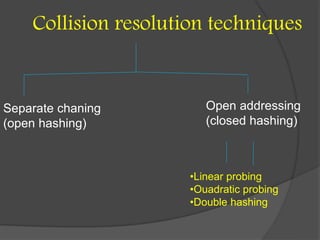
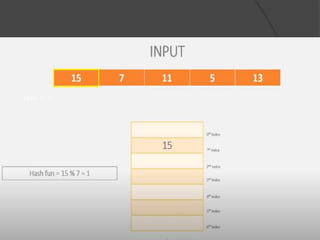
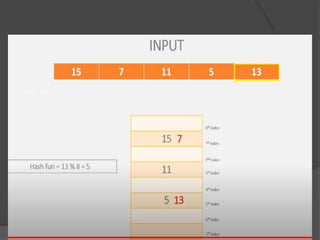
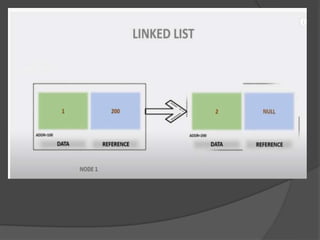
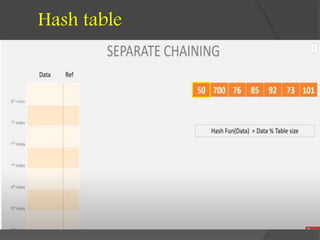
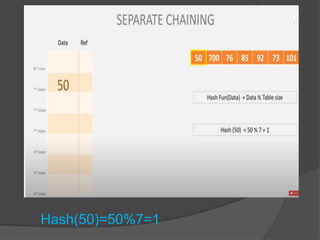
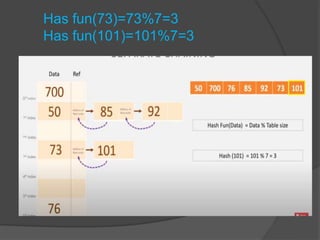
This document discusses hashing and separate chaining as a collision resolution technique for hashing. Hashing is a technique that maps data to array indexes using a hash function. Separate chaining handles collisions by linking each array index to a linked list, so multiple data items can be stored at each index. The document provides examples of calculating hash values for sample input data and inserting those values into a hash table using separate chaining to resolve collisions. Types of hashing and other collision resolution techniques are also briefly mentioned.