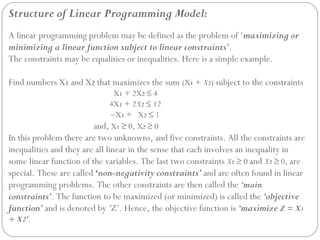
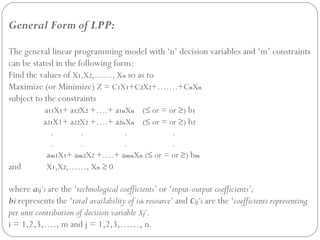
Linear programming deals with optimizing a linear objective function subject to linear constraints. It involves determining the values of decision variables to maximize or minimize the objective function. The general linear programming model involves maximizing or minimizing a linear combination of n decision variables subject to m linear constraints, along with non-negativity restrictions on the decision variables. Formulating a linear programming problem involves identifying decision variables, expressing constraints and the objective function linearly in terms of the variables, and adding non-negativity restrictions.