Liberalization, Privatization & Globalization
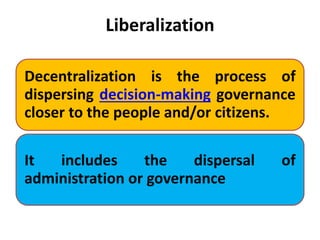
This document defines key terms like liberalization, privatization, disinvestment and globalization. It discusses how decentralization, privatizing state-owned businesses, and increasing international integration have contributed to globalization. Major organizations that facilitate globalization are identified as the IMF, World Bank and WTO, which aim to reduce trade barriers and establish rules for the global economy.