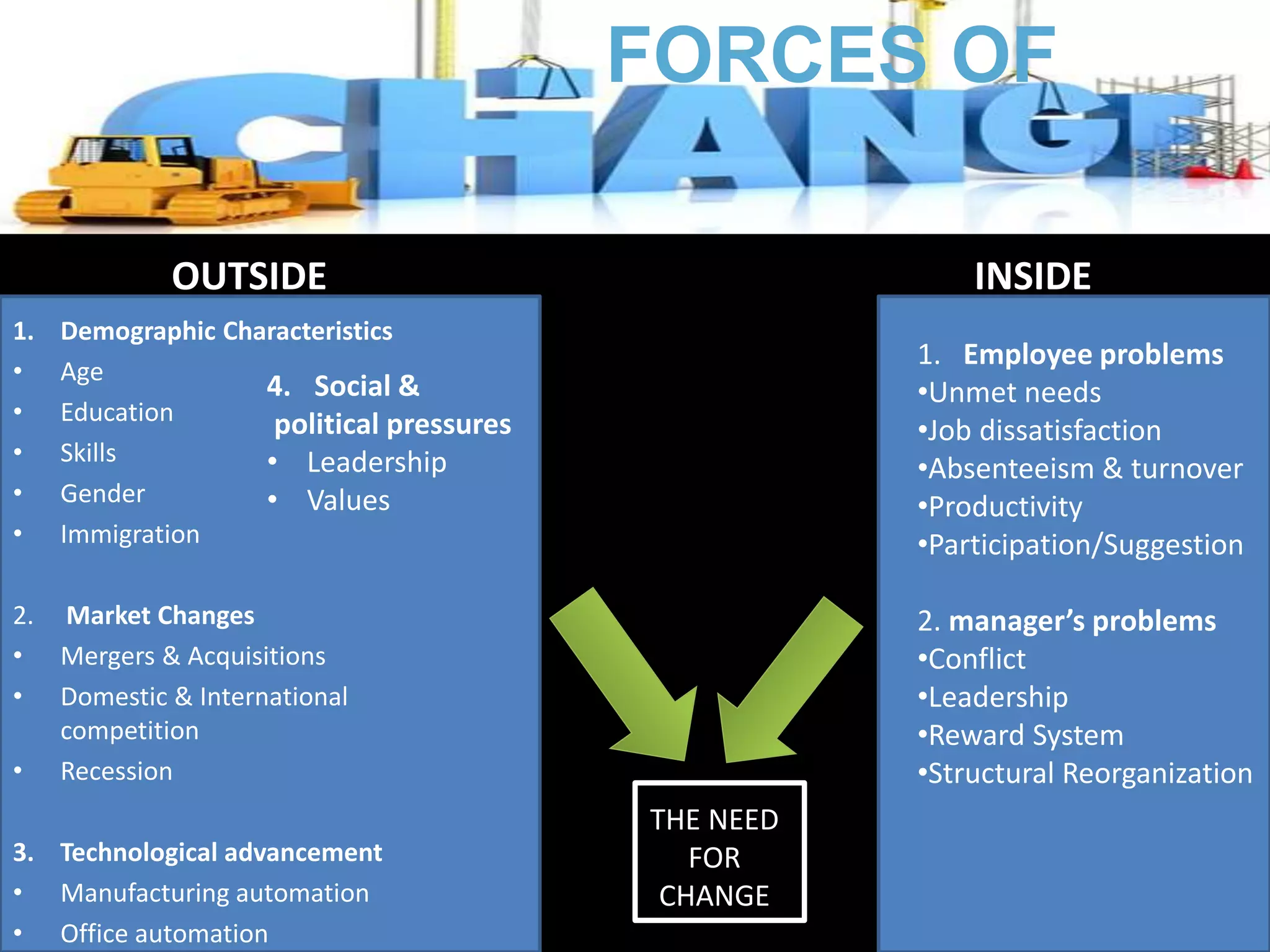
This document discusses organizational change and innovation. It outlines two types of change - reactive and proactive change. It also discusses forces of change inside and outside an organization, including demographic trends, market changes, technology, and social/political pressures. Areas where change is often needed include changing people, technology, structure, and strategy. The document then outlines models for organizational development, types of innovation (product, process, incremental, and radical), characteristics of innovation, fostering innovation, and leading organizational change using Lewin's change model and eight steps.