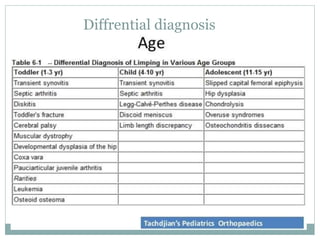
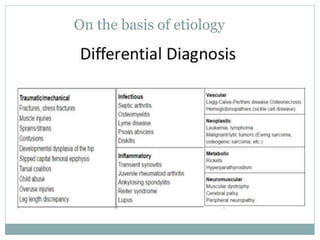
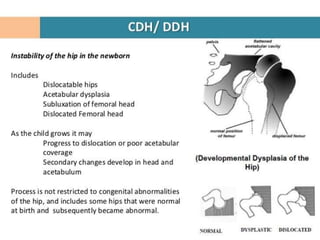
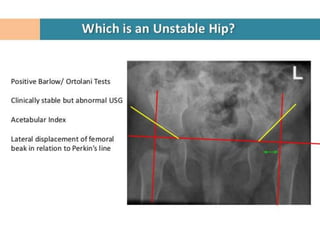
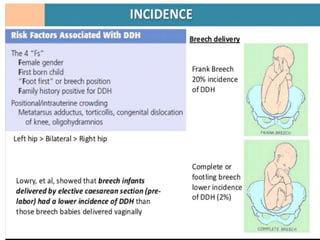
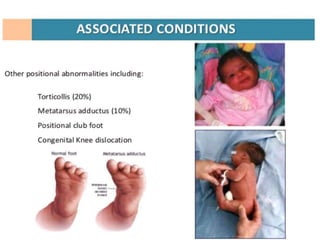
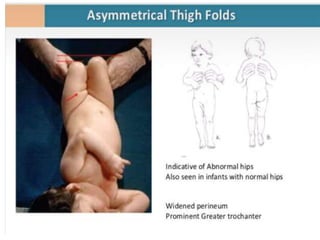
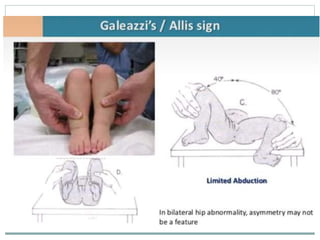
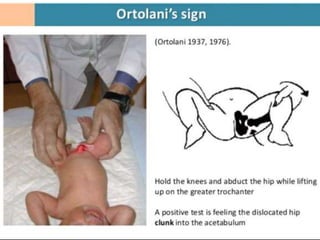
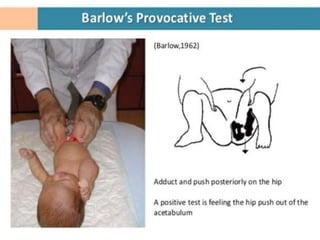
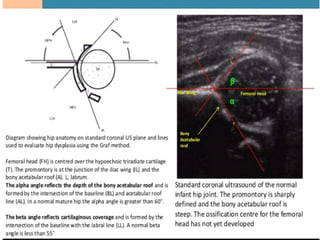
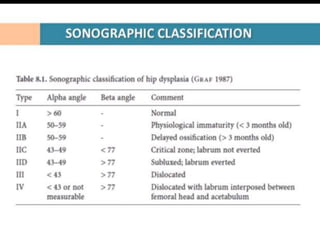
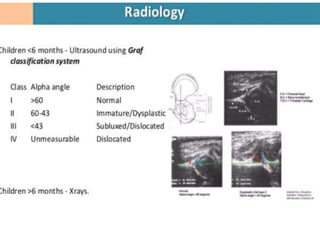
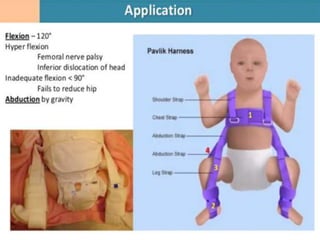
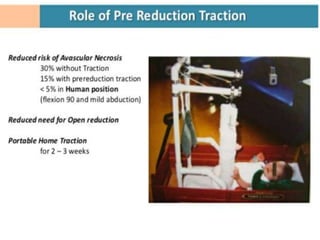
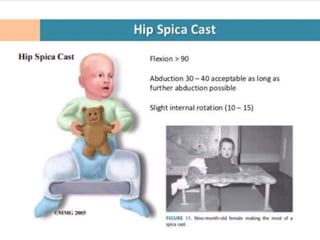
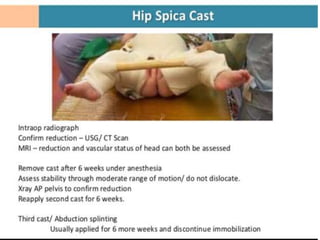
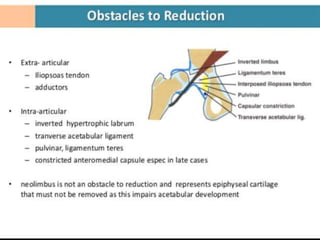
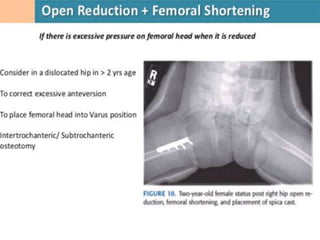
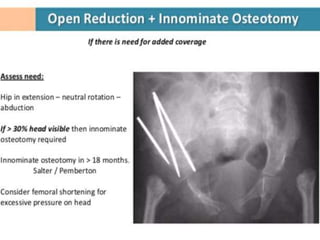
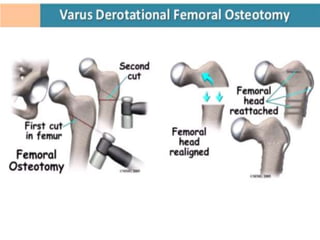
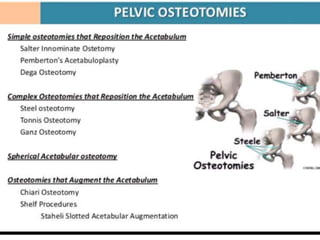
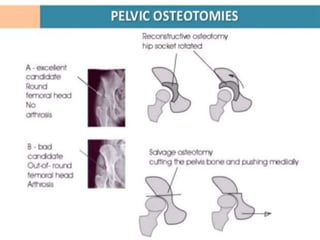
