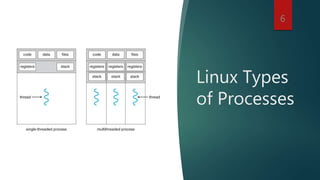
This document provides an overview of key Linux operating system fundamentals including: the Linux boot process; systemctl for managing services; process and memory management; filesystems; package management; kernel parameters; and shells. It outlines several common Linux directories and filesystem concepts. The document also describes process types in Linux and different types of memory. It discusses mounting, unmounting, and formatting filesystems as well as inodes. Linux package management topics such as repositories, installing, removing, updating, and listing packages are covered. Finally, it briefly discusses shells, shell profiles, environment variables, and popular shell types in Linux.