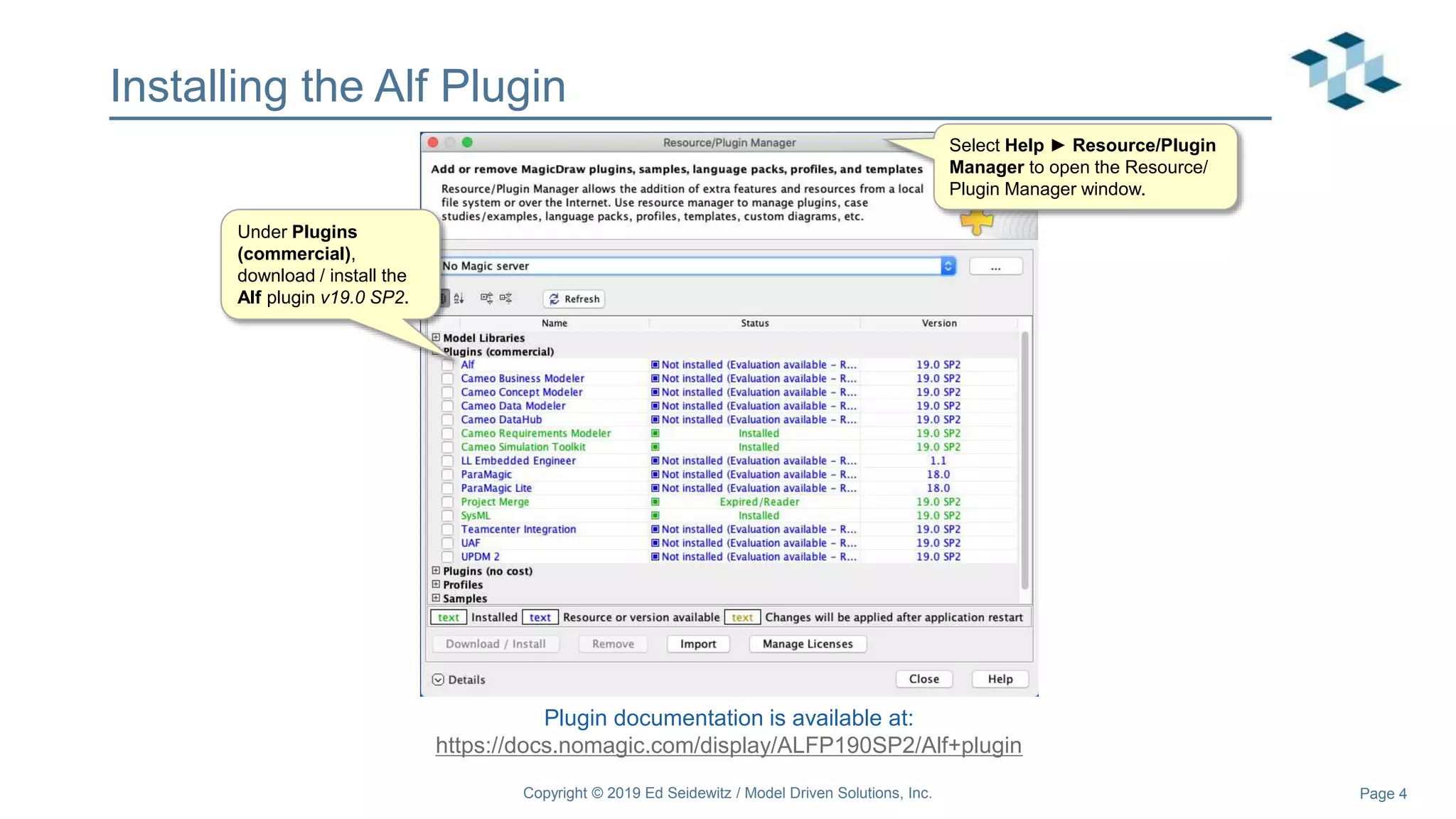
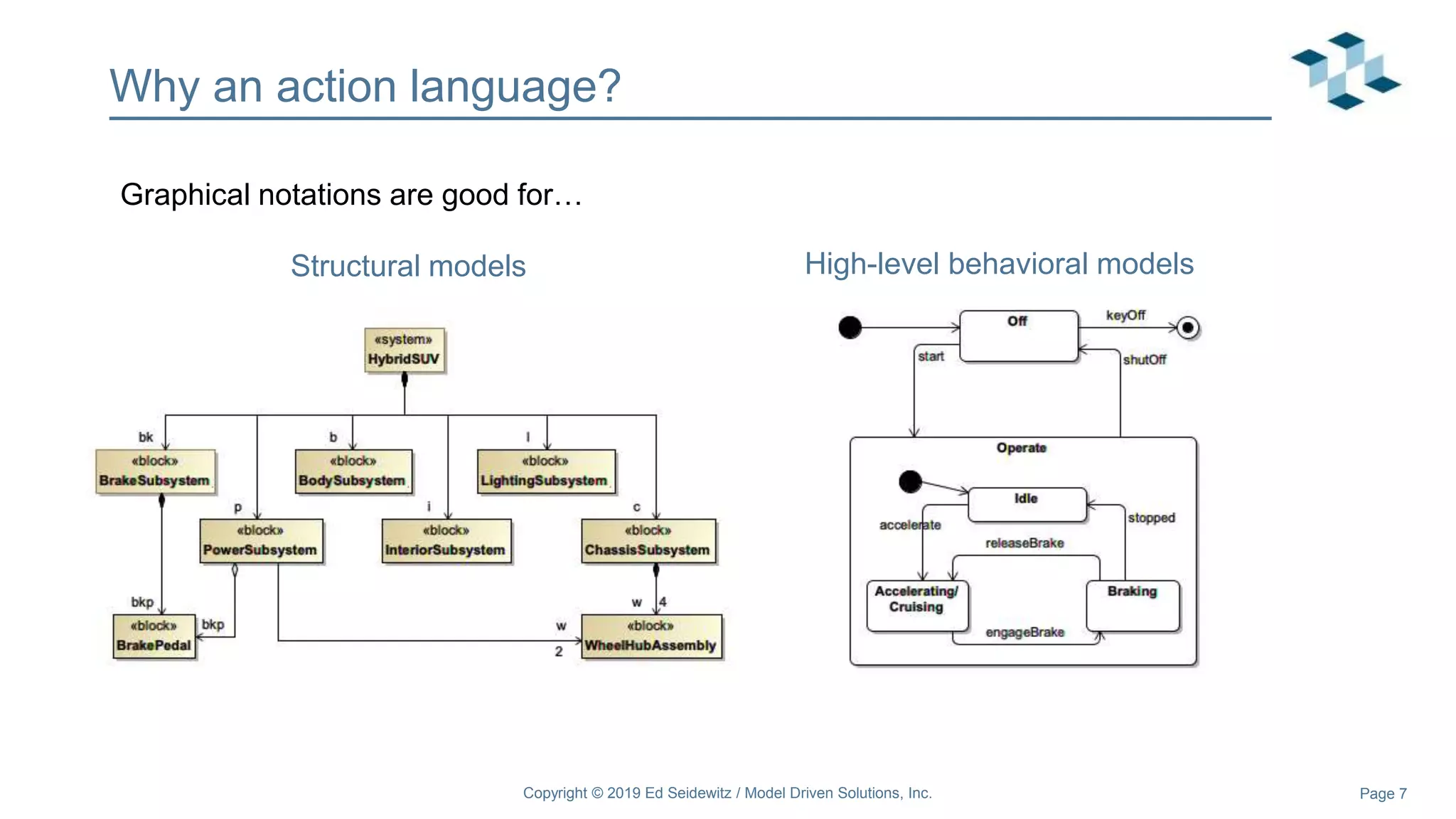
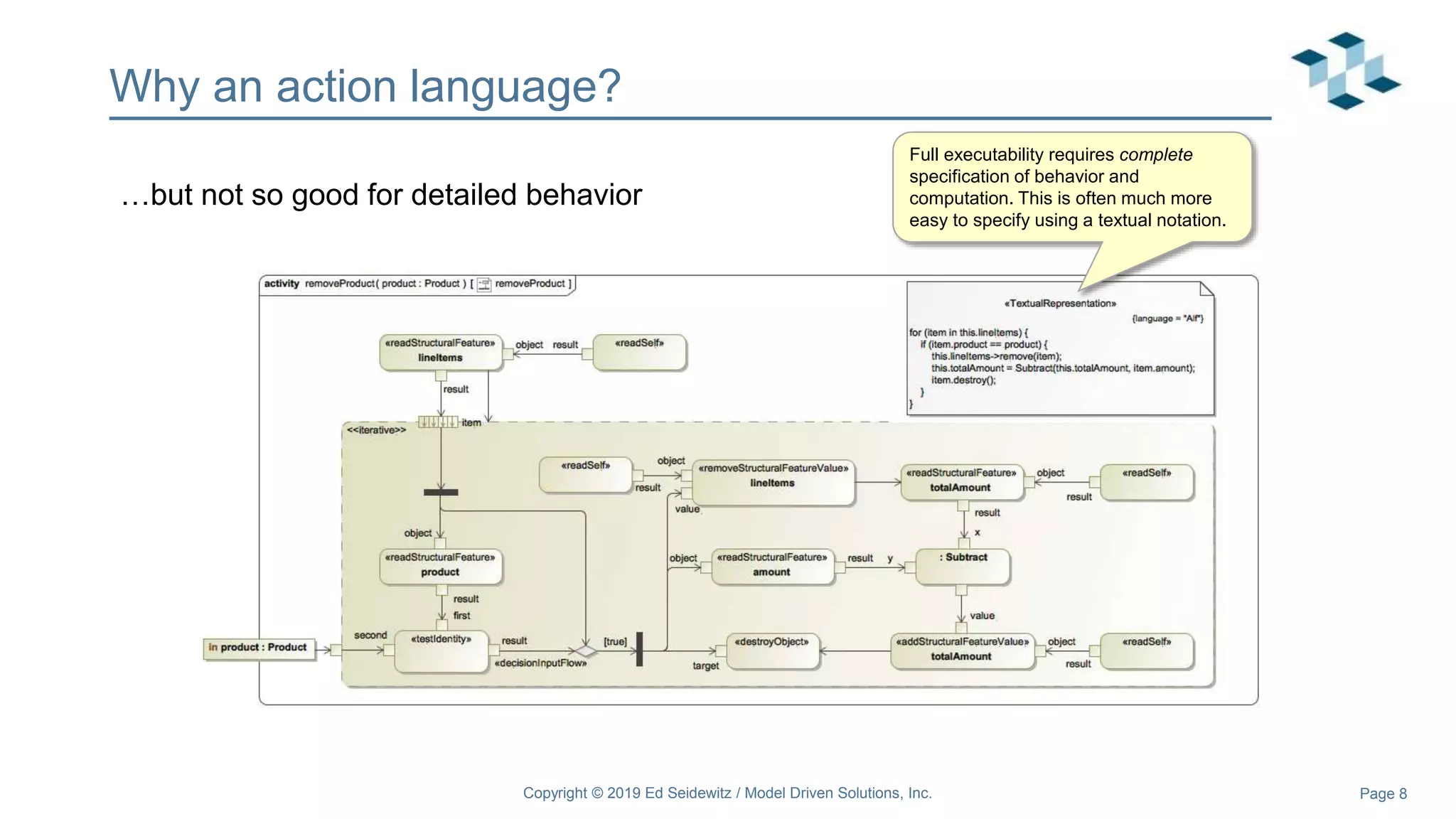
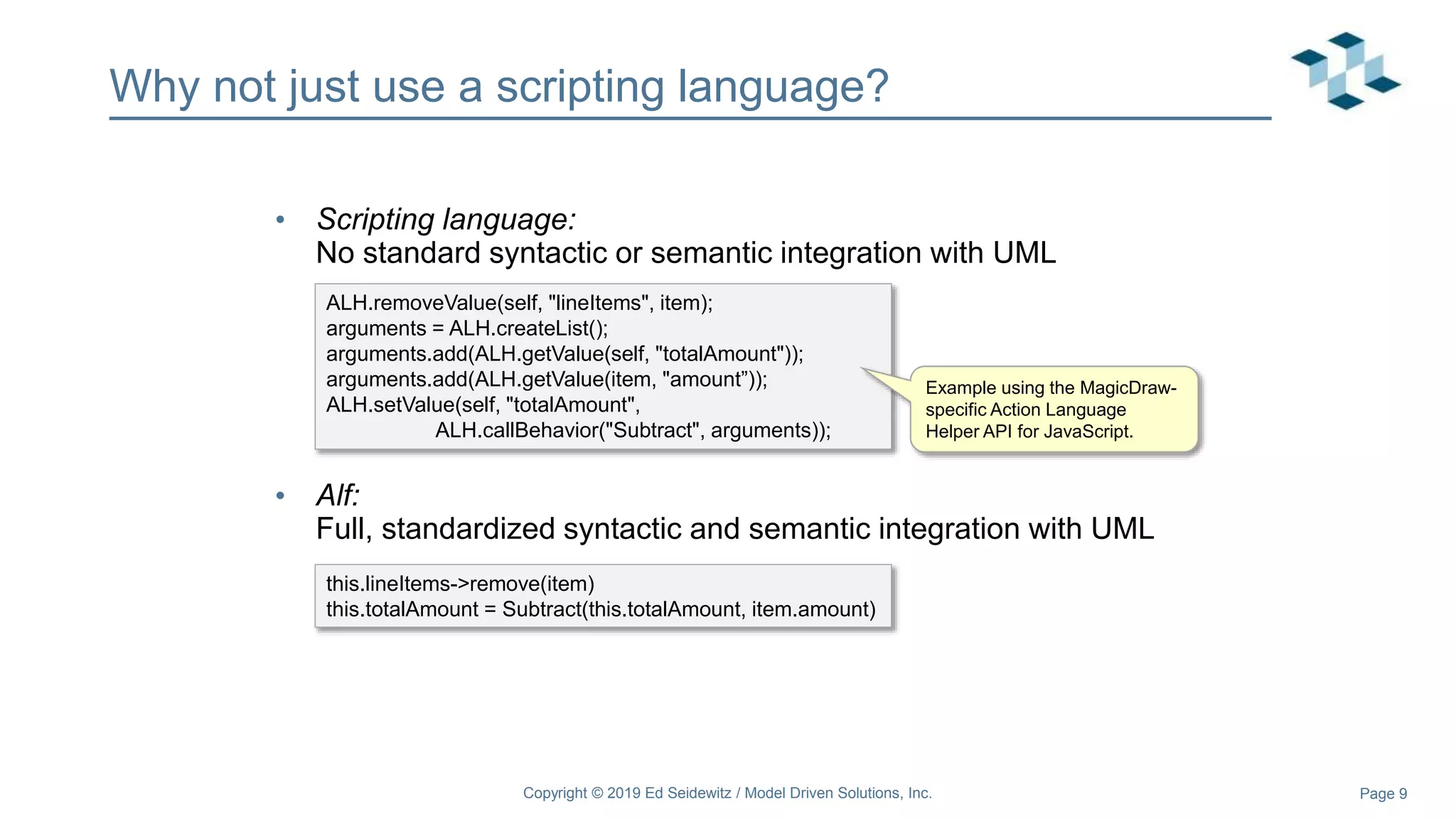
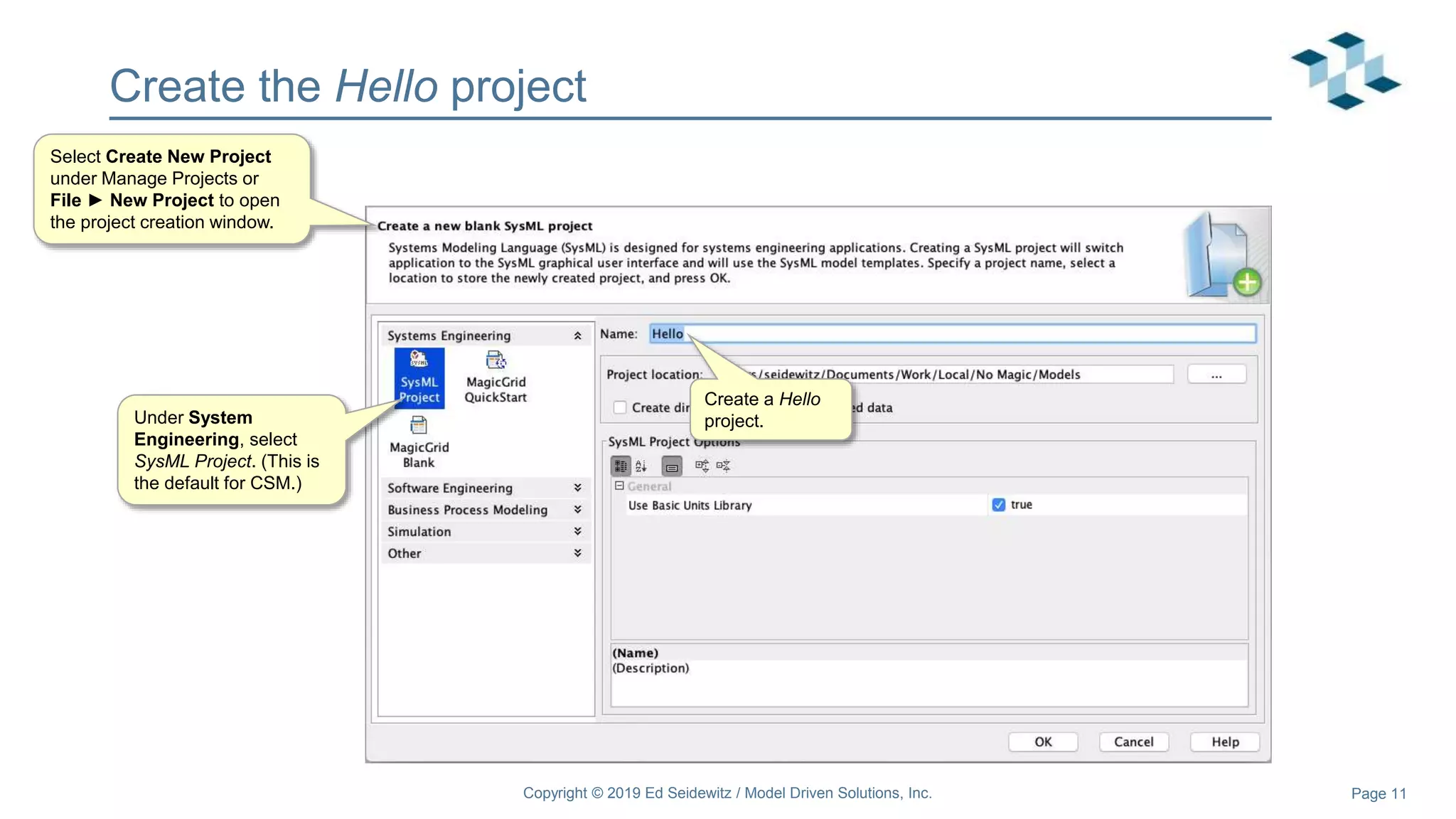
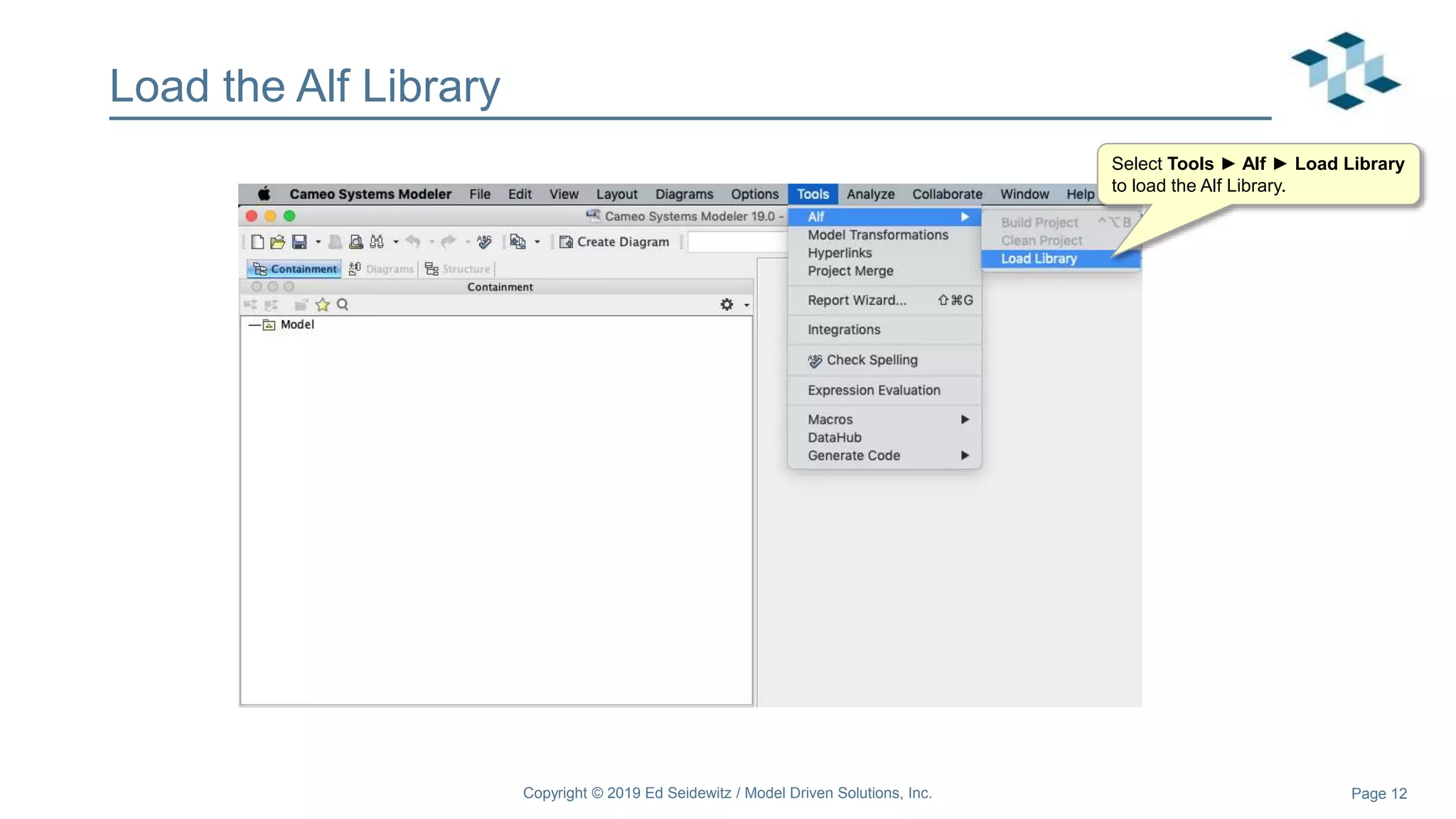
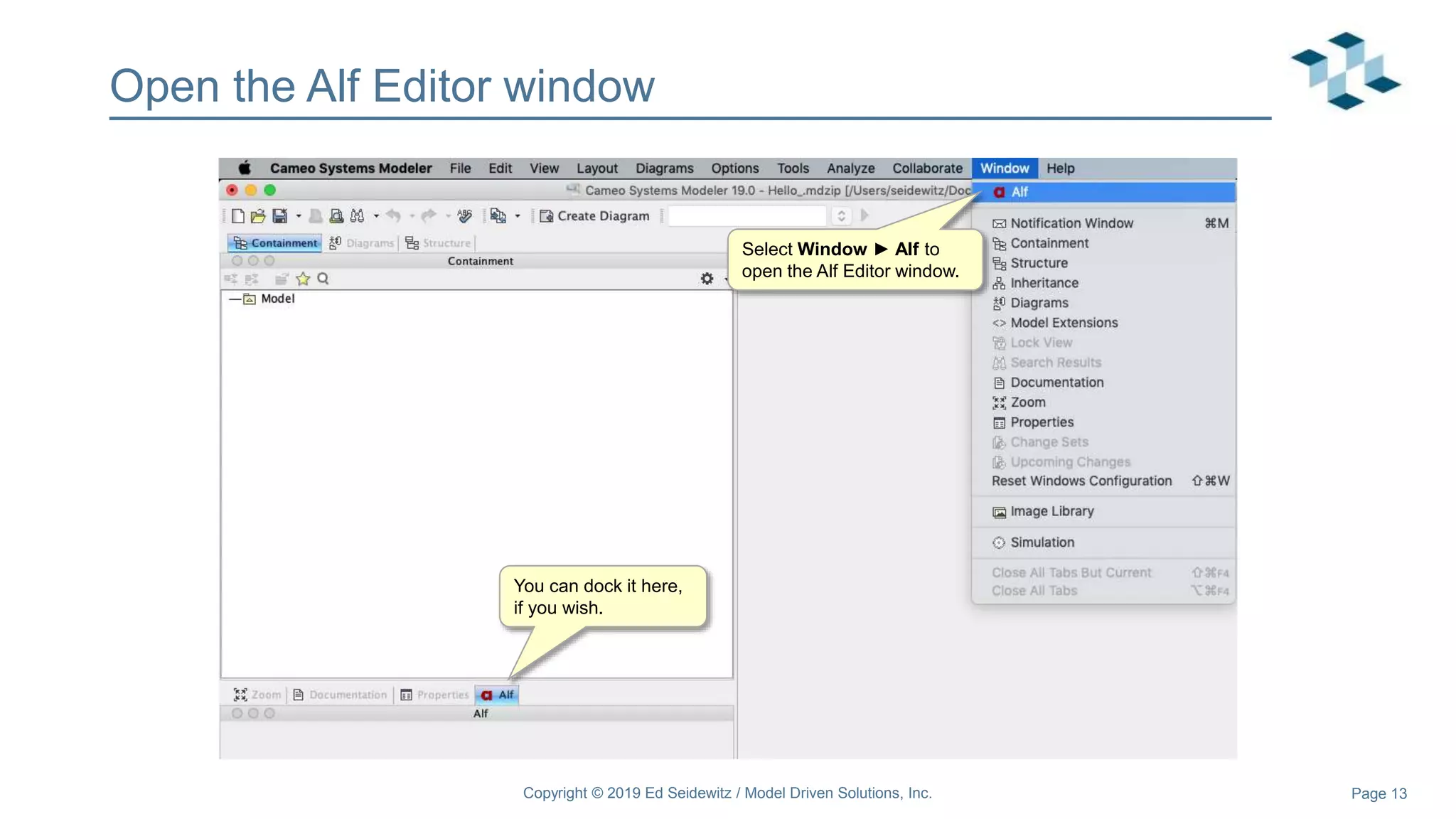