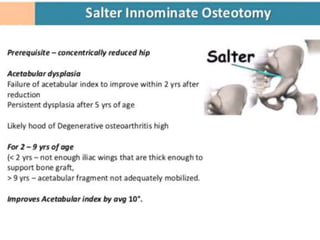
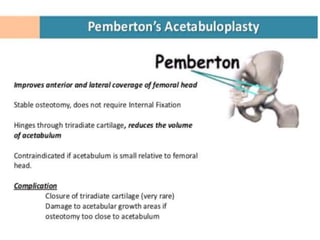
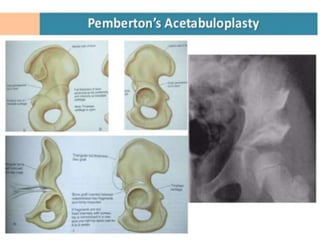
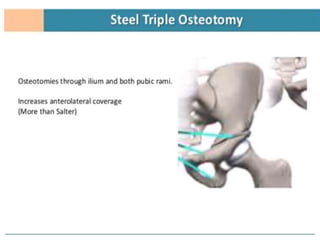
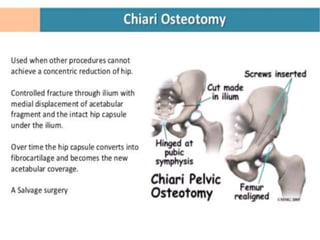
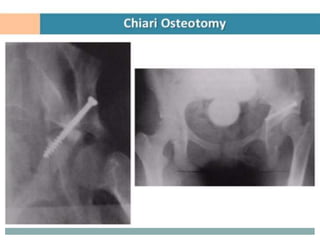
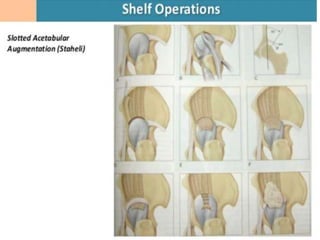
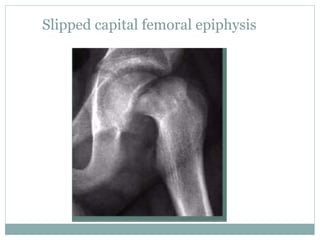
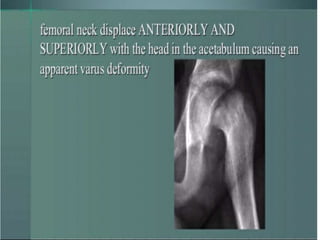
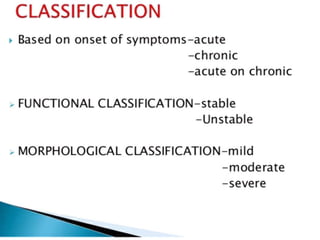
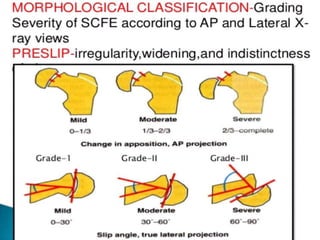
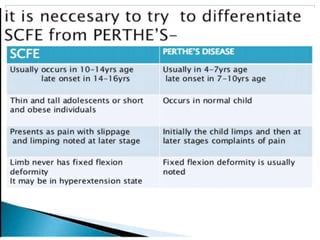
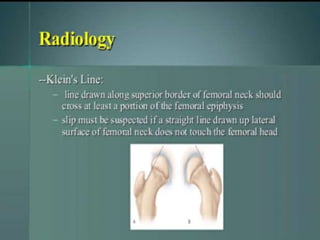
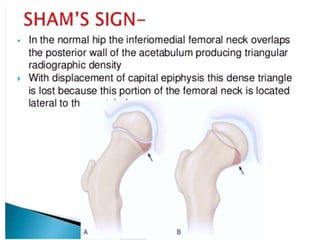
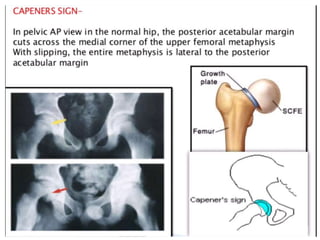
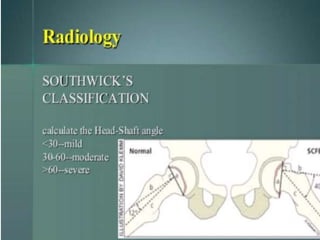
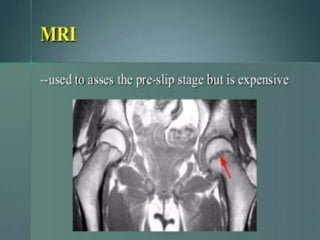
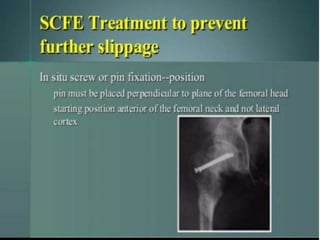
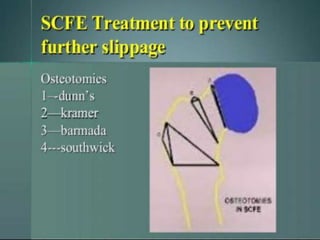
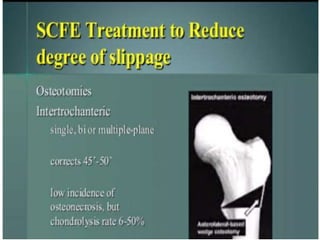
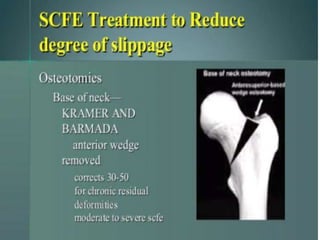
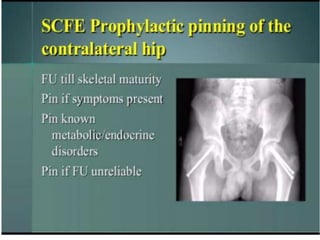
