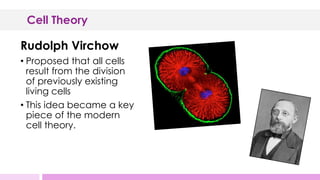
The document outlines the development of cell theory, beginning with Robert Hooke observing cells under a microscope in 1665. Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann concluded that plants and animals are composed of cells, respectively, forming the basis of cell theory. Rudolph Virchow added that cells only arise from preexisting cells, completing cell theory. The three main points of modern cell theory are: 1) all organisms are composed of cells, 2) cells are the basic unit of life, and 3) all cells arise from preexisting cells.