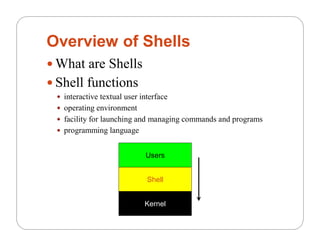
Shells provide an interactive command line interface for users to launch and manage programs. There are different types of shells like bash, csh, and ksh. The shell prompt and configuration are defined in files like /etc/bashrc. Common shell commands allow users to navigate directories, view and edit files, search for files, manage running processes, and set environment variables. Shells act as an interface between the user and the operating system kernel.








![Practive 4
Find - search for files in a directory hierarchy (-name or no, ‘’,” ”,
+n, -n)
find [-H] [-L] [-P] [path...] [expression]
Locate - find files by name
locate [OPTION]... PATTERN...
The database searched by default: /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db
Grep, egrep, fgrep - print lines matching a pattern
grep [options] PATTERN [FILE...]
Sed - stream editor for filtering and transforming text
sed [OPTION]... {script-only-if-no-other-script} [input-file]...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-1-usingtheshell-130320234400-phpapp02/85/2-1-using-the-shell-10-320.jpg)
![Practive 5
Tar - The GNU version of the tar archiving utility (-c, -x, -z, -j)
tar <operation> [options]
gzip (-d), gunzip (-d), zcat (-d) - gzip, gunzip, zcat - compress
or expand files
Zip, unzip
Bzip2 (-z, -d) - a block-sorting file compressor
Cpio - copy files to and from archives (-i, -o)
Example: find /tmp | cpio -o > etc.cpio
cpio -i < /etc.cpio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-1-usingtheshell-130320234400-phpapp02/85/2-1-using-the-shell-11-320.jpg)
![Managing Processes
Command or job is executed in a shell.
Unique process id number or PID.
Foreground and background
Create, Monitor, and Kill Processes.
Ps (tty?, pts?, who, ps), pstree, top, free
ps [options]
Kill (-9,-15), killall: terminal process
bg, fg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-1-usingtheshell-130320234400-phpapp02/85/2-1-using-the-shell-12-320.jpg)