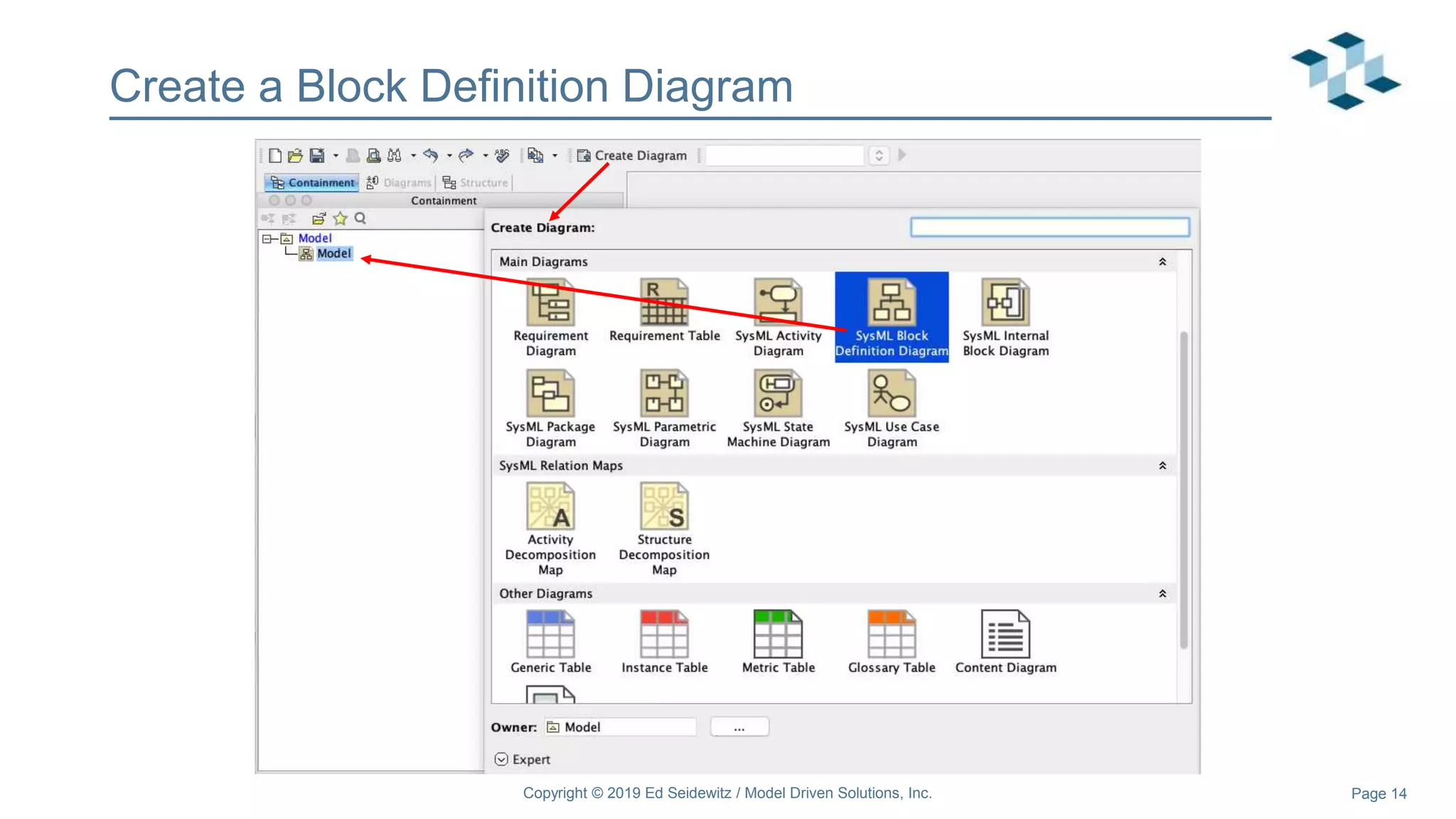
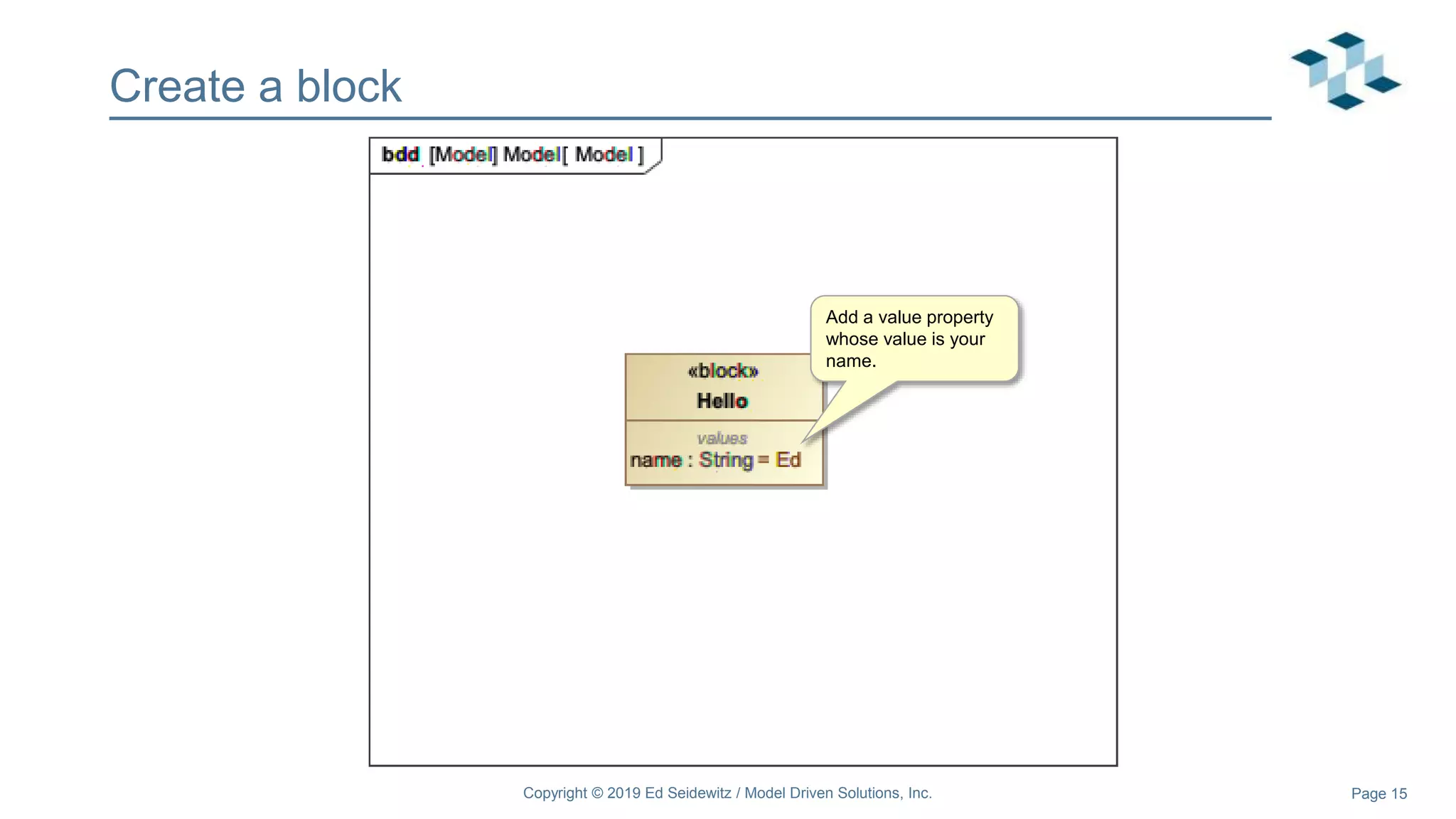
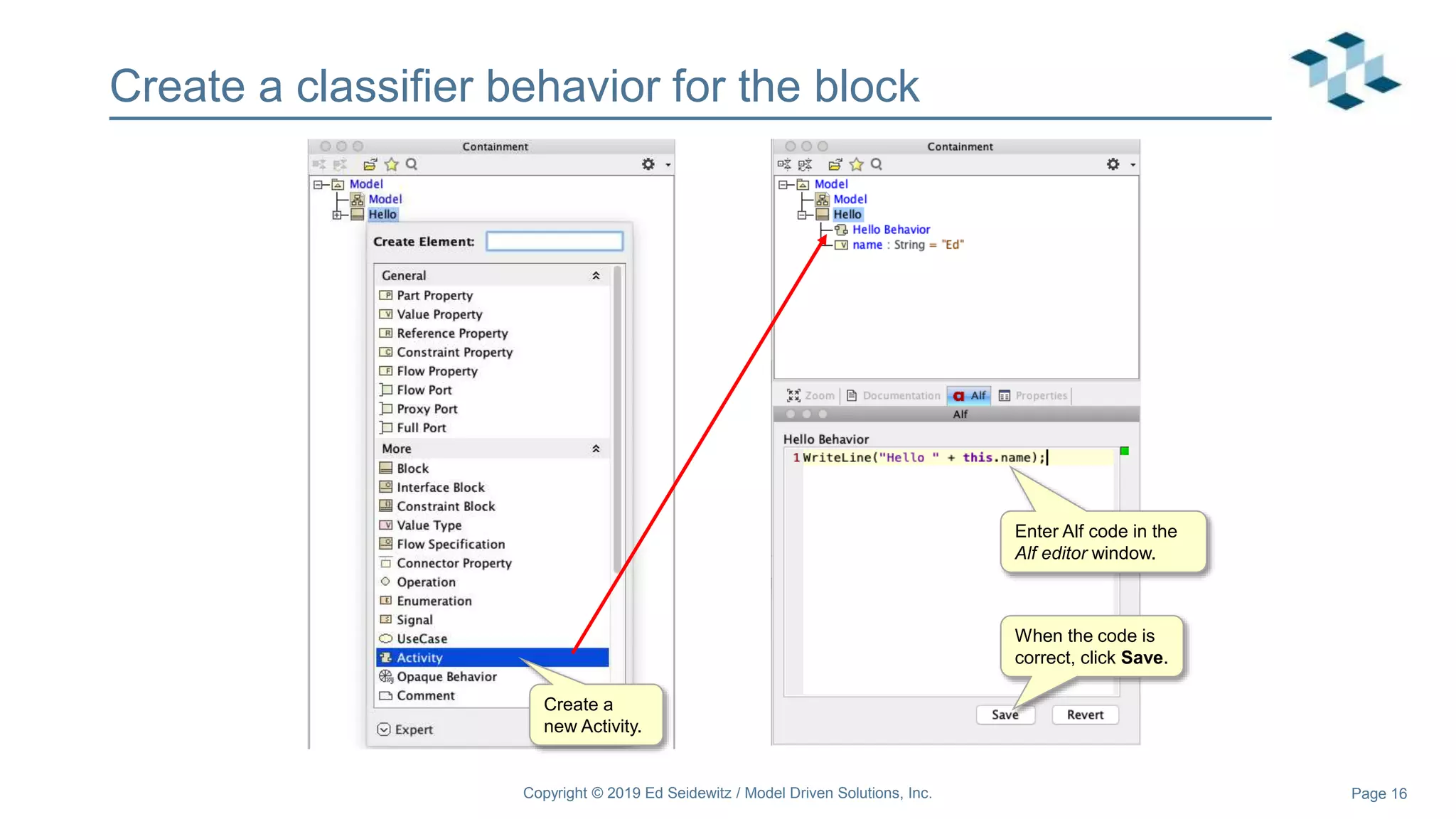
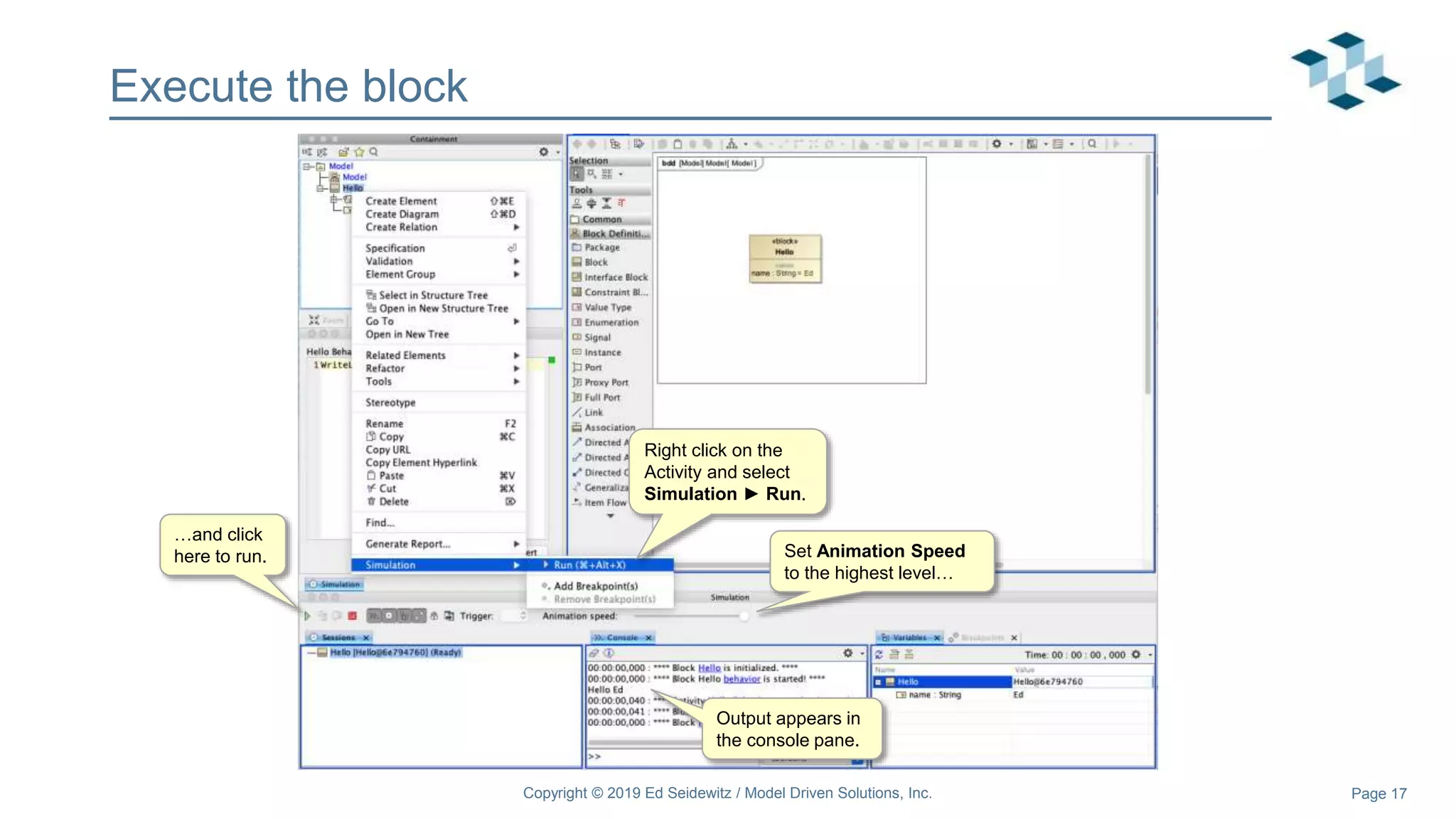
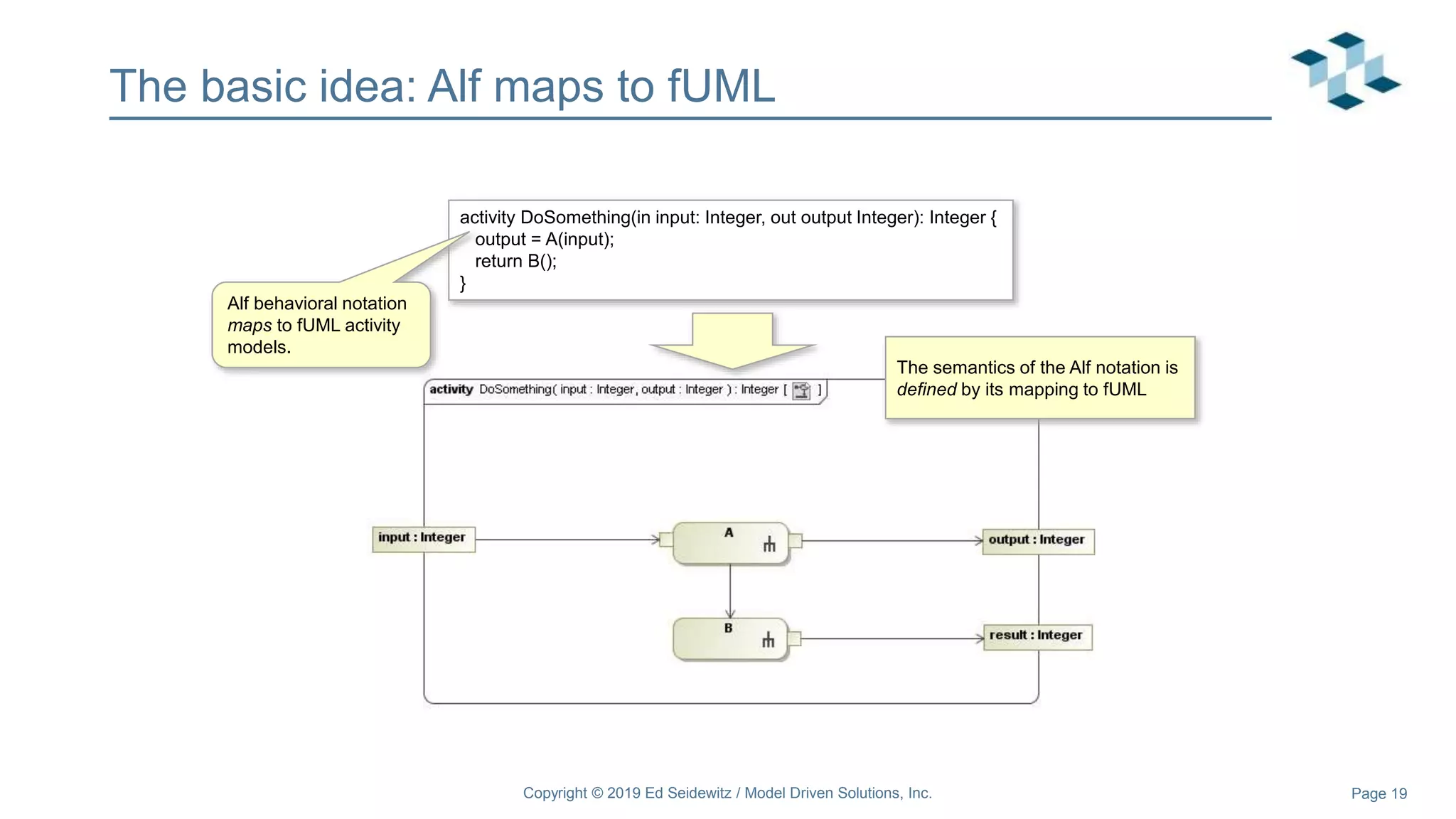
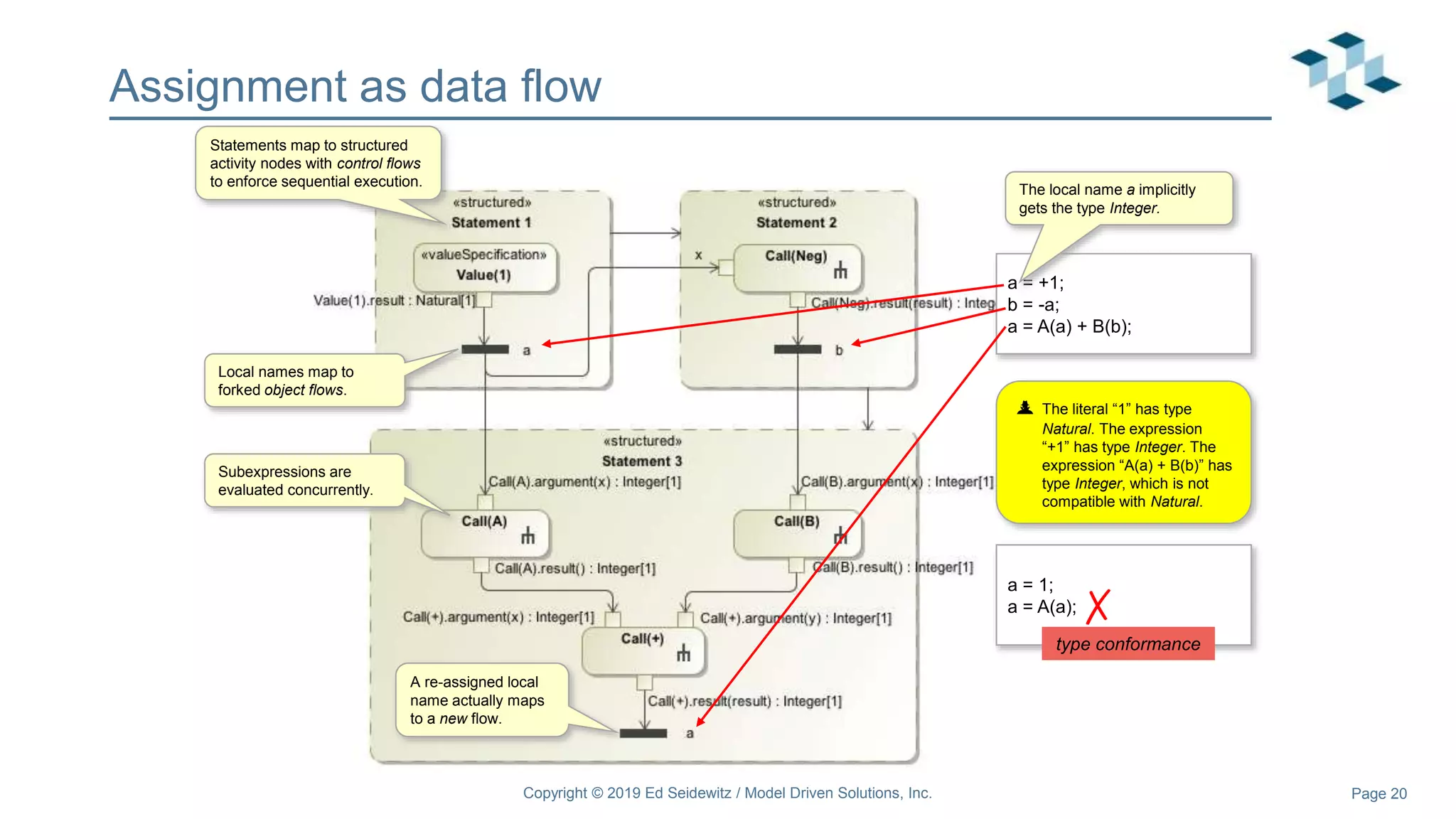
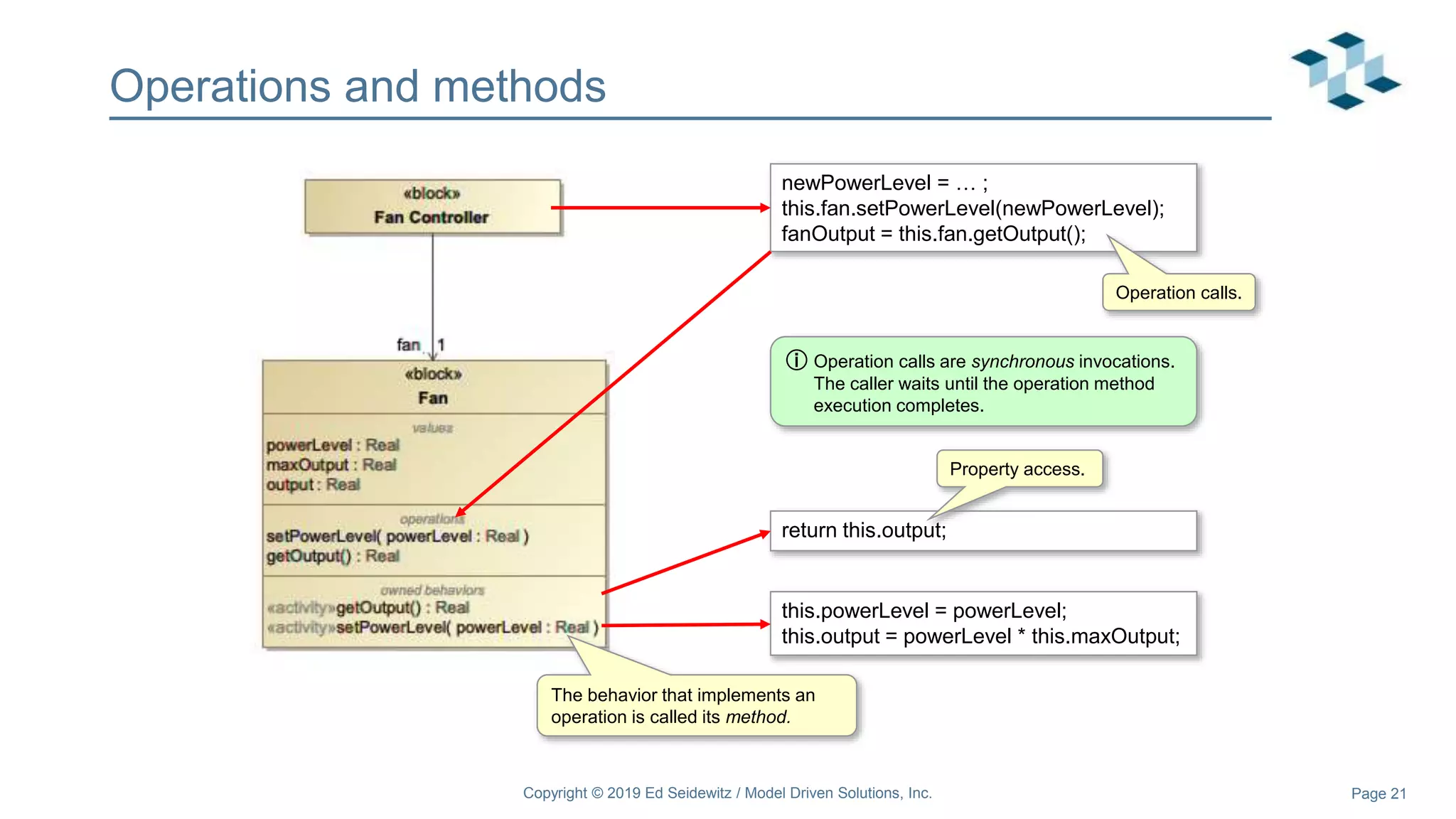
