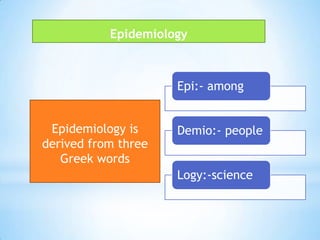
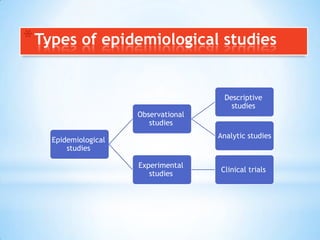
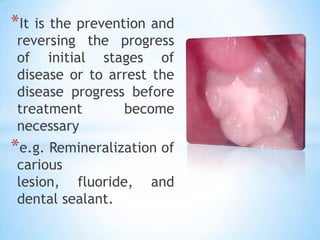
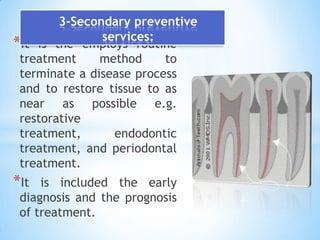
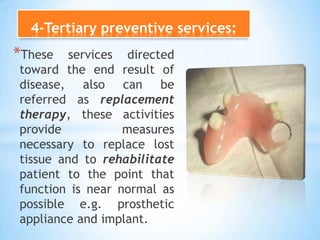
This document provides an introduction to dental public health and community dentistry. It discusses key topics including the definition of dental public health, the role of dental practitioners in both private and community practice, epidemiology and its uses in dental health, and the different levels of preventive services including primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. The goals of dental public health are outlined as educating the public, preventing and controlling dental diseases, applied dental research, and providing treatment programs.