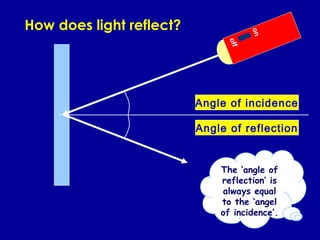
Here are explanations for your questions:
The light from the sun contains all the colors of the visible spectrum, whereas the light from the moon is reflected sunlight, so it appears white. An orange looks orange because it absorbs all colors of light except orange, which it reflects. The sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west because of the Earth's rotation. As the Earth spins on its axis, different parts are exposed to the sun, making it look like the sun is moving across the sky. We can't see anything without a light source because our eyes need light to bounce off objects in order to see their shape, color, and details. A periscope works by using two mirrors to redirect the light path -