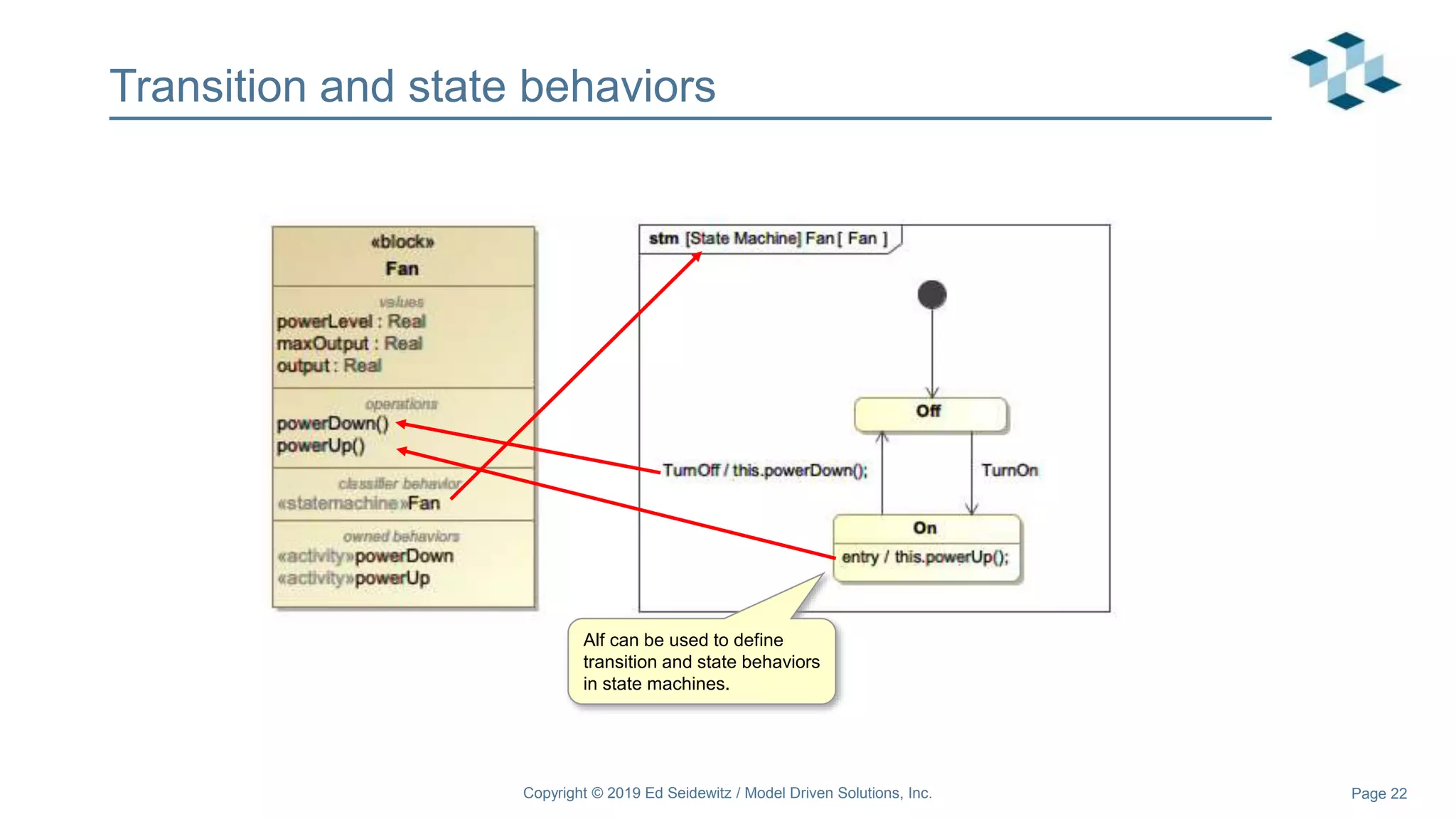
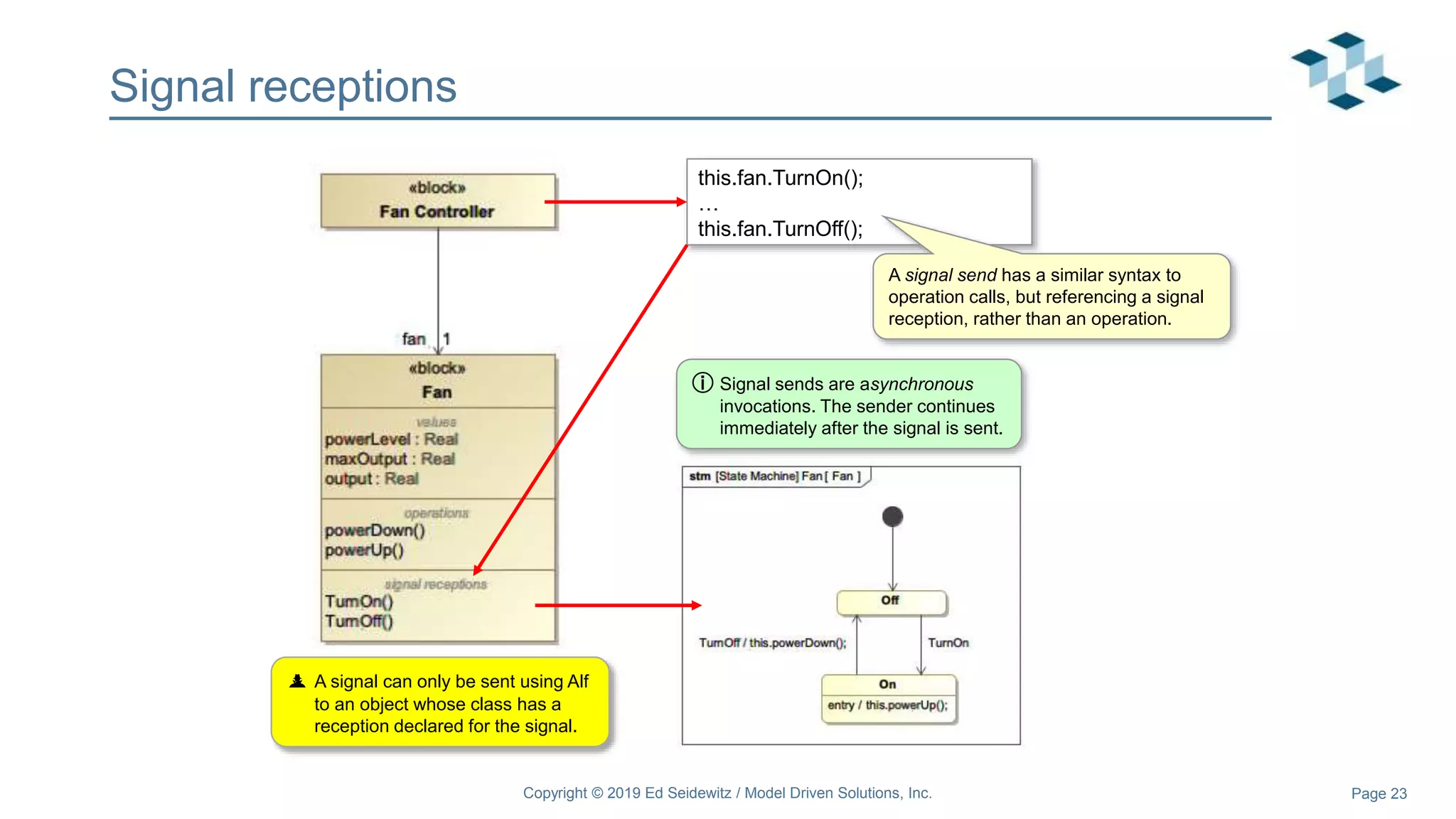
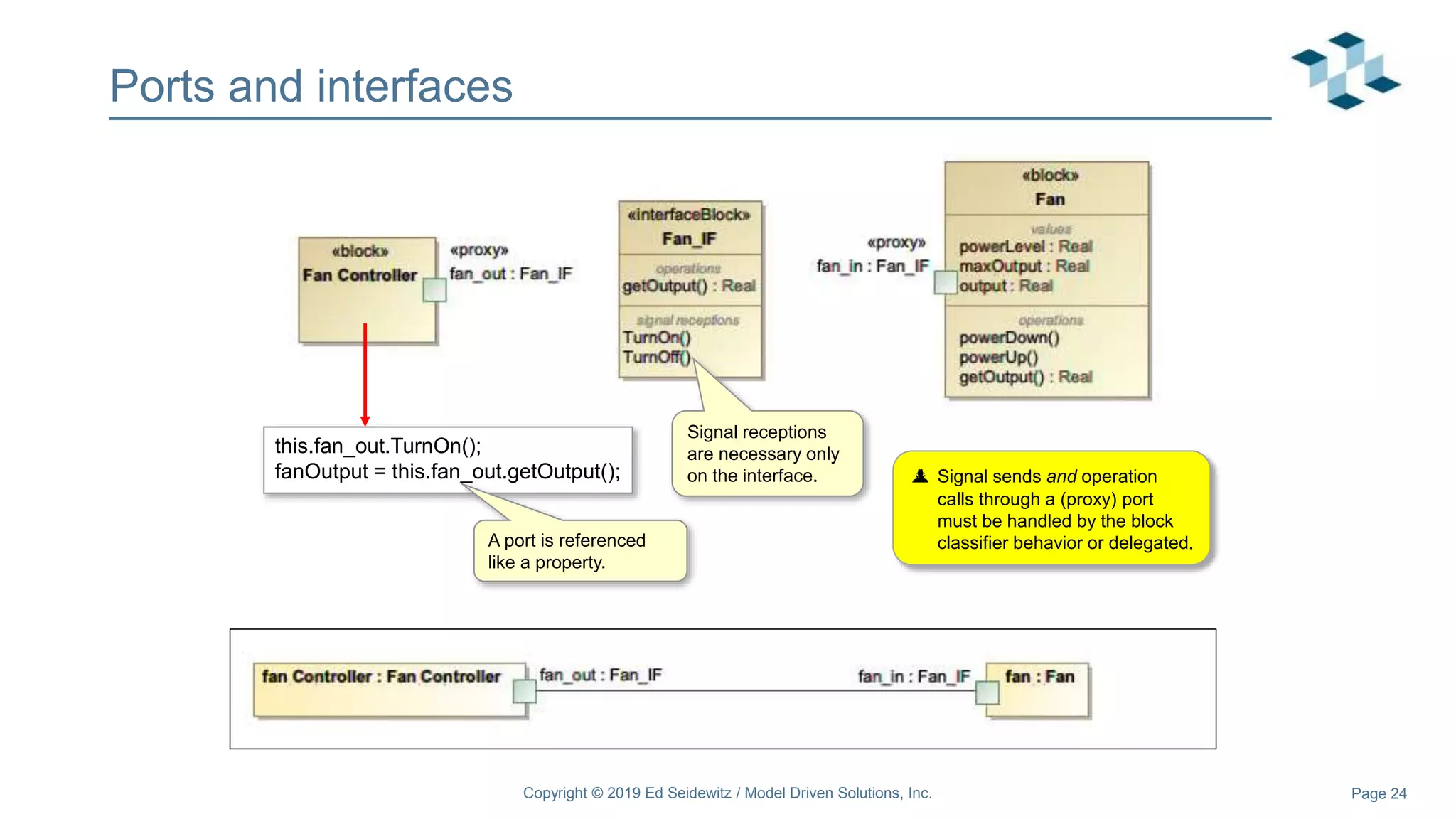
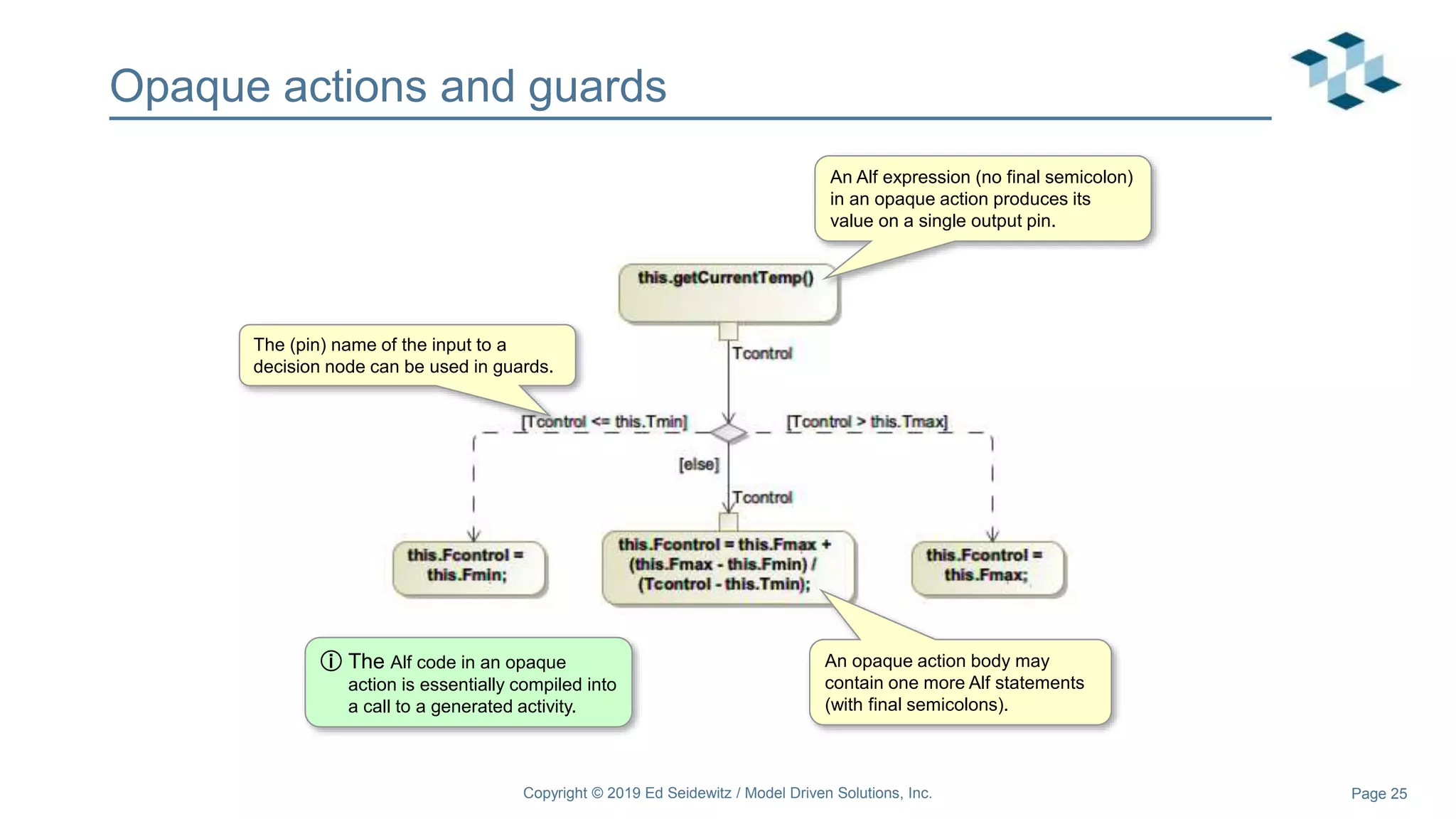
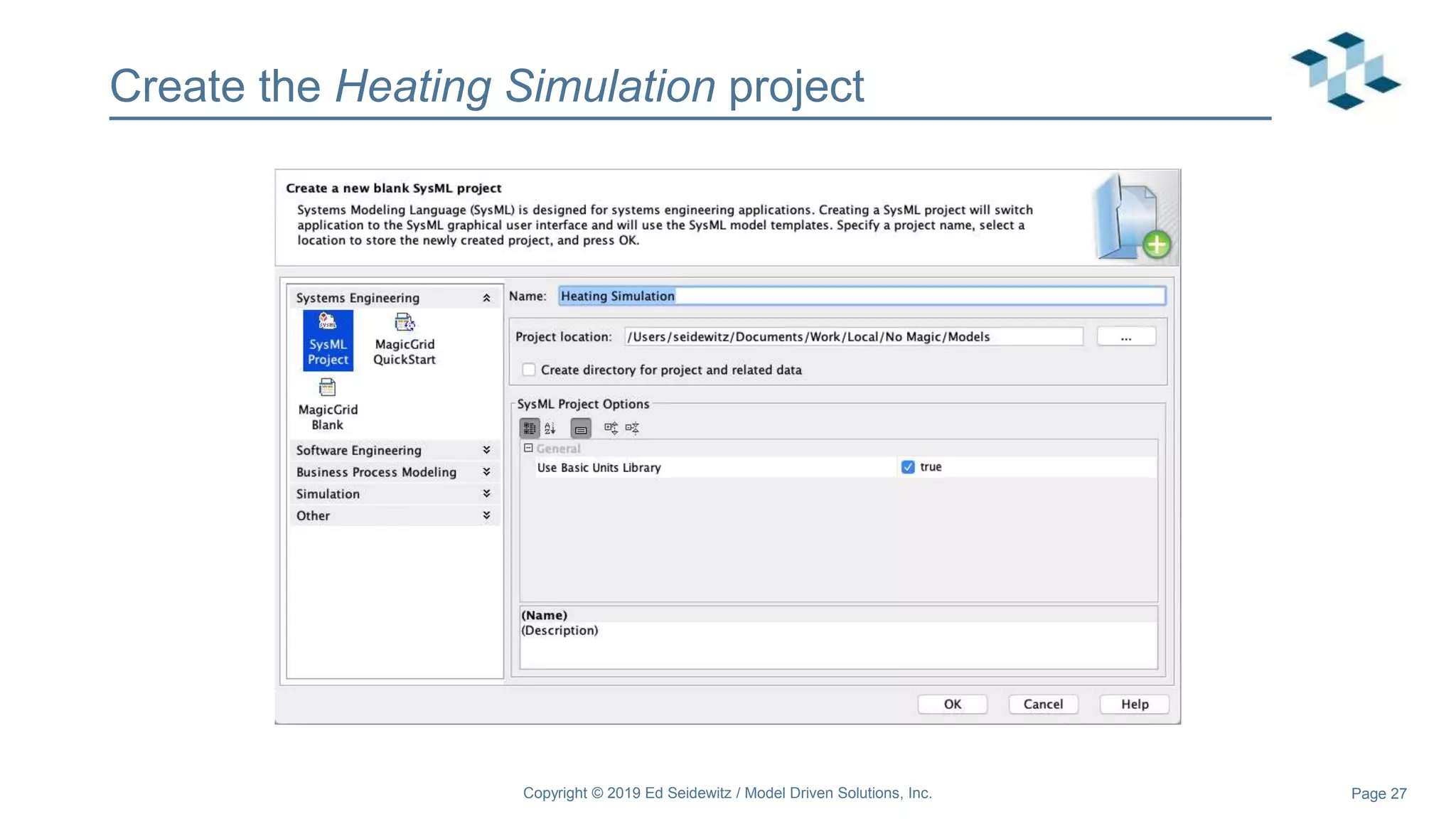
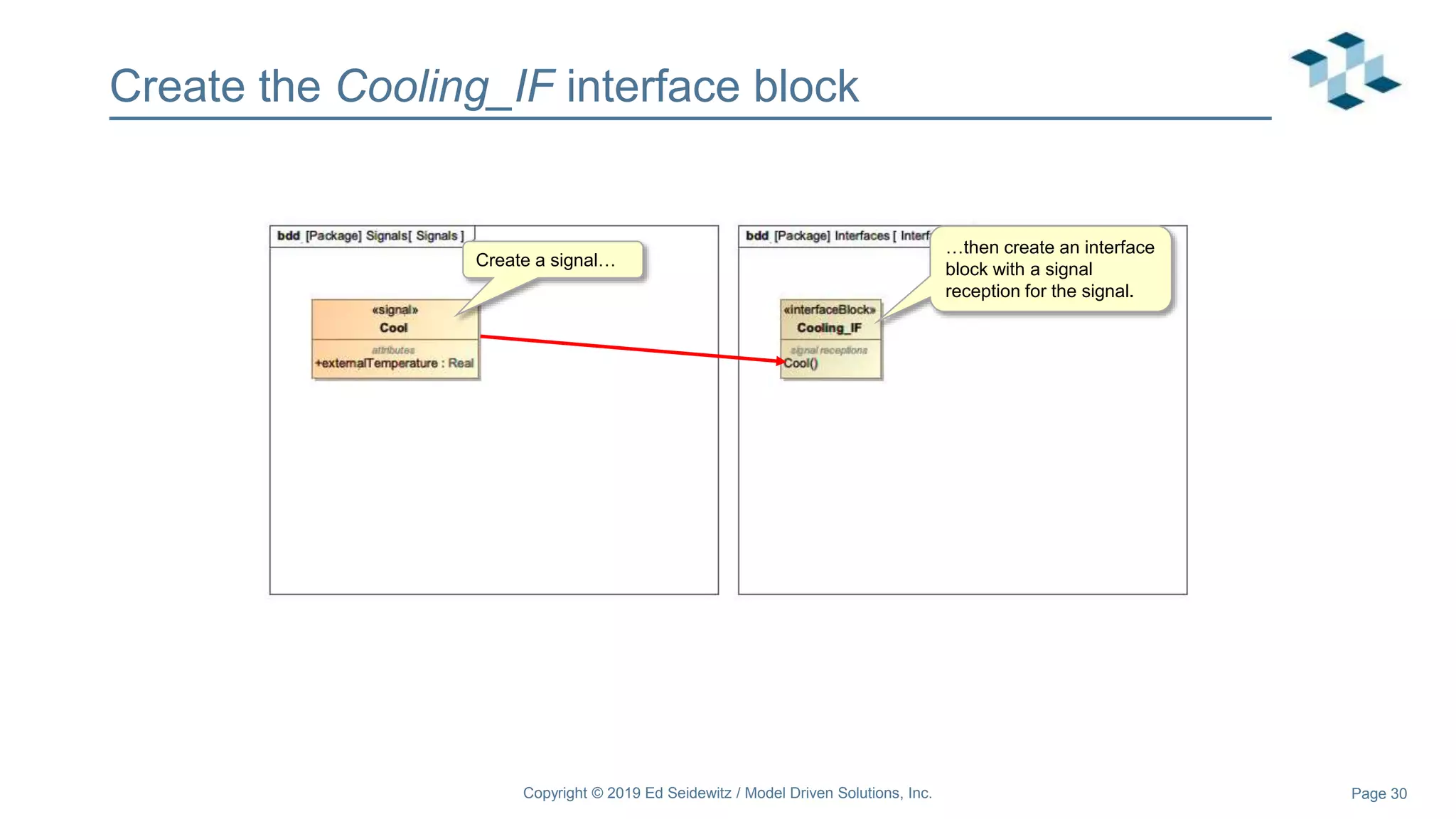
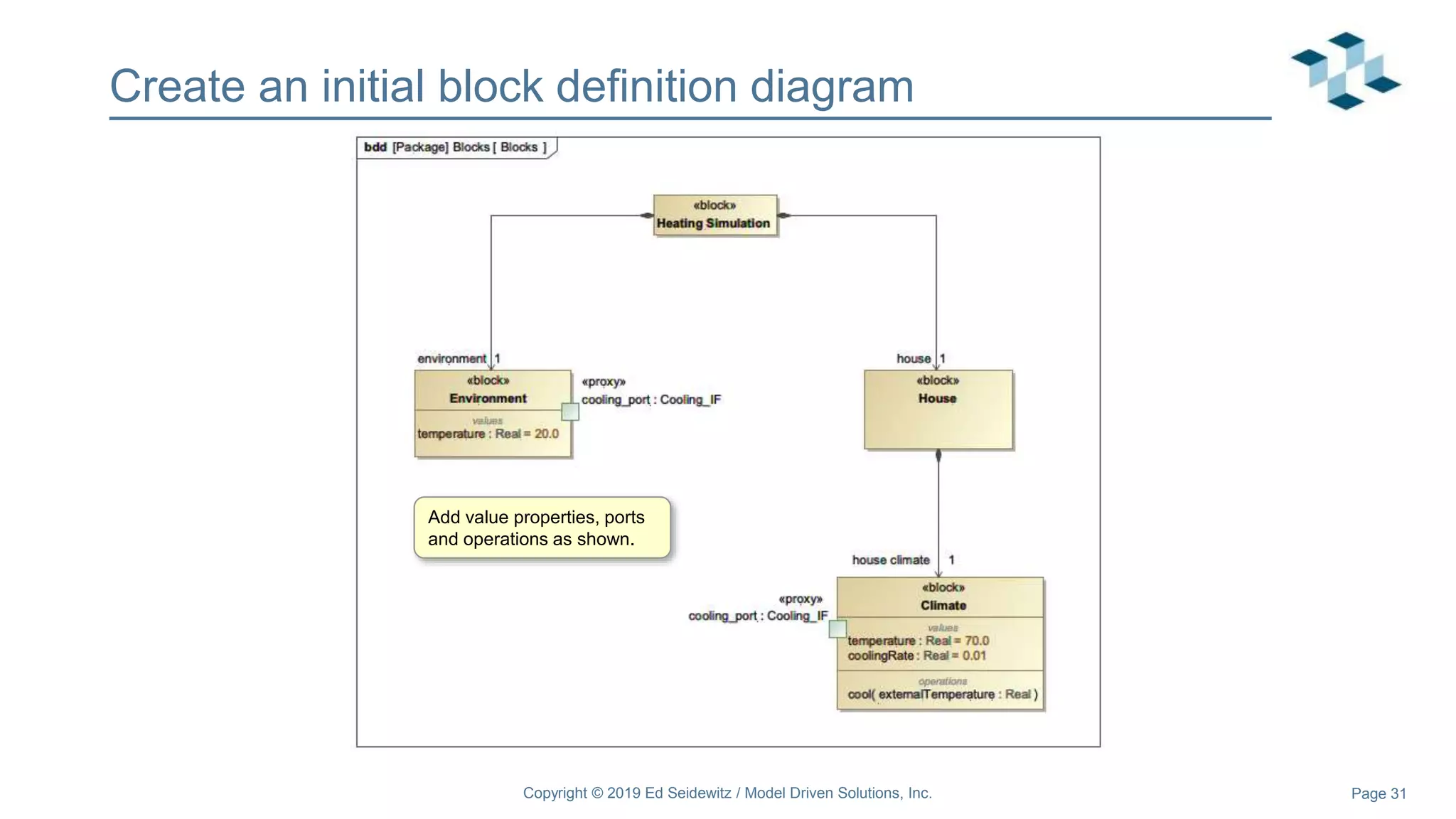
