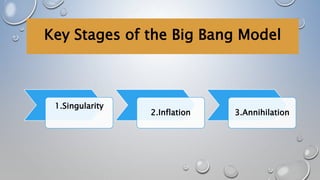
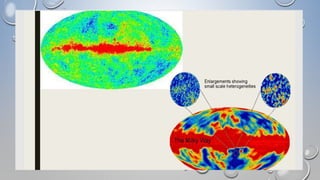
1. The document summarizes the key stages of the Big Bang theory, including the formation of the early light elements hydrogen and helium.
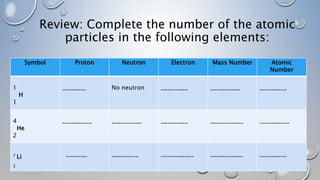
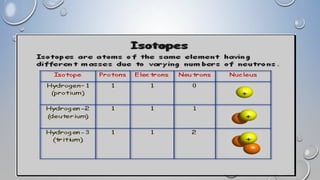
2. It describes how in the early universe, matter and antimatter annihilated each other, leaving an excess of matter. Nuclear fusion then formed the first atomic nuclei like deuterium and helium-3.
3. Eventually, hydrogen and helium nuclei combined to form the first stable atomic element, helium-4, accounting for about 25% of the elemental abundance we observe today.