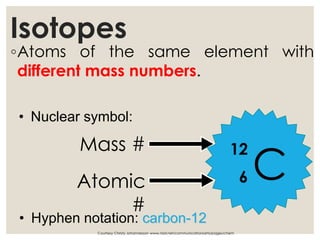
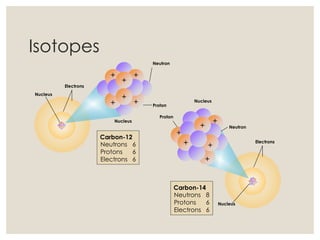
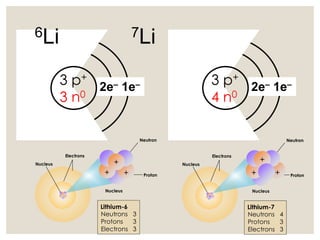
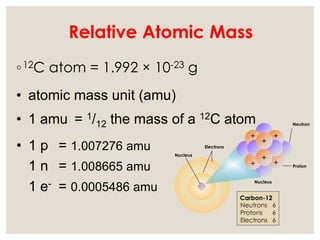
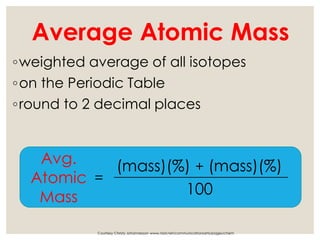
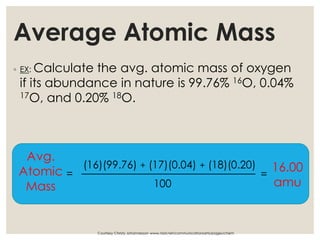
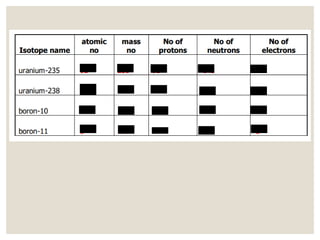
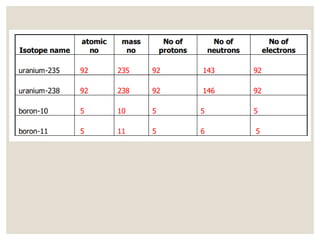
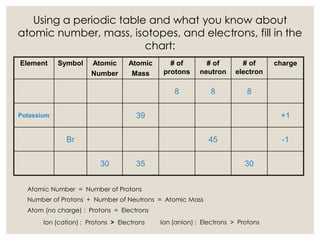
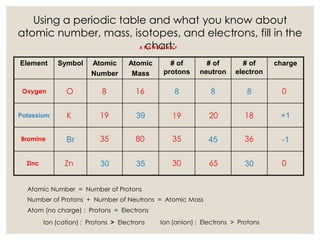
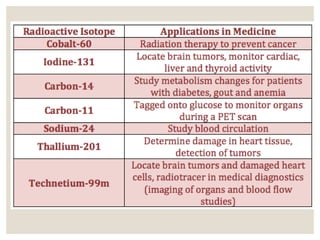
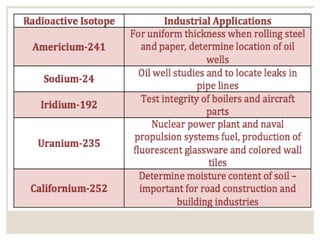
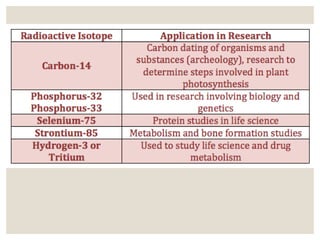
The document discusses isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different mass numbers, explaining their notation and examples such as carbon-12 and carbon-14. It also defines atomic mass as the weighted average of the masses of isotopes and provides examples for calculating average atomic mass using the abundance of different isotopes. Additionally, it includes instructions for filling out a chart related to the atomic characteristics of various elements.