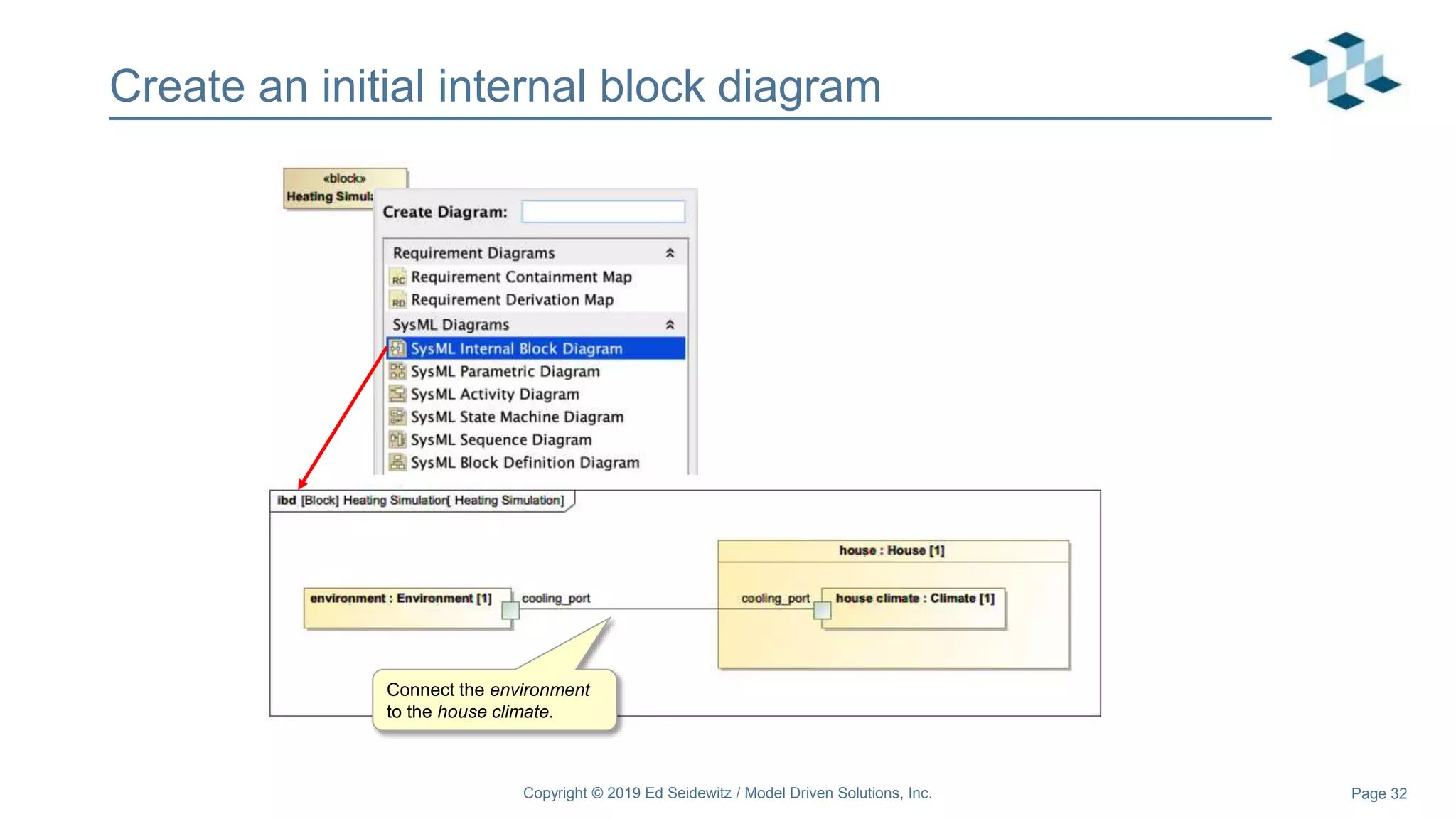
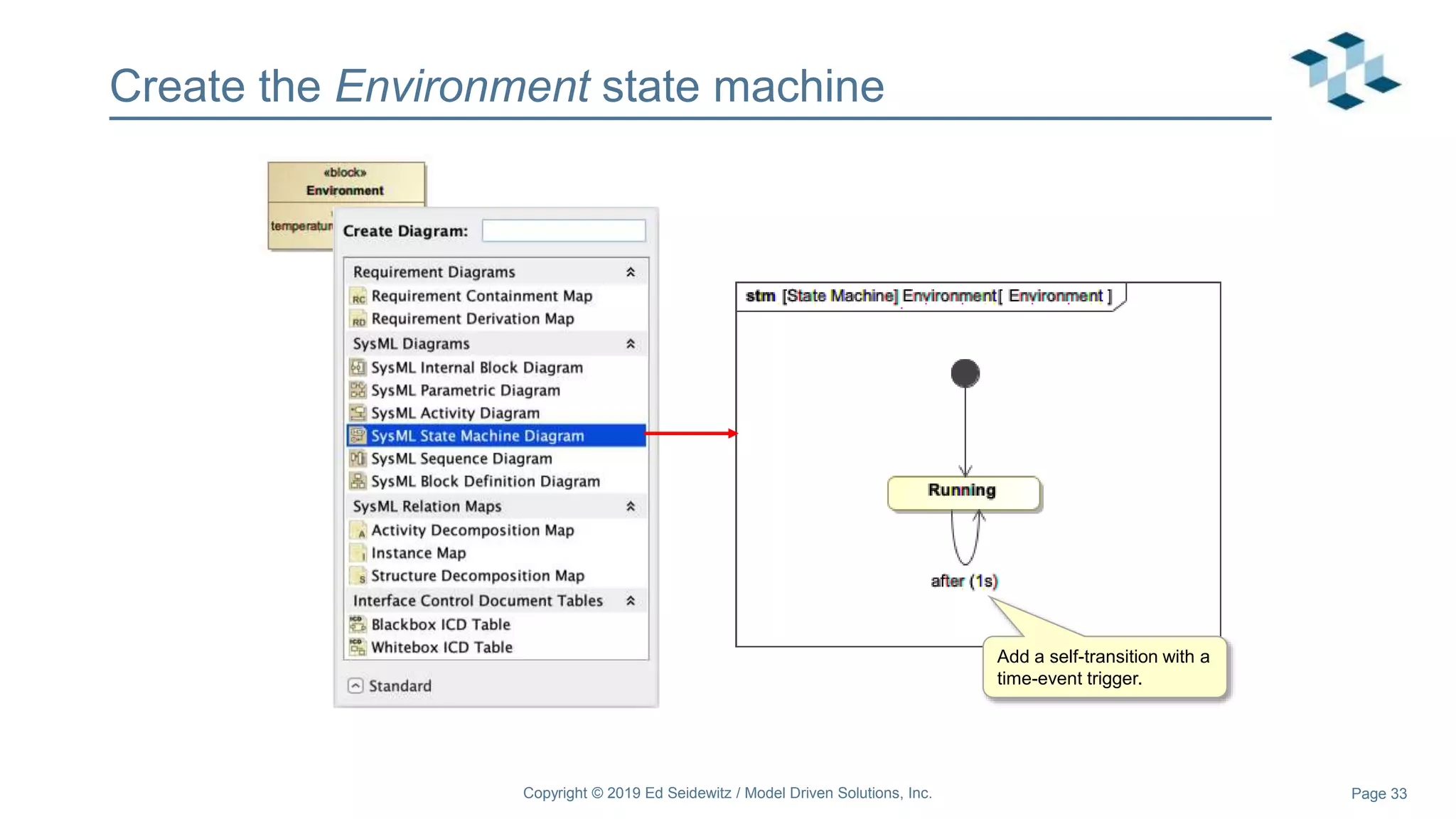
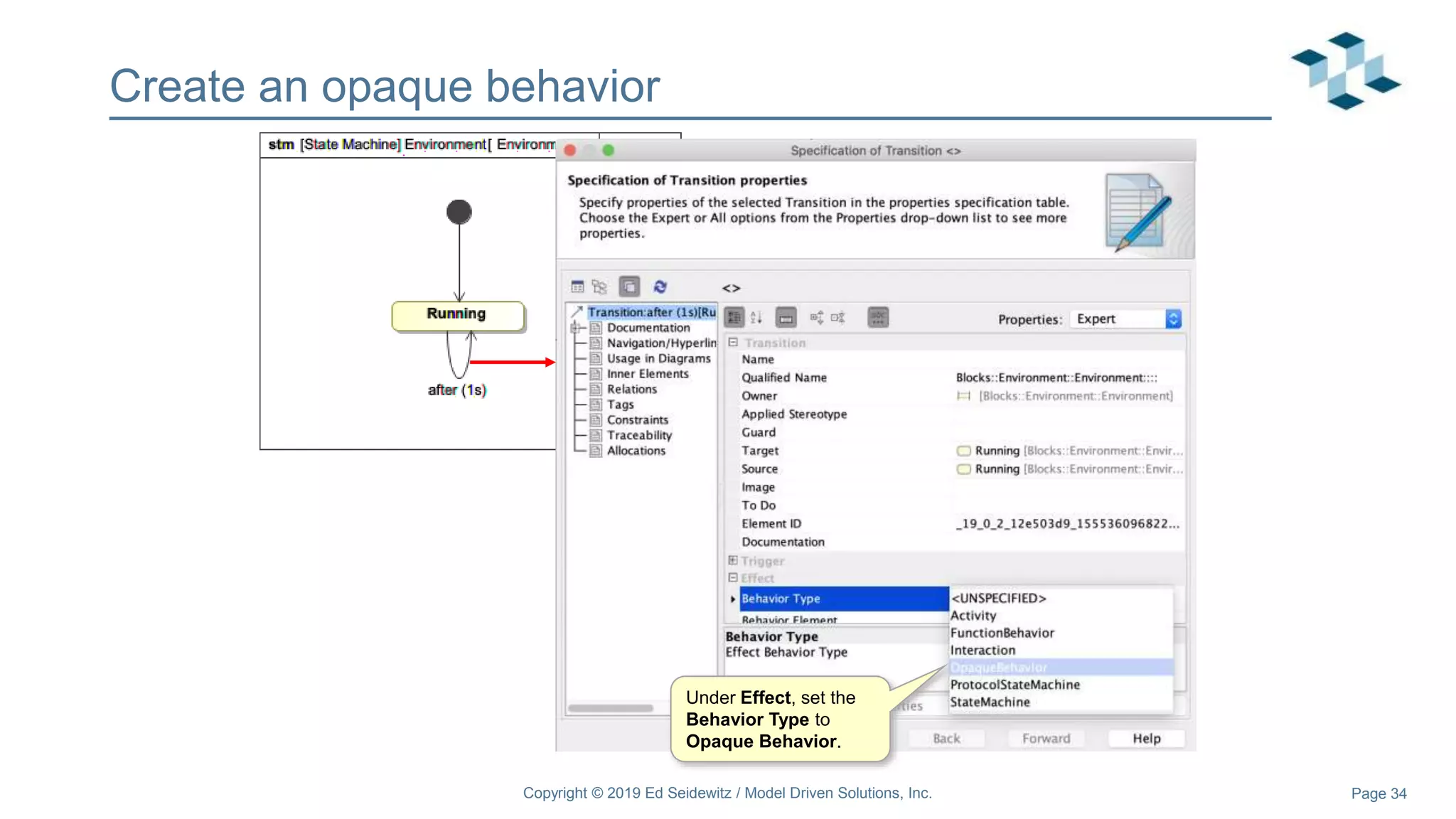
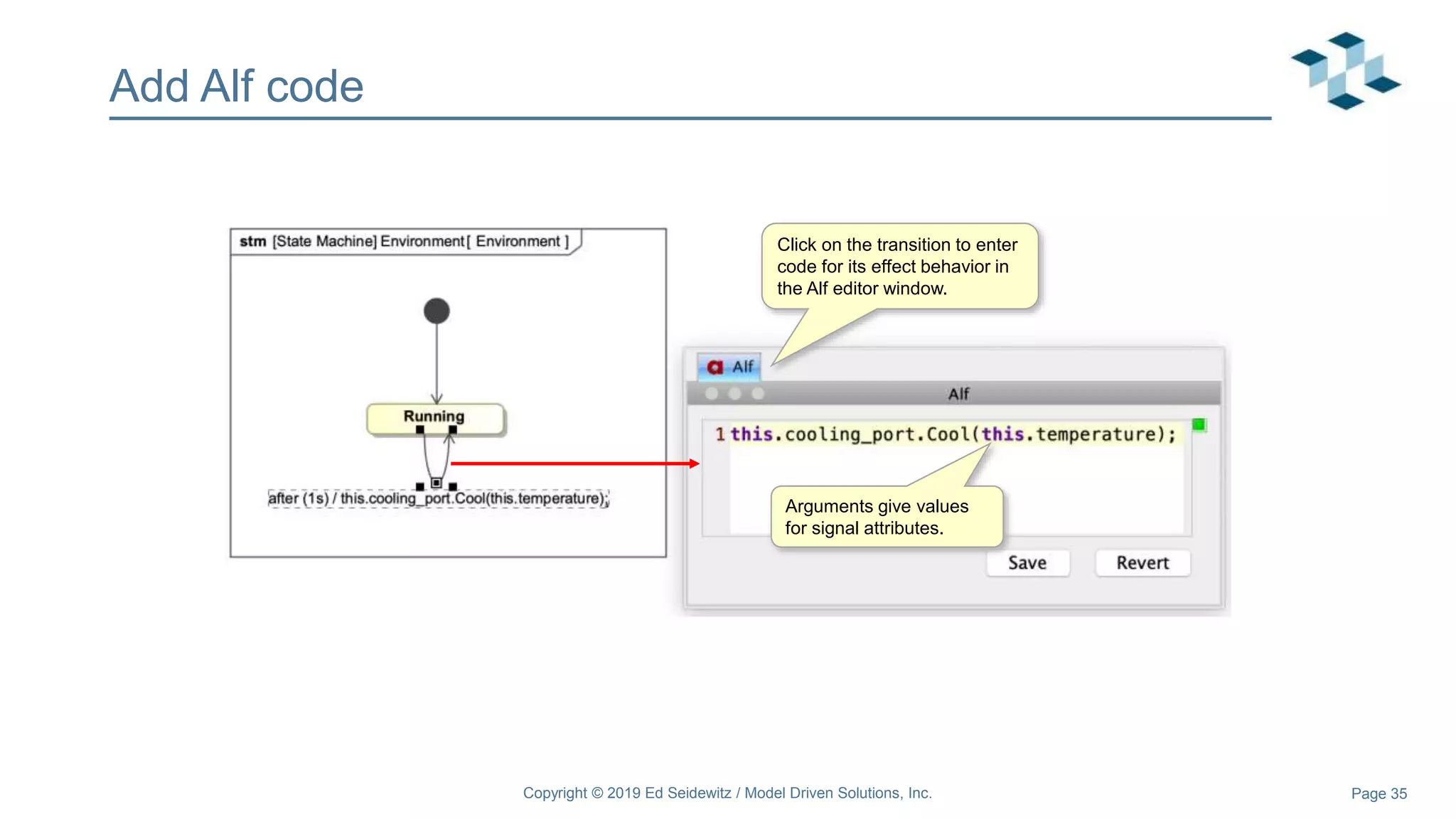
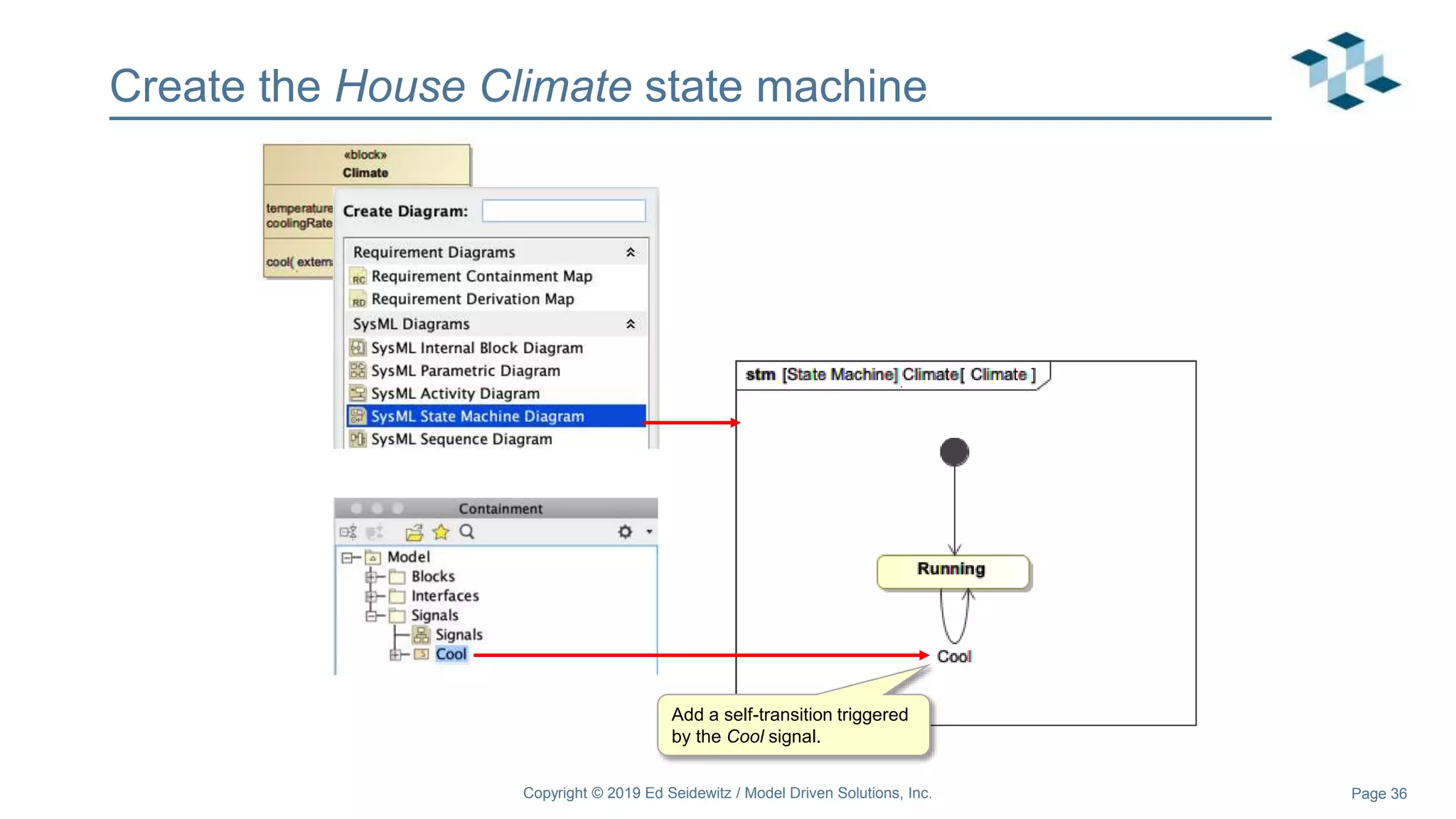
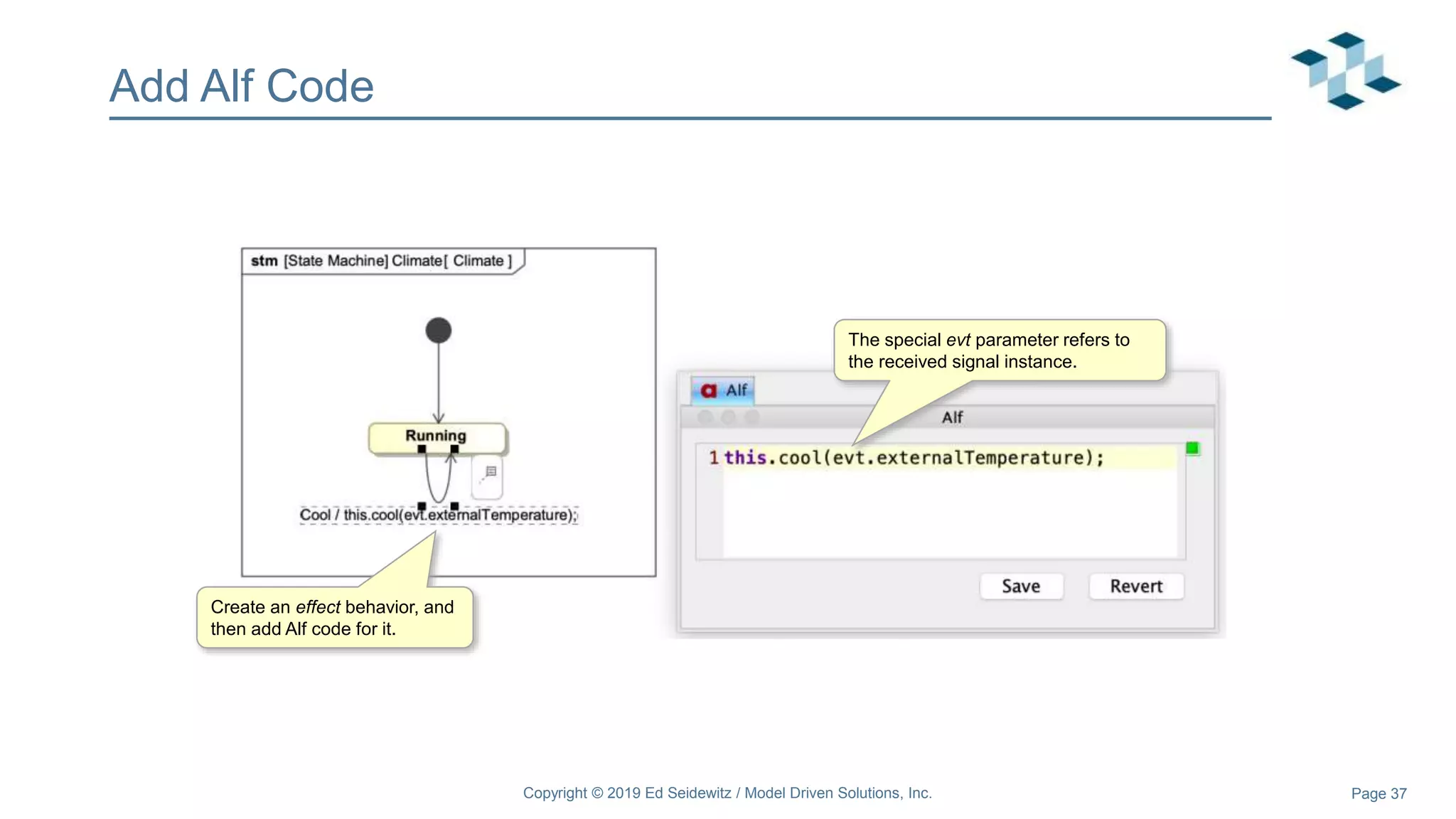
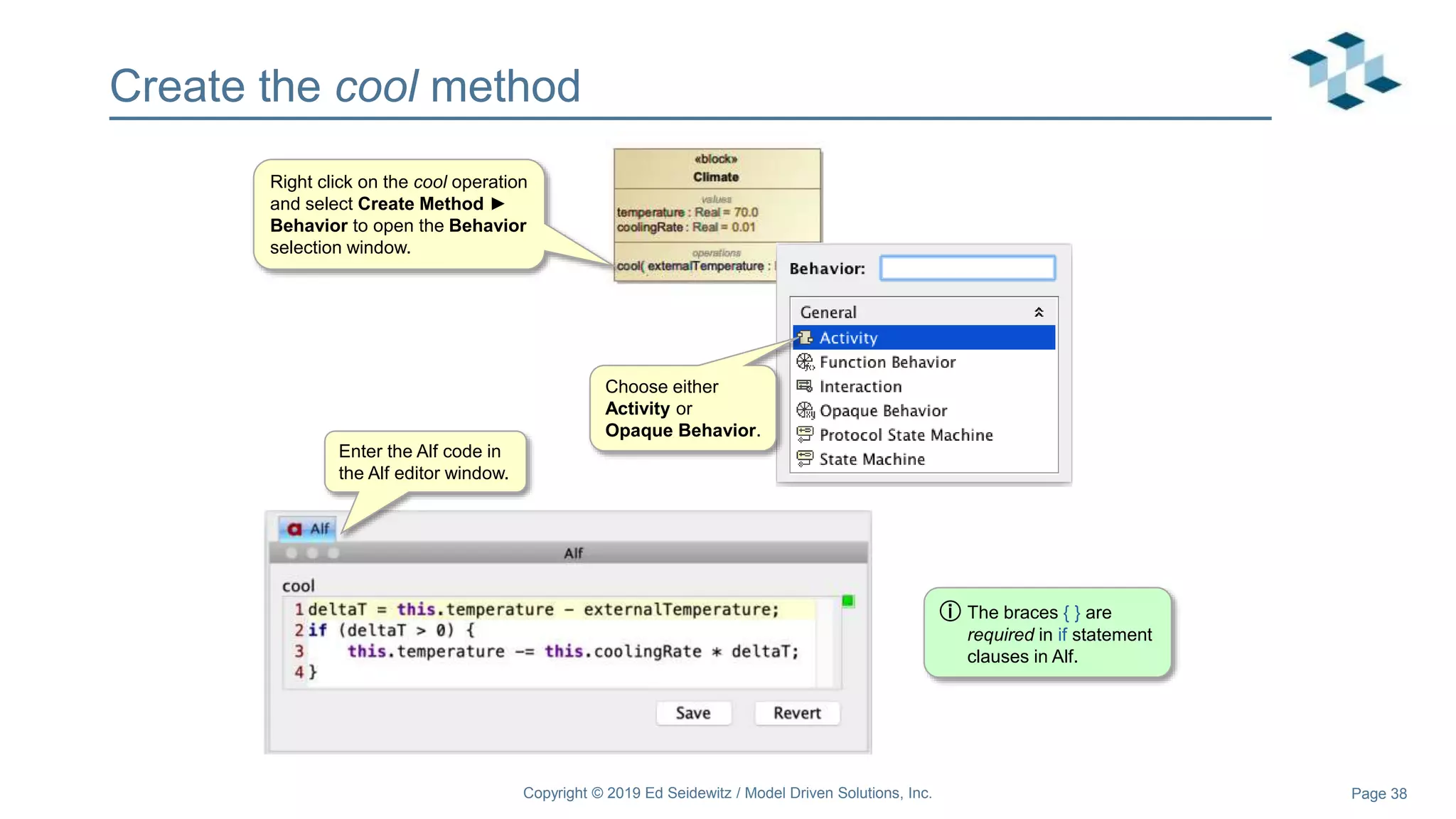
