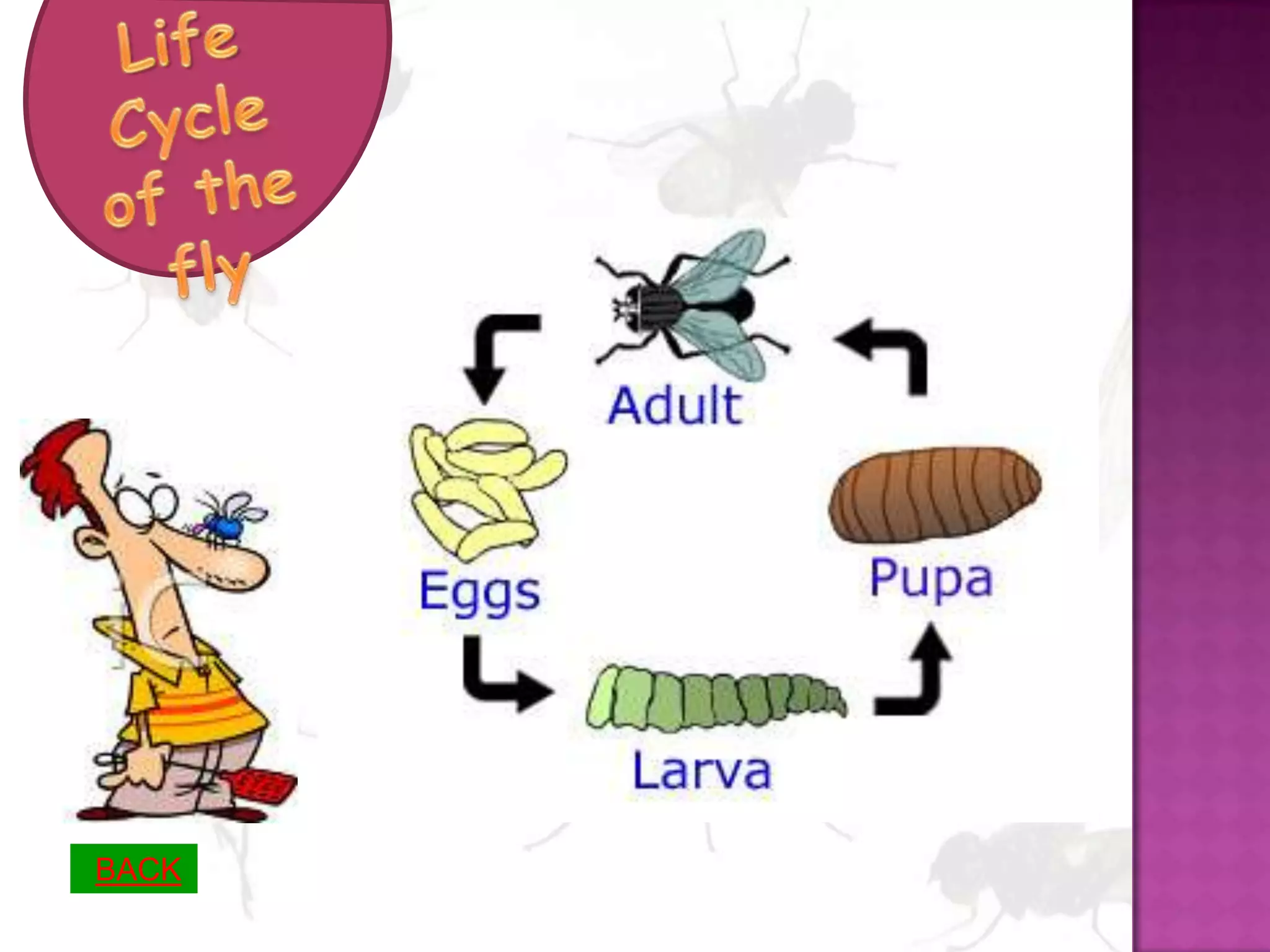
This document is an assessment submission by Rhonda Perrett for a teaching assignment on the living world. It includes an electronic learning tool about the life cycle of flies consisting of interactive pages with information and images about flies. It also includes an acknowledgement statement and links the content to curriculum essential learnings and lists references used.