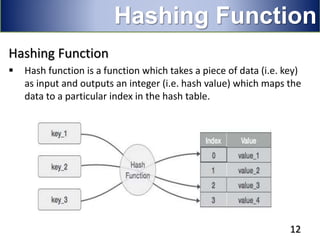
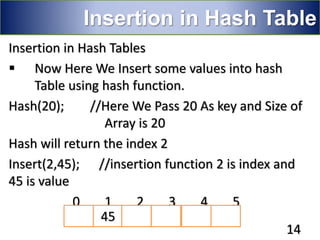
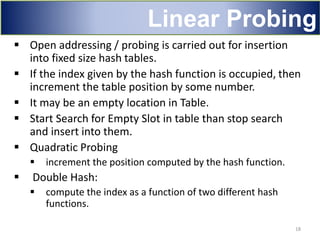
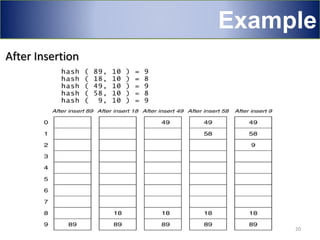
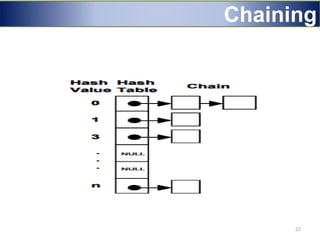
Hashing is a technique used to map data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size. It works by using a hash function to compute an index into an array/table from the search key. This allows for very fast average case performance of O(1) time for operations like insertion, deletion and searching. However, collisions can occur when two keys map to the same index, degrading performance. Common techniques to handle collisions include linear probing, quadratic probing and chaining via linked lists. Hashing is widely used to implement symbol tables in compilers and data structures like sets and maps.









![Function Find(int x)
{
While(start<=end)
{
Int mid=(start+end)/2;
If(x==A[mid]
{
cout<<X<<“ Value Successfully found In Given Array”<<endl;
Break;
}
Else if(x>A[mid])
{
Start=mid+1;
}
Else
End=mid-1;
}
If(x==-1)
{
Cout<<“Element not Found in Array”<<endl;
}
10
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashingdata-180317000937/85/Hashing-data-10-320.jpg)