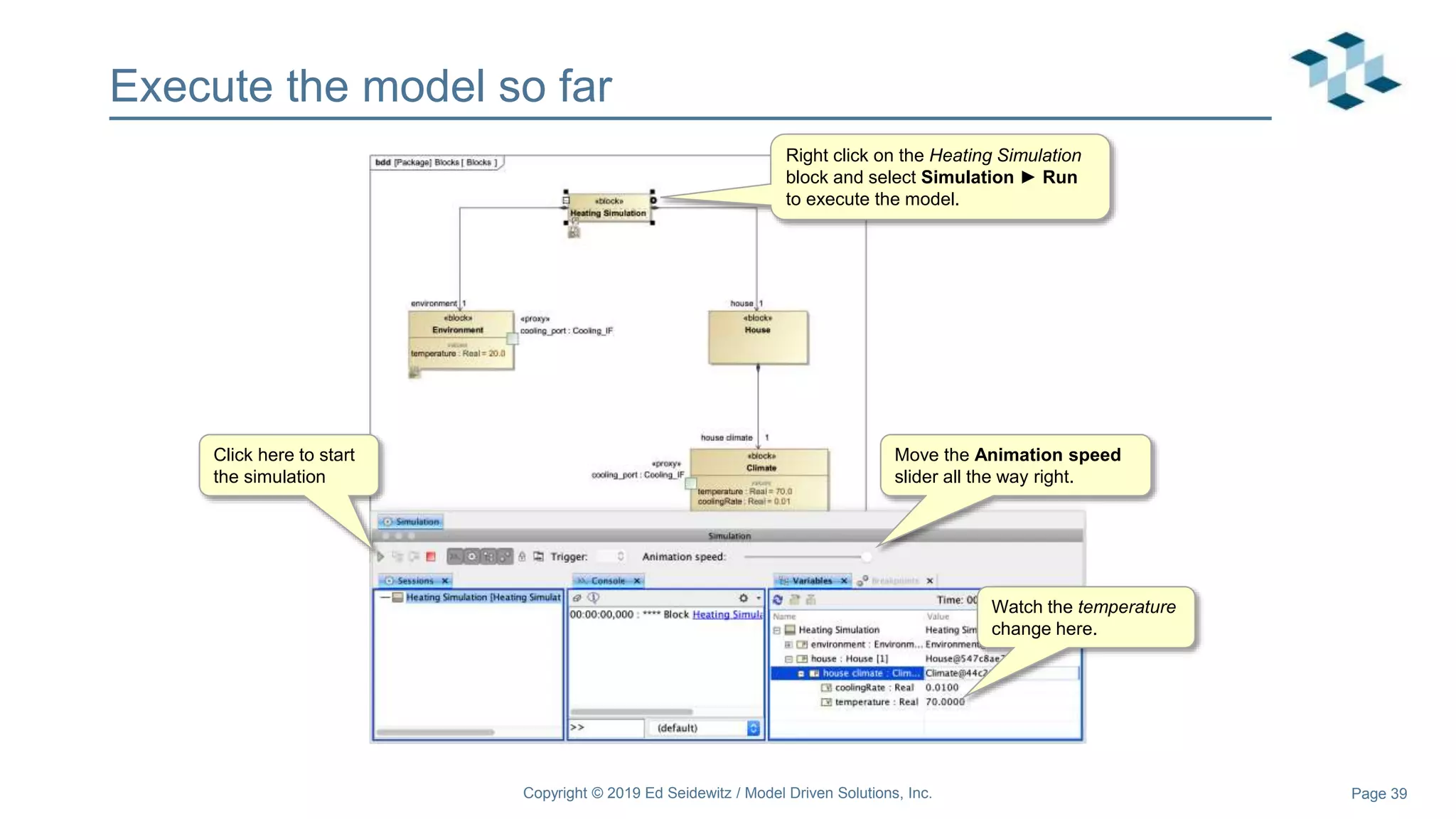
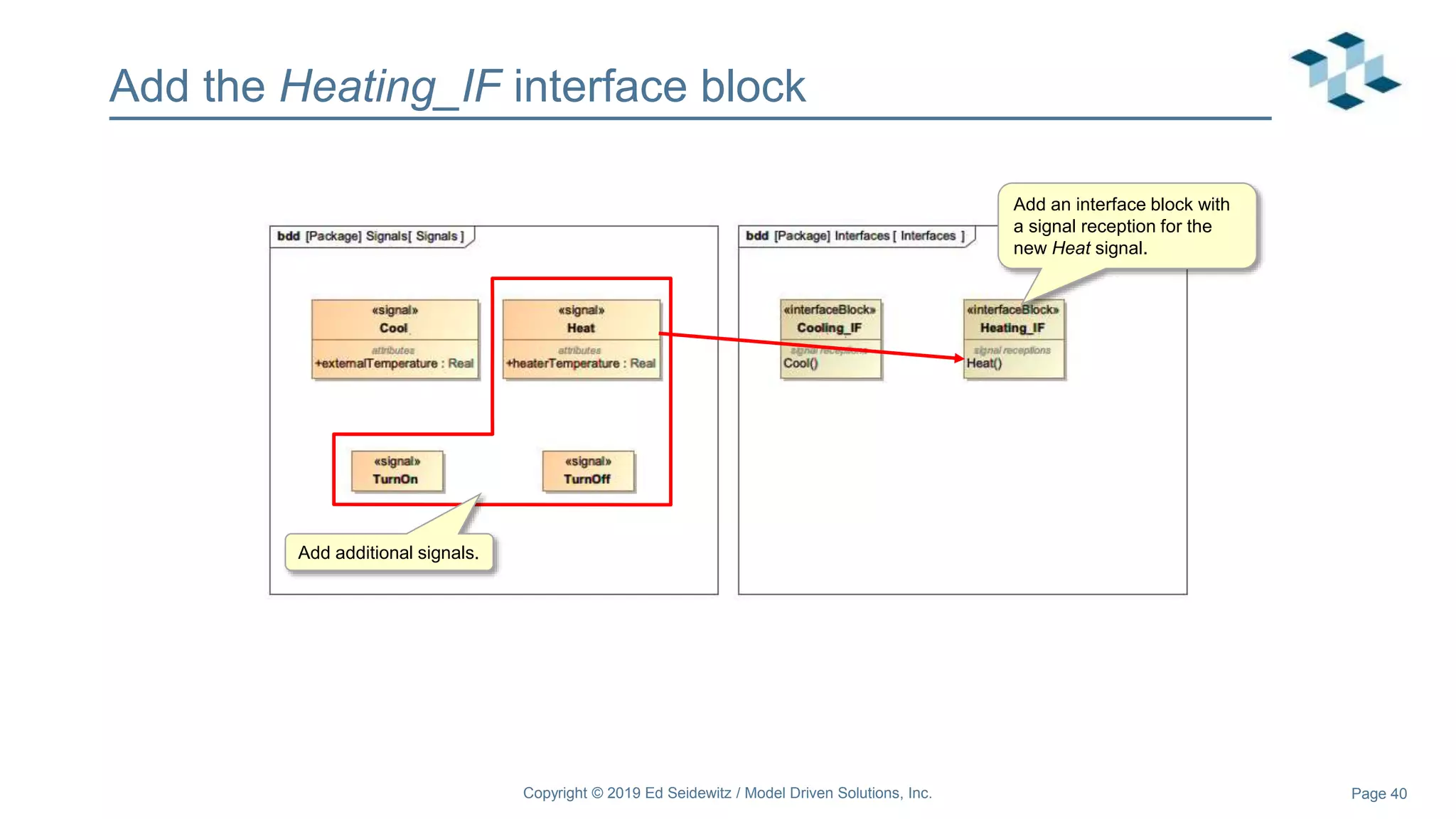
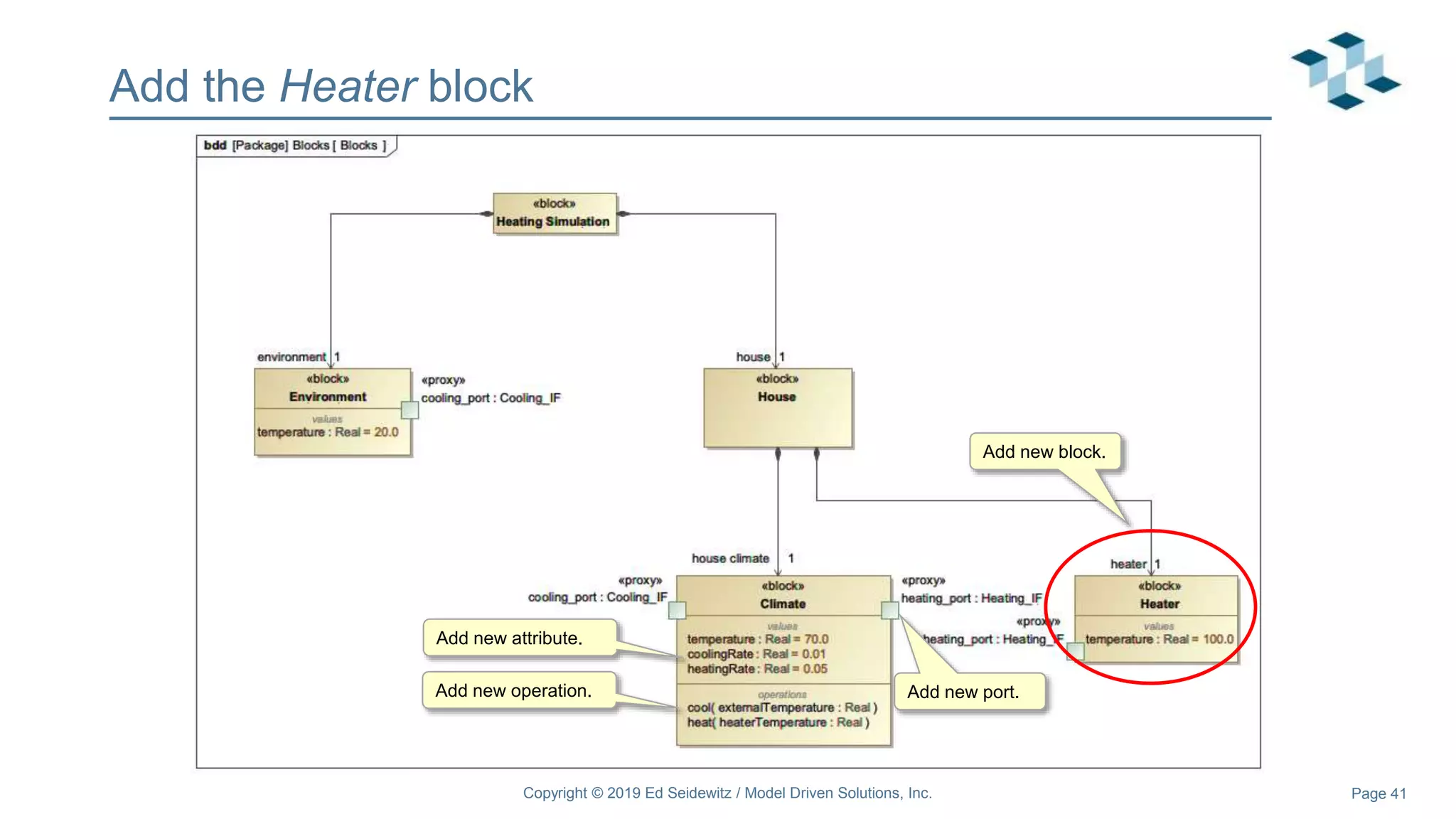
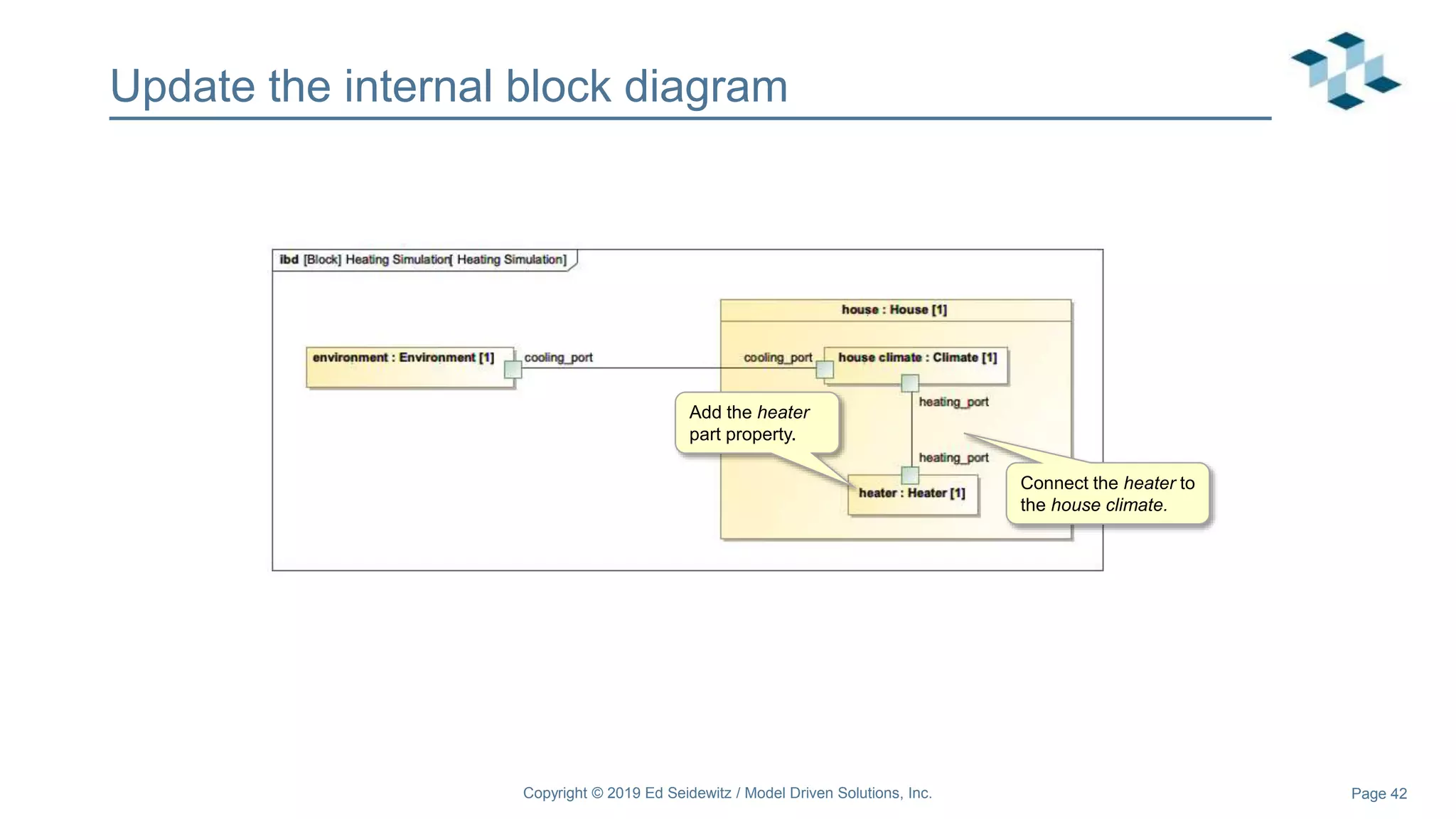
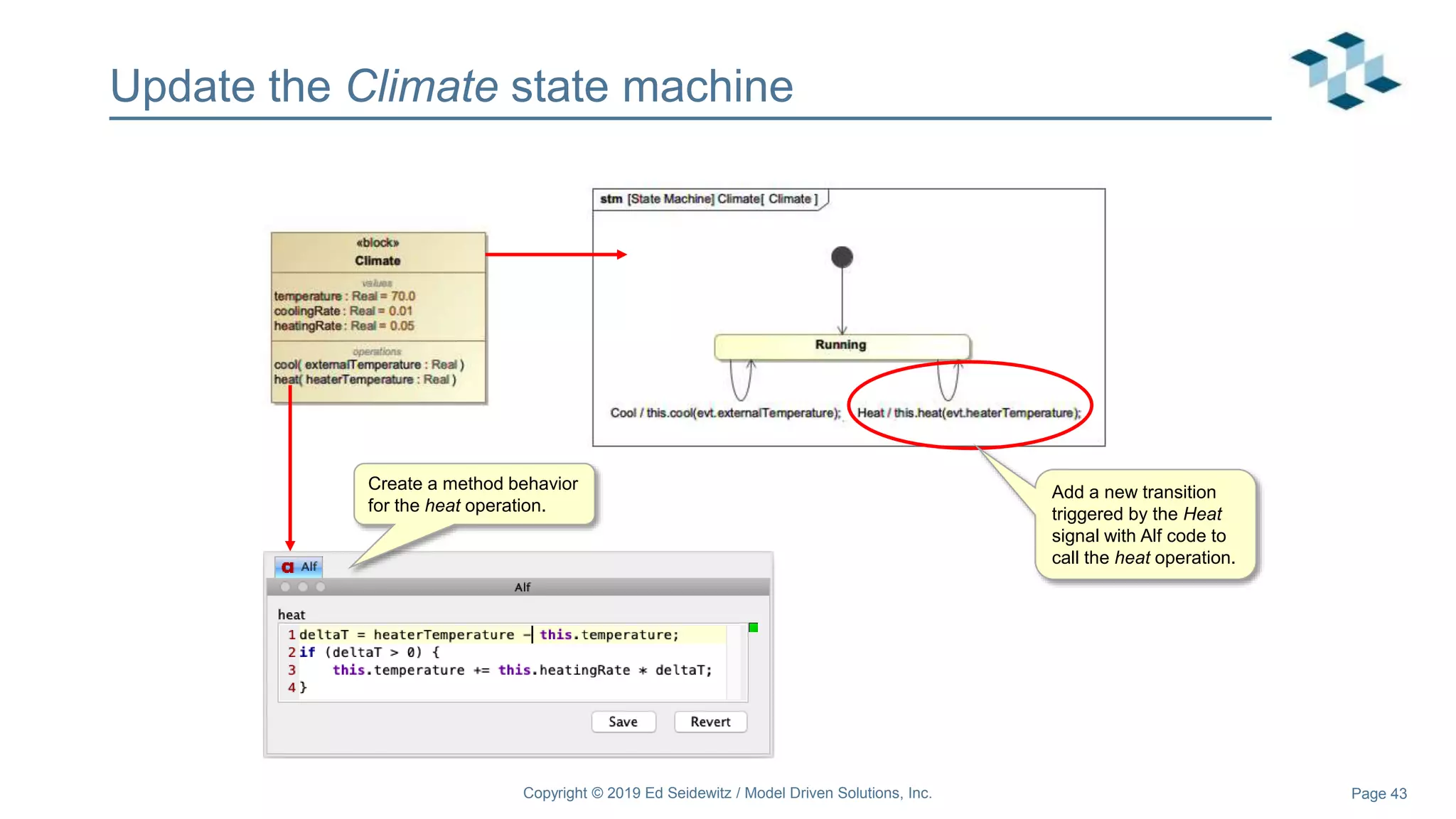
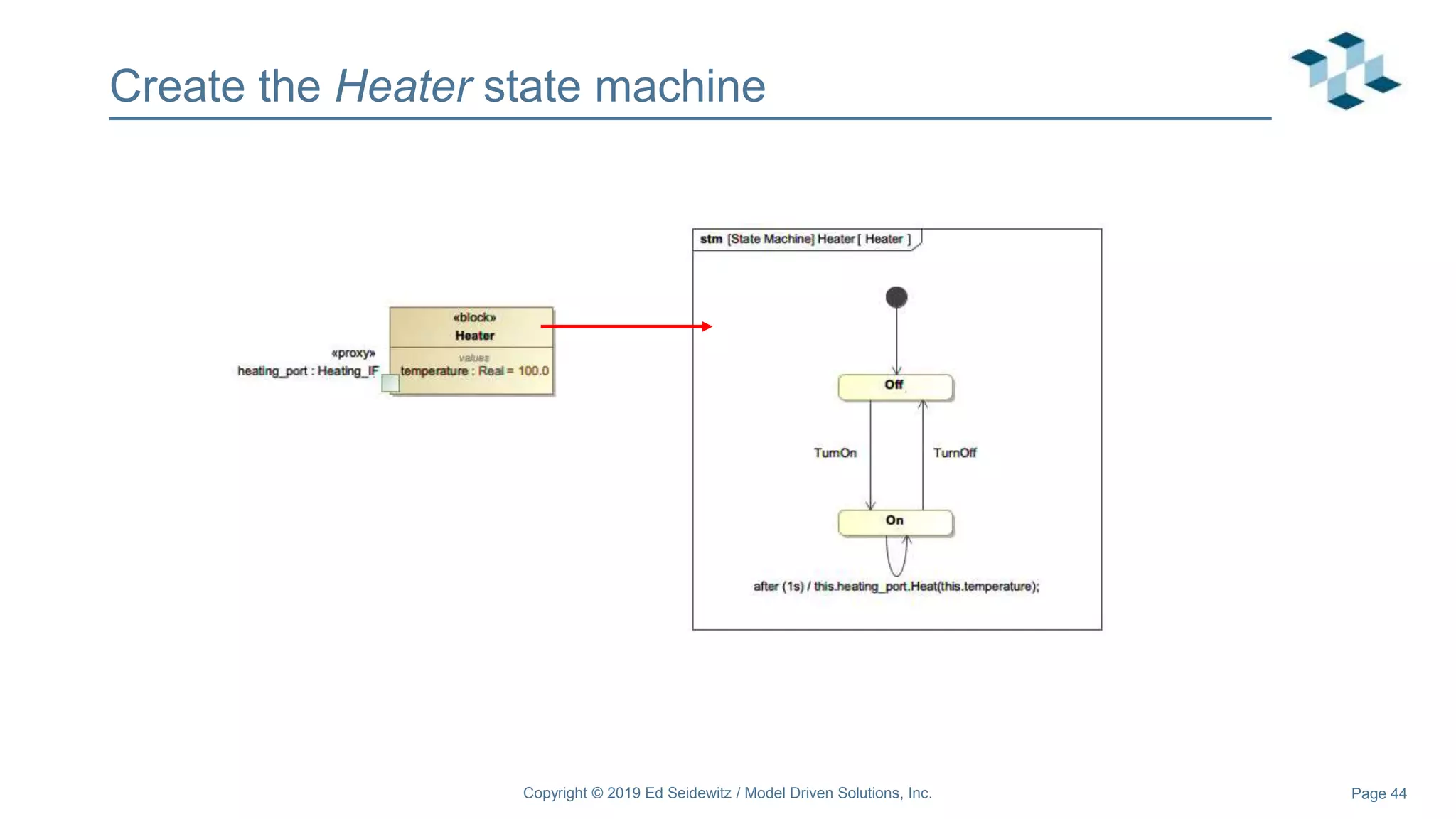
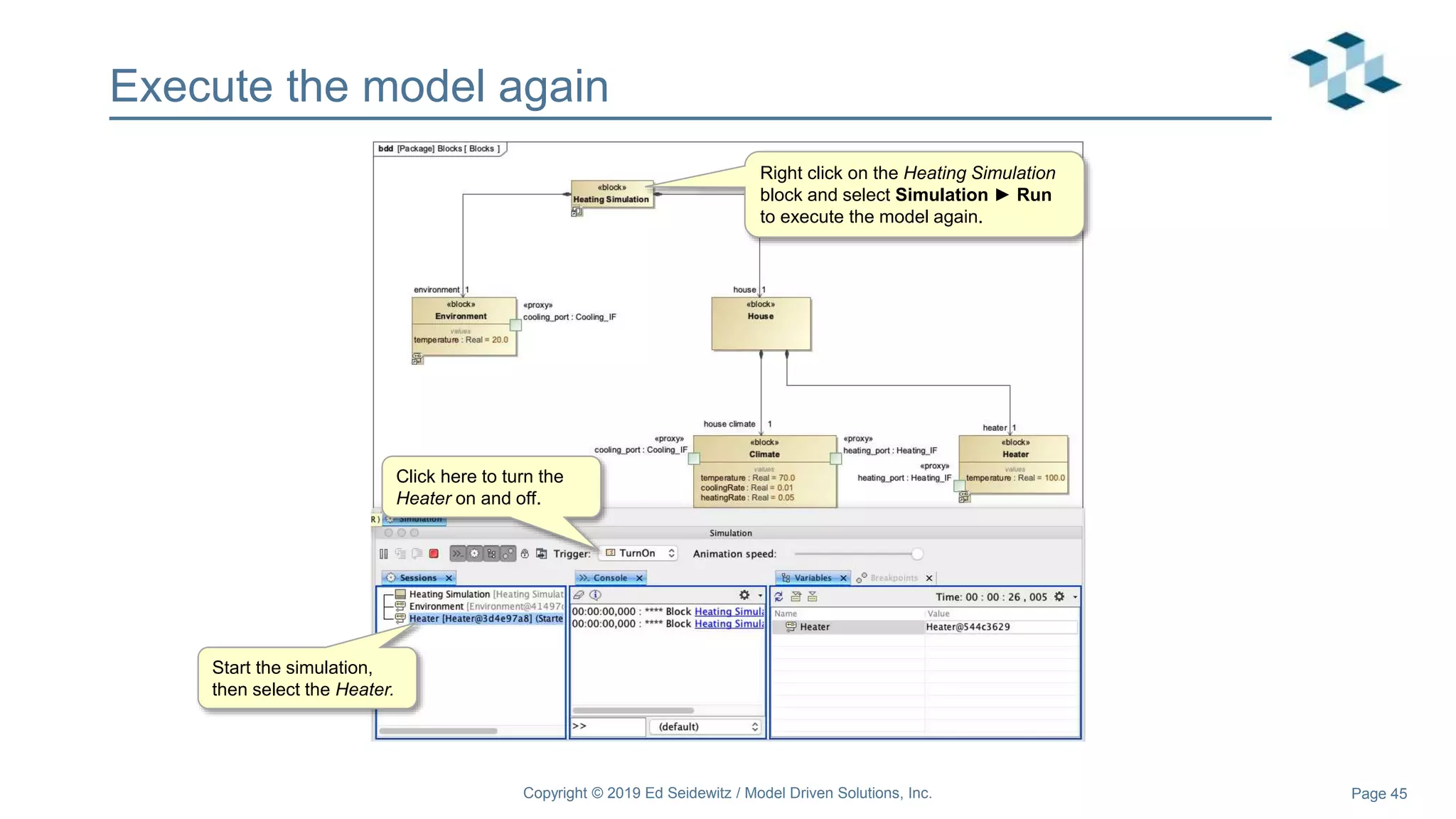