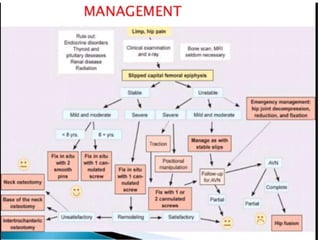
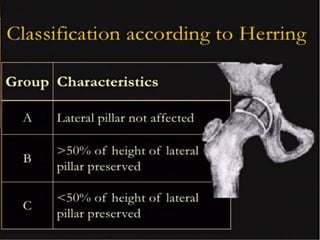
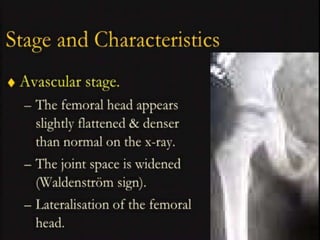
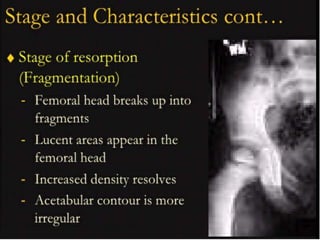
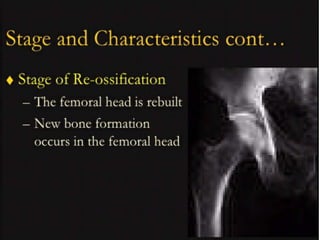
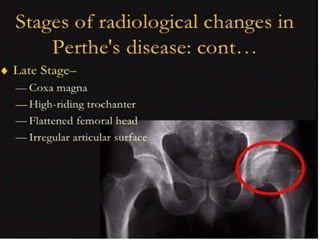
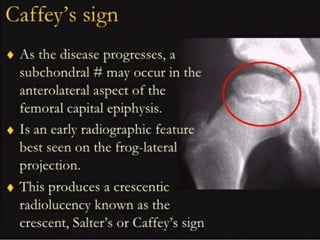
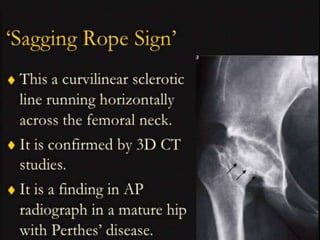
This document discusses differential diagnoses for a limping child based on etiology. It covers congenital/developmental causes like developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), providing details on diagnostic imaging techniques like the Hilgenreiners line and acetabular index. The pathoanatomy of DDH is described, from changes in newborns to changes in older walking children. Clinical presentation of DDH is outlined, noting delayed walking and characteristic gait abnormalities. Other causes discussed briefly include slipped capital femoral epiphysis and Perthes disease.