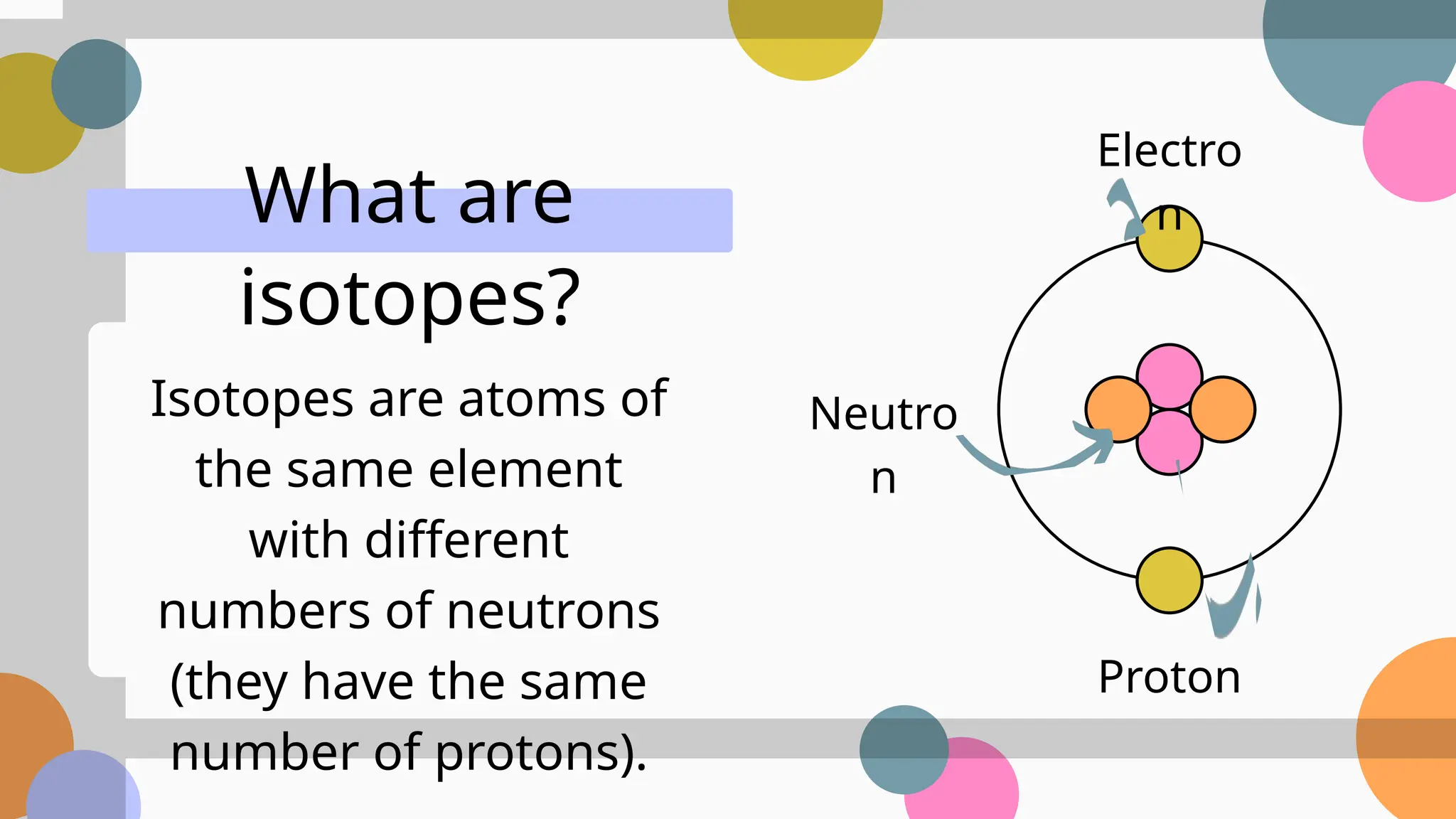
The document provides an overview of atomic structure, focusing on subatomic particles, atomic numbers, and isotopes. It explains that the atomic number identifies elements by the number of protons in the nucleus, while isotopes are variants of elements with the same number of protons but different neutrons. It also discusses the calculation of relative atomic mass, considering the abundance of isotopes.