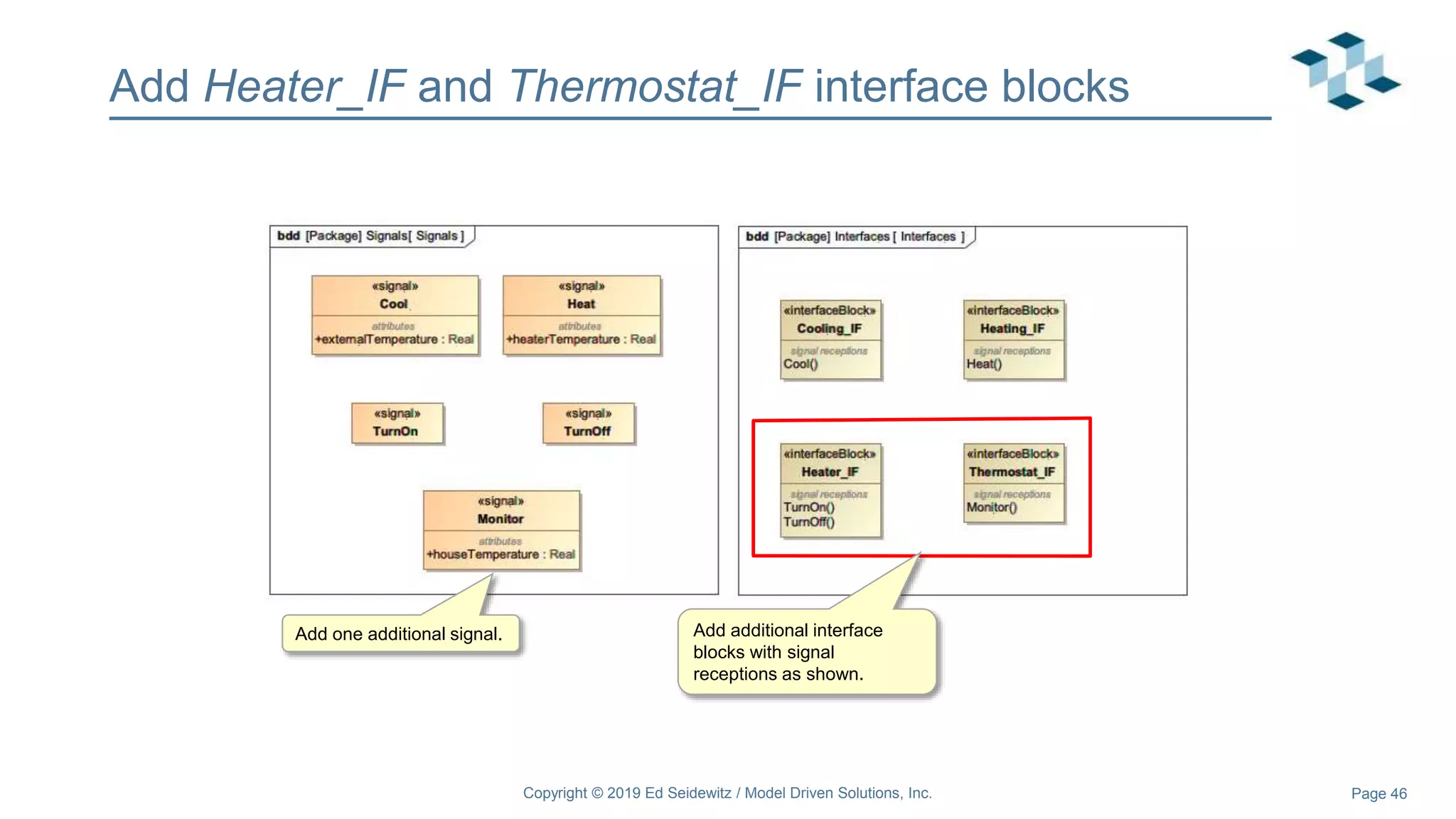
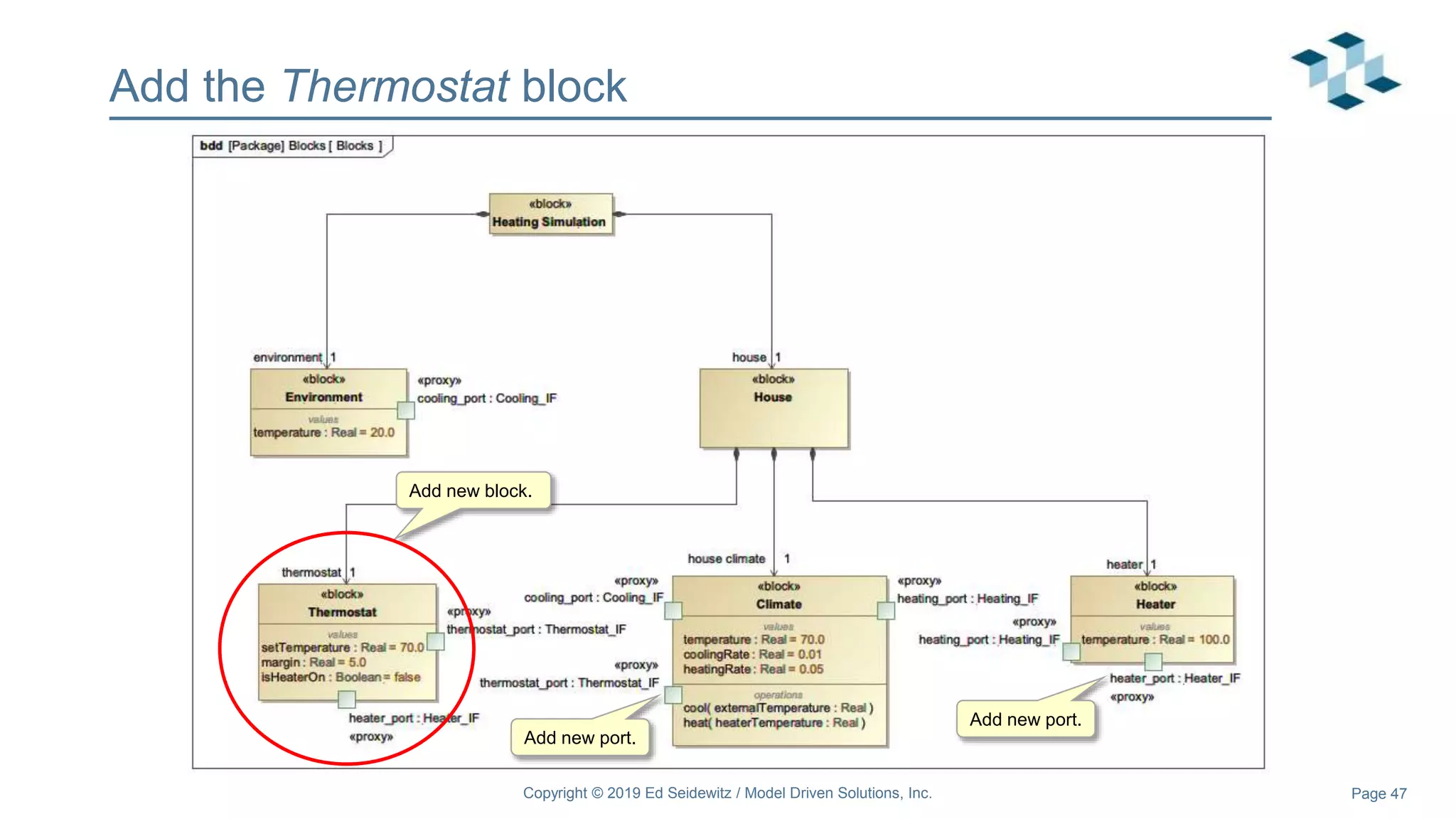
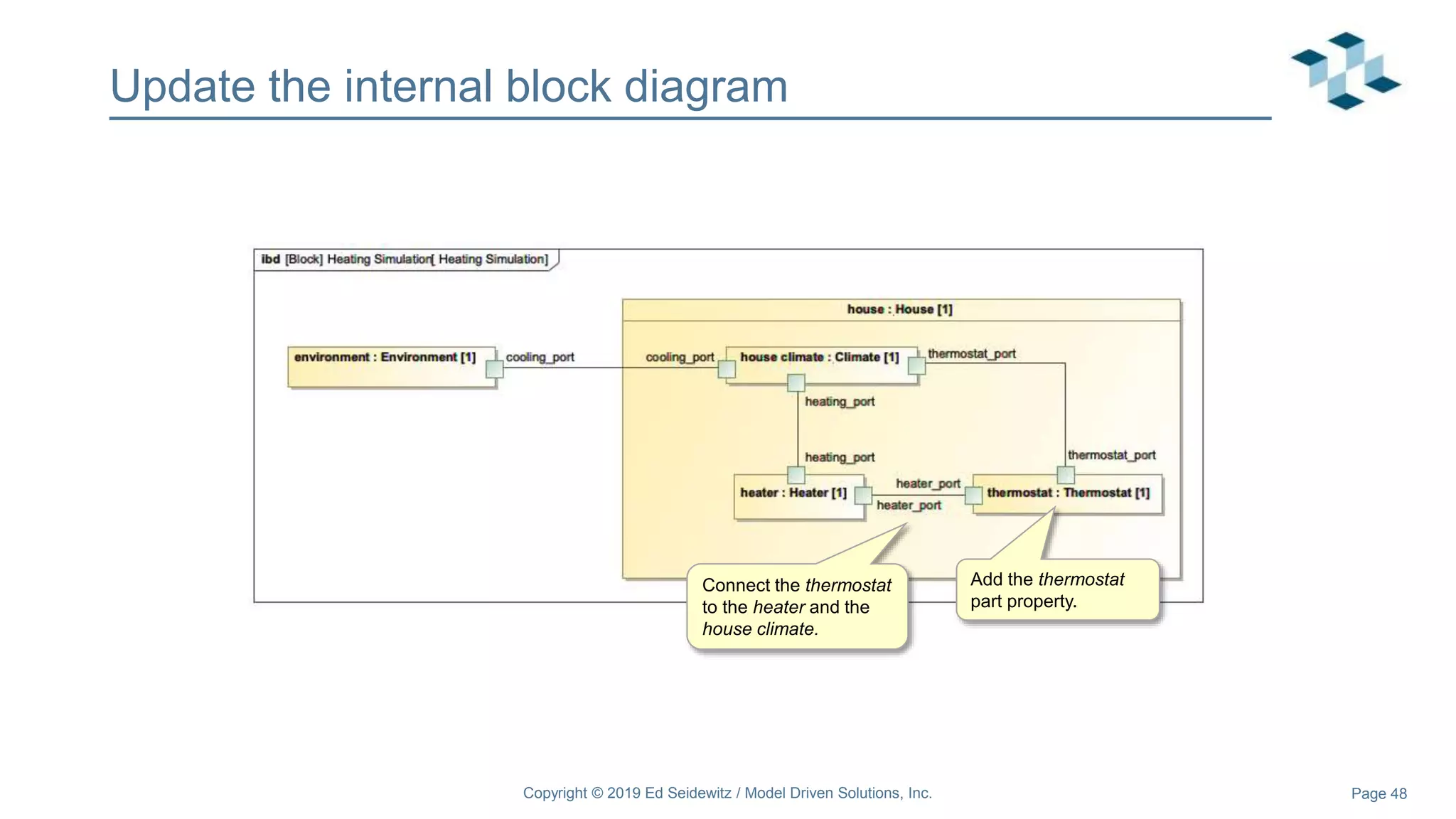
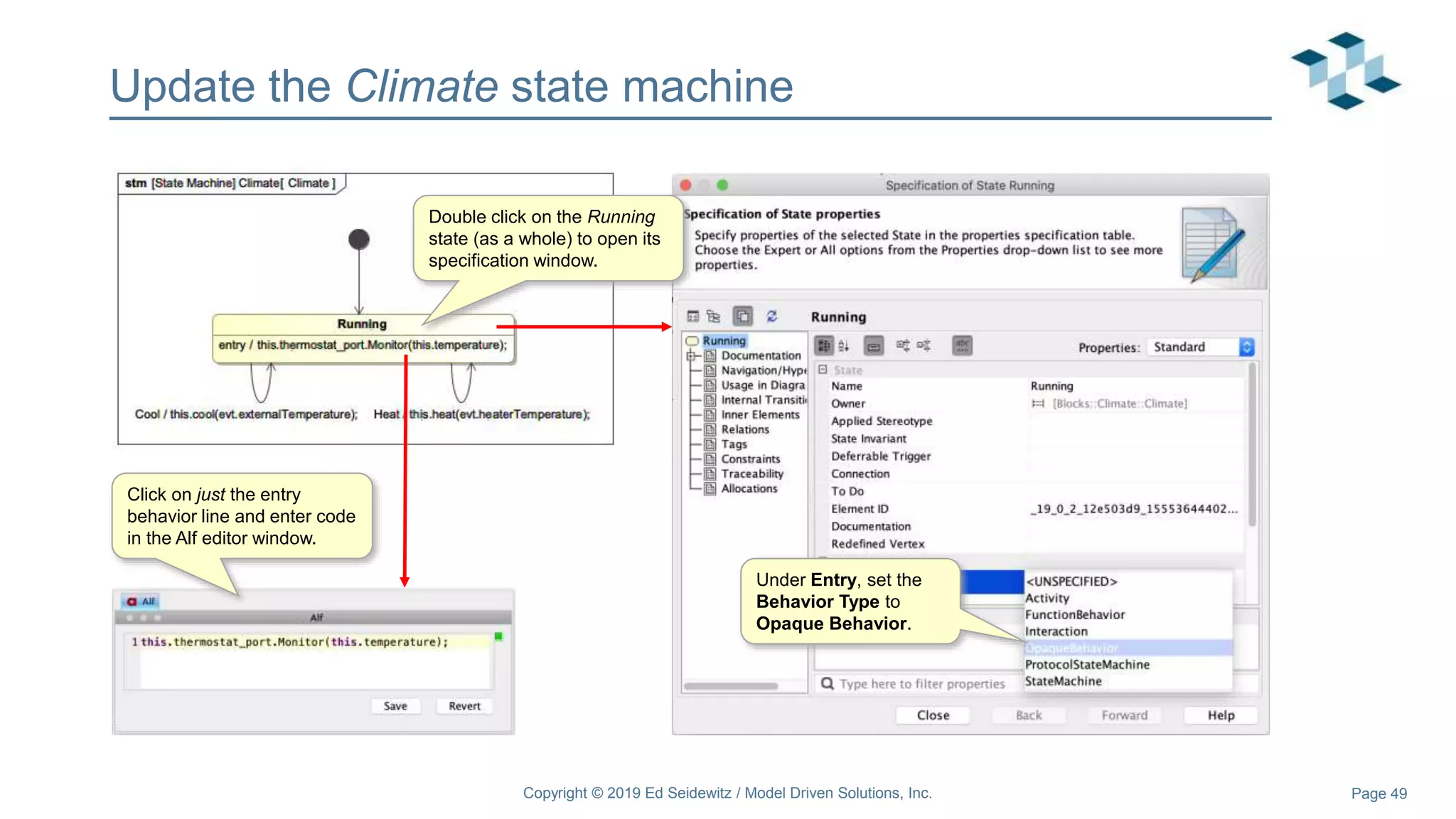
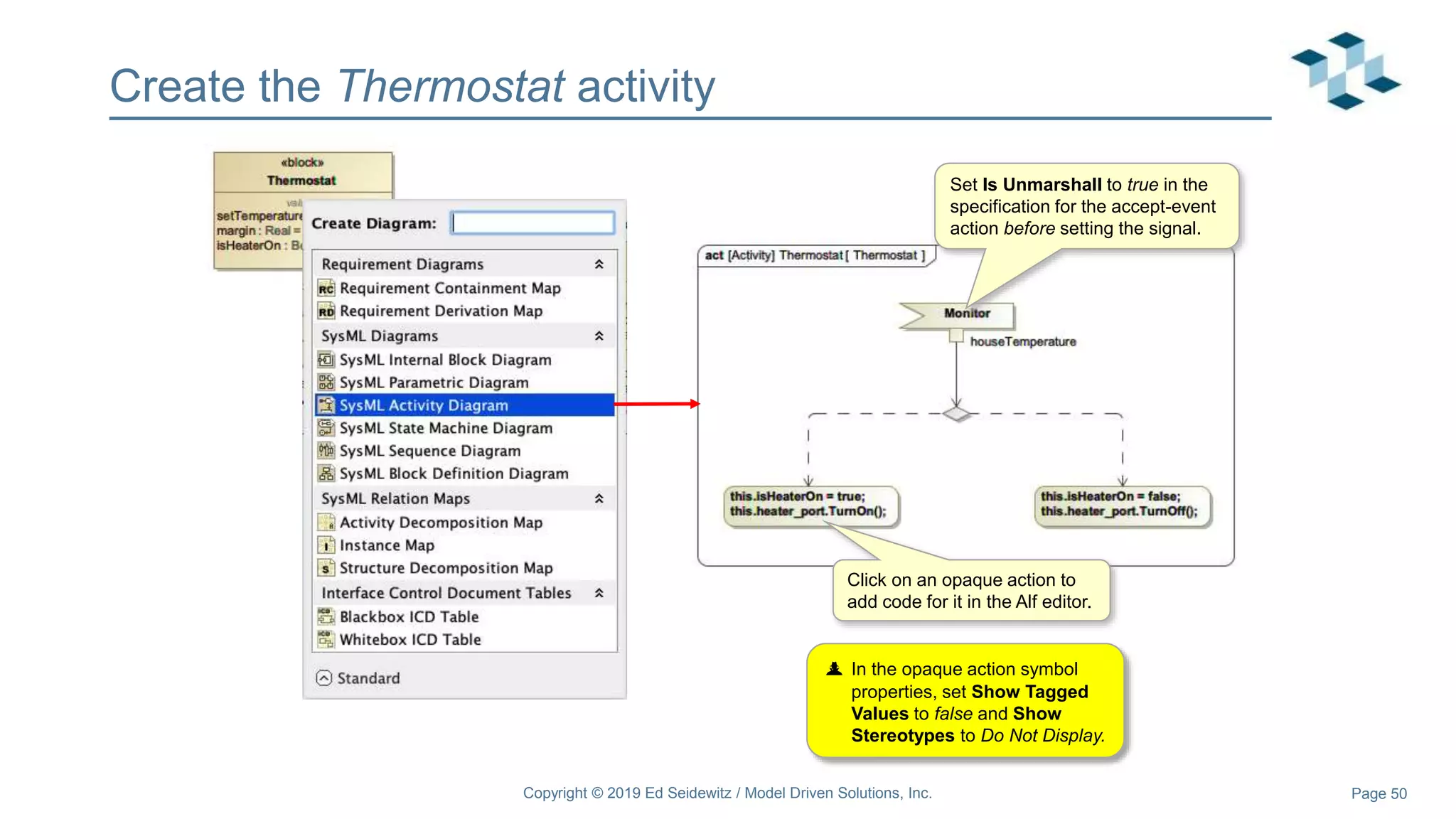
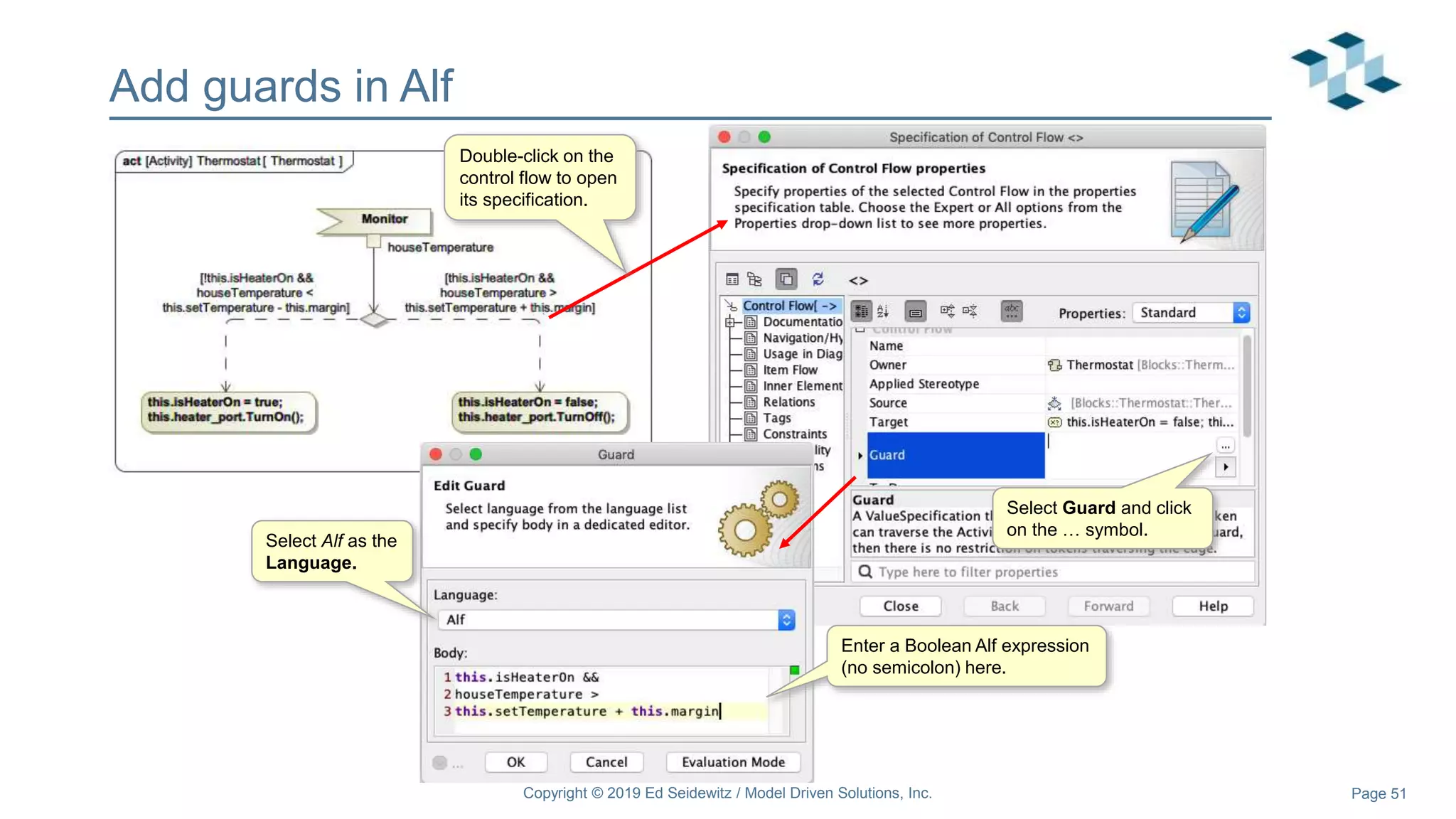
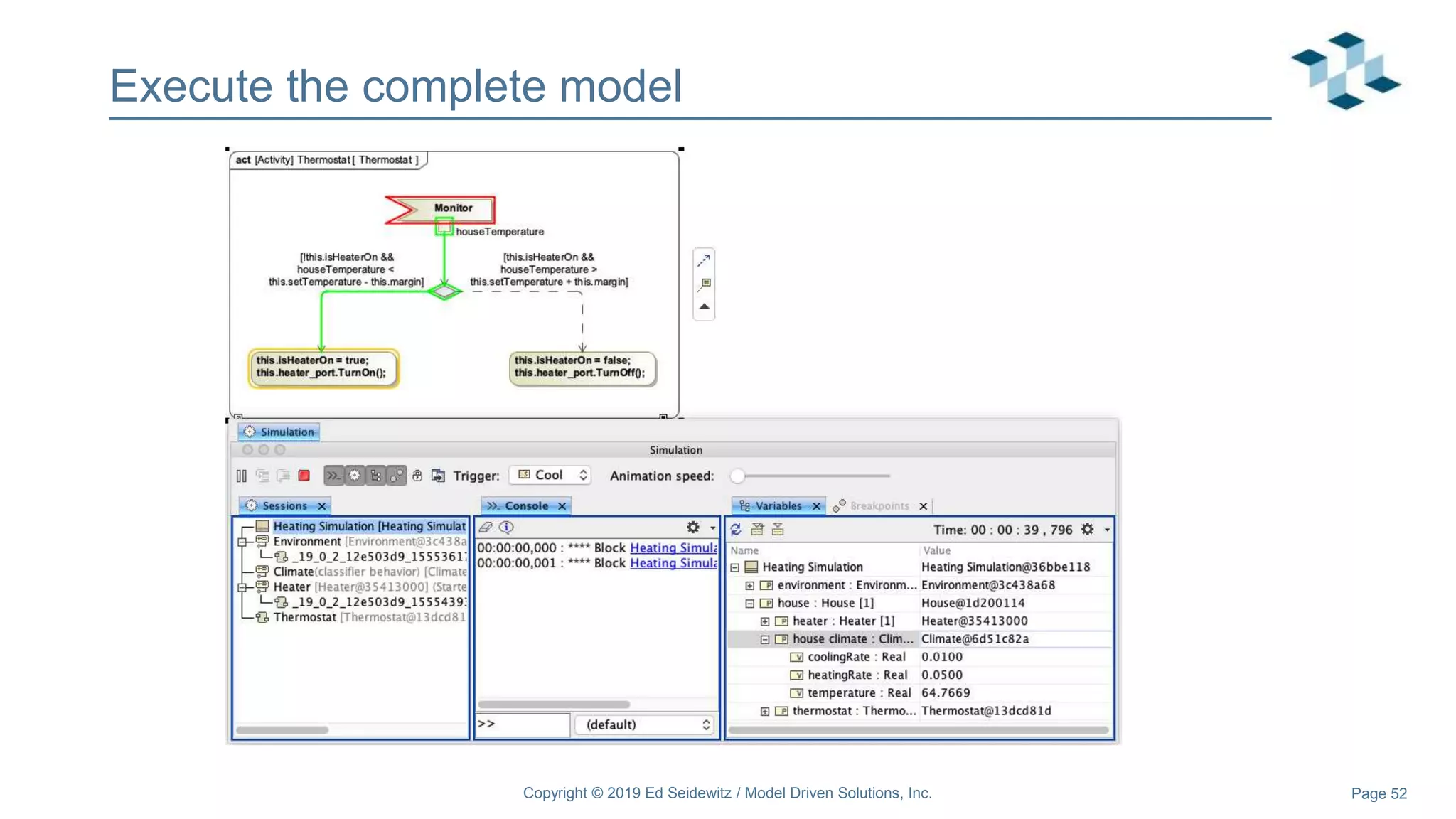
