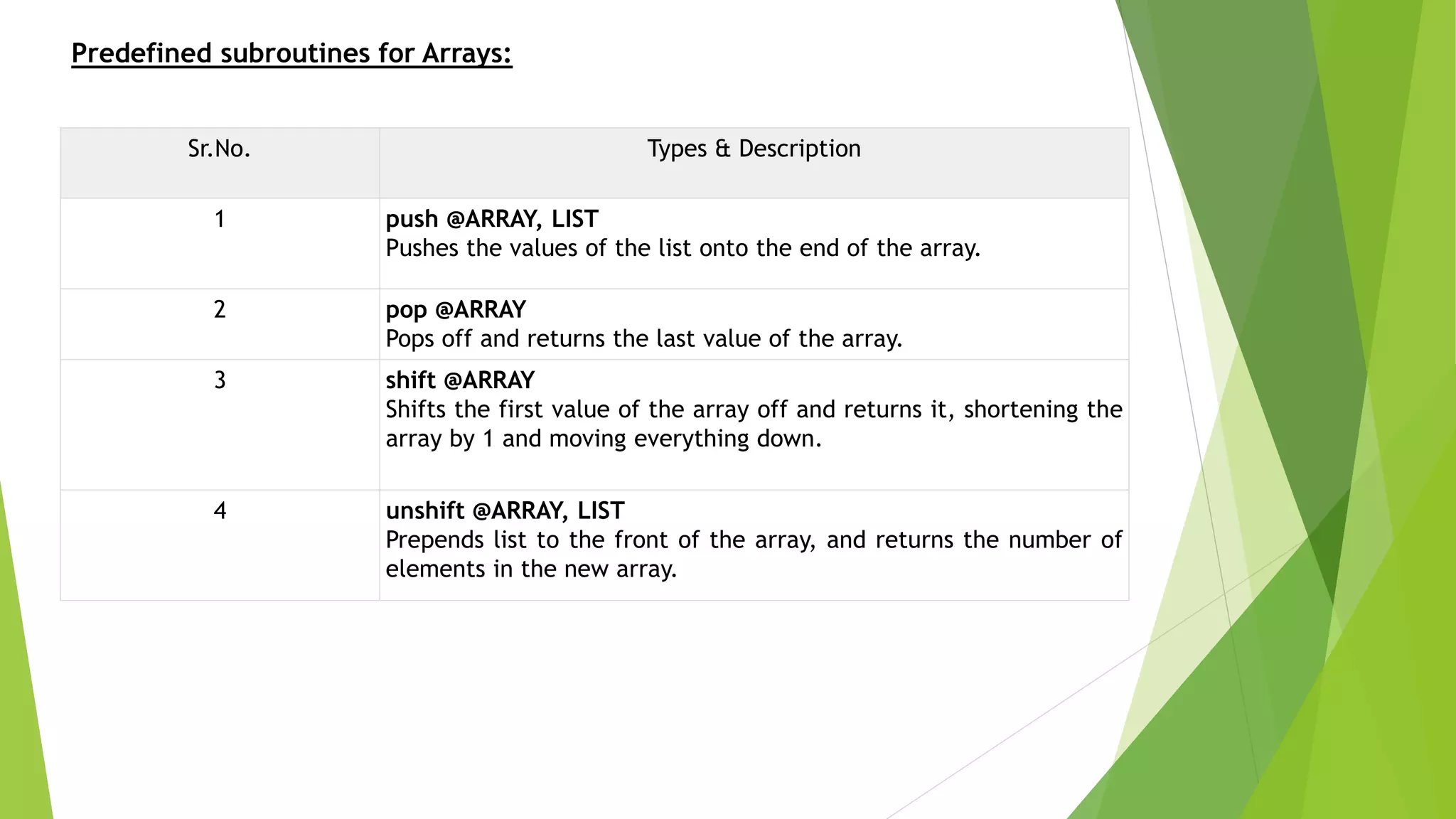
print "After Element pushingn";
push(@sorted_arr, "99n"); #add one Element at the end of array
print @sorted_arr;
print "New size of the array is :---".scalar @sorted_arr."n";
print "After unshifting ---- Adding element at begining n";
unshift (@sorted_arr,"555n"); #add element at the begining of the array
print @sorted_arr;
print "After poping ------ removing element from end n";
pop(@sorted_arr);
print @sorted_arr;
print "After shifting ------ removing element from beginning n";
shift(@sorted_arr);
print @sorted_arr;
OUTPUT:
Size of the array is : - 3
Your sorted array is : -
3
7
9
After Element pushing
3
7
9
99
New size of the array is :---4
After unshifting ---- Adding element at begining
555
3
7
9
99
After poping ------ removing element from end
555
3
7
9
After shifting ------ removing element from beginning
3
7
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxperl-190316125336/75/Linux-And-perl-23-2048.jpg)


