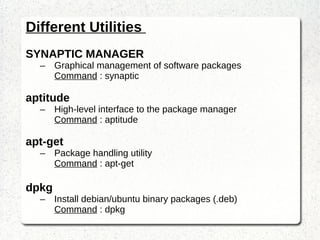
The document summarizes topics covered in a Linux workshop from January 20th to 25th at IIT Kanpur. It includes introductions to vi text editor commands, Linux shell, finding and searching files, grep command, SSH, SCP, processes and process handling, GUI desktop environments, text editors, terminal, and installing software using package managers.




![Searching for a file : locate – find files by name Find – search for files in a directory hierarchy Note : Difference between both is that , locate finds files using locate database (if it exists) and therefor it is much faster. Whereas find search for a file or directory in present working directory. Usage : locate [options] pattern find ~ -iname file.txt find ~ -name file.txt Note : -maxdepth (optional argument for find command)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day3-100122030149-phpapp02/85/Linux-Workshop-Day-3-5-320.jpg)
![Printing a matching pattern : grep It print lines matching a pattern. Syntax : grep [Options] PATTERN [FILE..] Example : grep capacity: /proc/acpi/battery/C245/info Optional Parameters : -i , -w , -c , -n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day3-100122030149-phpapp02/85/Linux-Workshop-Day-3-6-320.jpg)

![Provide secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. Syntax : ssh username@server [-p port] Additional Arguments : -4 Forces ssh to use IPv4 addresses only. -6 Forces ssh to use IPv6 addresses only. Note : ssh exits with the exit status of the remote command or with 255 if an error occurred.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day3-100122030149-phpapp02/85/Linux-Workshop-Day-3-8-320.jpg)




![Kill – Cancels a job.(Sends a signal to a process) Syntax : kill [-s] %pid -s Specify the signal to send Examples : kill -9 pid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day3-100122030149-phpapp02/85/Linux-Workshop-Day-3-13-320.jpg)