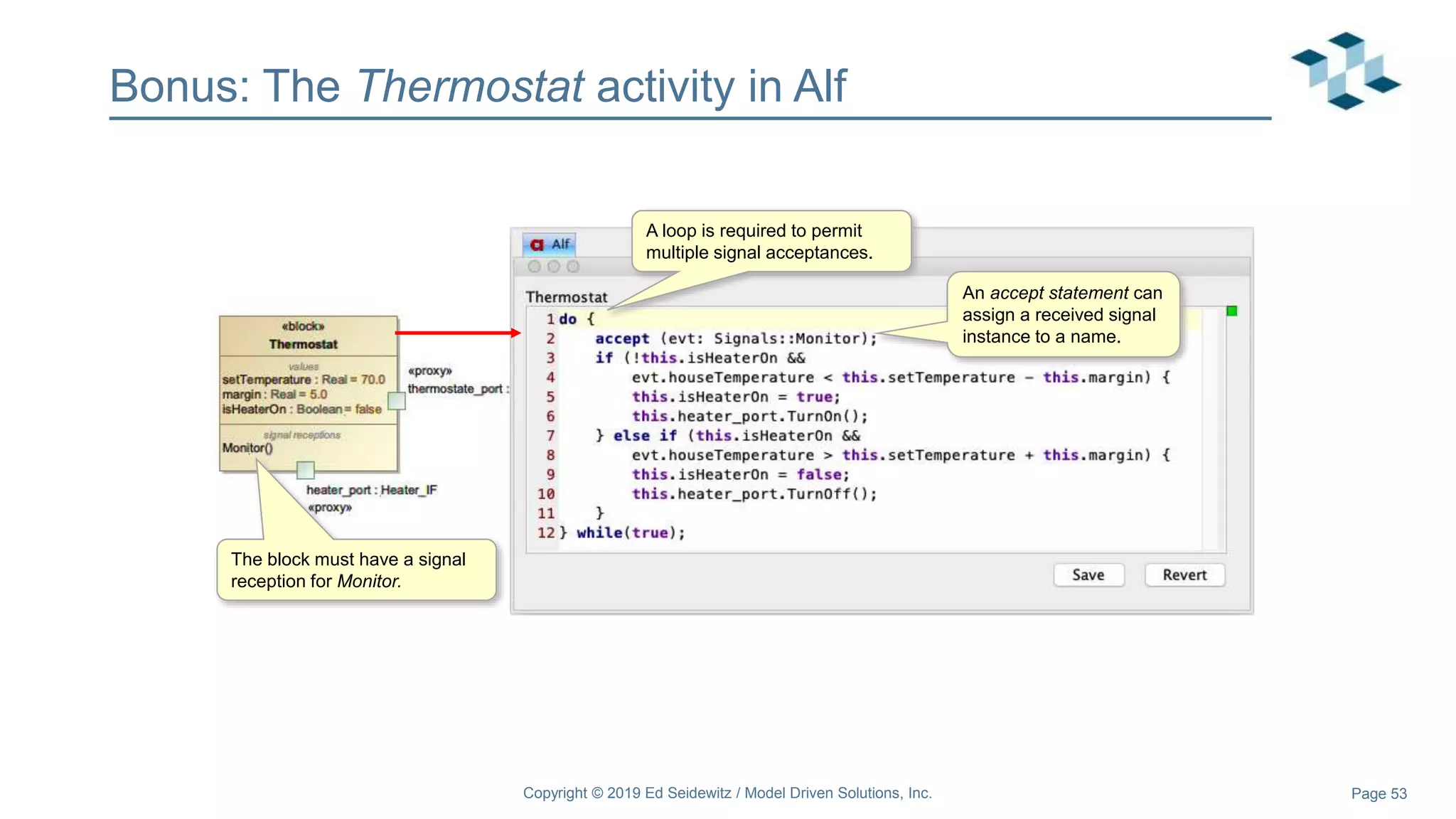
The document discusses leveraging the Alf action language for executable modeling in SysML. It provides an overview and introduction to using Alf with SysML, including hands-on exercises to create a heating simulation model. The key topics covered include installing the Alf plugin, the basics of Alf syntax and semantics, mapping Alf to fUML, using Alf for operations, state machines, signals, and more. Hands-on steps demonstrate creating blocks, activities, and state machines with Alf code to model and execute a heating simulation.