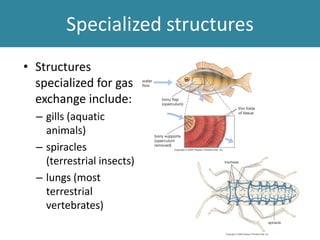
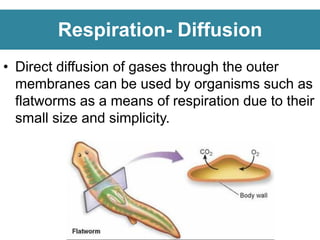
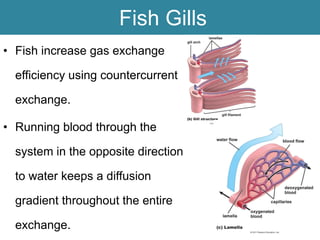
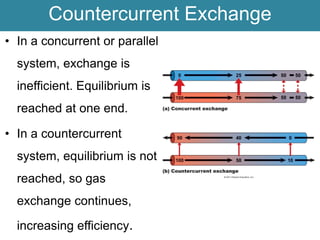
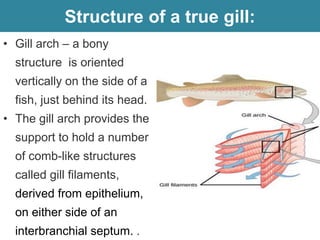
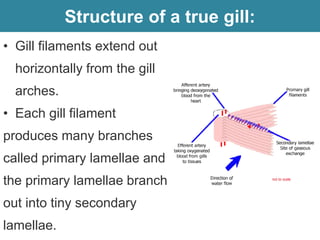
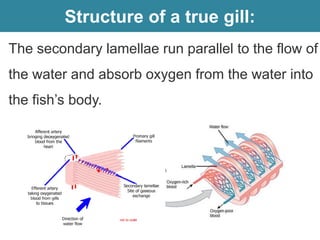
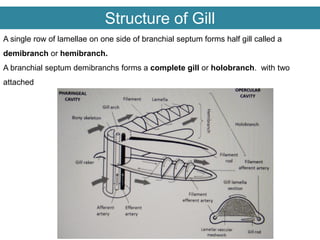
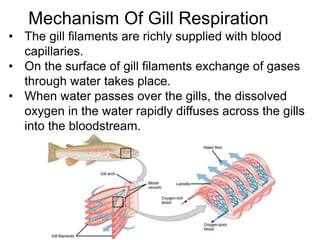
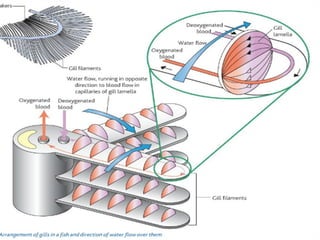
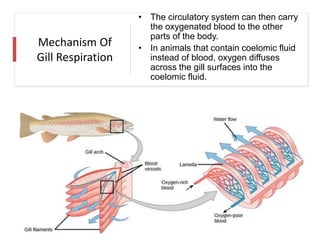
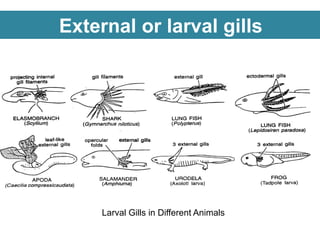
Respiration requires the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. Aquatic animals like fish have evolved gills for gas exchange with water, while most terrestrial vertebrates use lungs. Gills are thin, highly-branched tissue that increase the surface area for diffusion. In fish, blood flows countercurrently to water through the gills, maintaining an oxygen gradient for continuous gas exchange. Lungs in land animals facilitate gas exchange with air.